Abstract
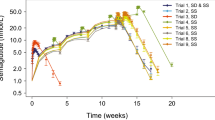
Piroxicam is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug used to alleviate symptoms of osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. CYP2C9 genetic polymorphism significantly influences the pharmacokinetics of piroxicam. The objective of this study was to develop and validate the piroxicam physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) model related to CYP2C9 genetic polymorphism. PK-Sim® version 10.0 was used for the PBPK modeling. The PBPK model was evaluated by predicted and observed plasma concentration–time profiles, fold errors of predicted to observed pharmacokinetic parameters, and a goodness-of-fit plot. The turnover number (kcat) of CYP2C9 was adjusted to capture the pharmacokinetics of piroxicam in different CYP2C9 genotypes. The population PBPK model overall accurately described and predicted the plasma concentration–time profiles in different CYP2C9 genotypes. In our simulations, predicted AUCinf in CYP2C9*1/*2, CYP2C9*1/*3, and CYP2C9*3/*3 genotypes were 1.83-, 2.07-, and 6.43-fold higher than CYP2C9*1/*1 genotype, respectively. All fold error values for AUC, Cmax, and t1/2 were included in the acceptance criterion with the ranges of 0.57–1.59, 0.63–1.39, and 0.65–1.51, respectively. The range of fold error values for predicted versus observed plasma concentrations was 0.11–3.13. 93.9% of fold error values were within the two-fold range. Average fold error, absolute average fold error, and root mean square error were 0.93, 1.27, and 0.72, respectively. Our model accurately captured the pharmacokinetic alterations of piroxicam according to CYP2C9 genetic polymorphism.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abduljalil K, Badhan RKS (2020) Drug dosing during pregnancy-opportunities for physiologically based pharmacokinetic models. J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn 47(4):319–340. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10928-020-09698-w
Al-Shakargi SDMS (2012) Bioequivalency of two piroxicam products in plasma by high performance liquid chromatography. Tikret Journal of Pharmceutical Sciences 8(2):242–247
Bae JW, Choi CI, Jang CG, Lee SY (2011a) Effects of CYP2C9*1/*13 on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of meloxicam. Br J Clin Pharmacol 71(4):550–555. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2125.2010.03853.x
Bae JW, Choi CI, Kim MJ, Oh DH, Keum SK, Park JI, Kim BH, Bang HK, Oh SG, Kang BS, Park HJ, Kim HD, Ha JH, Shin HJ, Kim YH, Na HS, Chung MW, Jang CG, Lee SY (2011b) Frequency of CYP2C9 alleles in Koreans and their effects on losartan pharmacokinetics. Acta Pharmacol Sin 32(10):1303–1308. https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2011.100
Bae JW, Choi CI, Lee HI, Lee YJ, Jang CG, Lee SY (2012) Effects of CYP2C9*1/*3 and *1/*13 on the pharmacokinetics of losartan and its active metabolite E-3174. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther 50(9):683–689. https://doi.org/10.5414/cp201467
Bae JW, Oh KY, Yoon SJ, Shin HB, Jung EH, Cho CK, Lim CW, Kang P, Choi CI, Jang CG, Lee SY, Lee YJ (2020) Effects of CYP2D6 genetic polymorphism on the pharmacokinetics of metoclopramide. Arch Pharm Res 43(11):1207–1213. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-020-01293-4
Benveniste C, Striberni R, Dayer P (1990) Indirect assessment of the enterohepatic recirculation of piroxicam and tenoxicam. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 38(6):547–549. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00278579
Berg J, Fellier H, Christoph T, Grarup J, Stimmeder D (1999) The analgesic NSAID lornoxicam inhibits cyclooxygenase (COX)-1/-2, inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), and the formation of interleukin (IL)-6 in vitro. Inflamm Res 48(7):369–379. https://doi.org/10.1007/s000110050474
Blanco FJ, Guitian R, Moreno J, de Toro FJ, Galdo F (1999) Effect of anti-inflammatory drugs on COX-1 and COX−2 activity in human articular chondrocytes. J Rheumatol 26(6):1366–1373
Blocka KL, Richardson CJ, Wallace SM, Ross SG, Verbeeck RK (1988) The effect of age on piroxicam disposition in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 15(5):757–763
Boudinot FD, Ibrahim SS (1988) High-performance liquid chromatographic assay for piroxicam in human plasma. J Chromatogr 430(2):424–428. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0378-4347(00)83181-3
Brogden RN, Heel RC, Speight TM, Avery GS (1981) Piroxicam: a review of its pharmacological properties and therapeutic efficacy. Drugs 22(3):165–187. https://doi.org/10.2165/00003495-198122030-00001
Byeon JY, Lee YJ, Kim YH, Kim SH, Lee CM, Bae JW, Jang CG, Lee SY, Choi CI (2018) Effects of diltiazem, a moderate inhibitor of CYP3A4, on the pharmacokinetics of tamsulosin in different CYP2D6 genotypes. Arch Pharm Res 41(5):564–570. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-018-1030-6
Byeon JY, Lee CM, Lee YJ, Kim YH, Kim SH, Jung EH, Chae WK, Lee YJ, Jang CG, Lee SY (2019) Influence of CYP2D6 genetic polymorphism on pharmacokinetics of active moiety of tolterodine. Arch Pharm Res 42(2):182–190. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-018-1099-y
Caldwell JR (1994) Comparison of the efficacy, safety, and pharmacokinetic profiles of extended-release ketoprofen and piroxicam in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Ther 16(2):222–235
Calvo AM, Santos GM, Dionísio TJ, Marques MP, Brozoski DT, Lanchote VL, Fernandes MHR, Faria FAC, Santos CF (2016) Quantification of piroxicam and 5′-hydroxypiroxicam in human plasma and saliva using liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry following oral administration. J Pharm Biomed Anal 120:212–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2015.12.042
Calvo AM, Zupelari-Gonçalves P, Dionísio TJ, Brozoski DT, Faria FA, Santos CF (2017) Efficacy of piroxicam for postoperative pain after lower third molar surgery associated with CYP2C8*3 and CYP2C9. J Pain Res 10:1581–1589. https://doi.org/10.2147/jpr.S138147
Campbell AJ, Ferry DG, Edwards IR (1985) Pharmacokinetic projections for isoxicam and piroxicam in old and young subjects. Br J Rheumatol 24(2):176–178. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/24.2.176
Cho CK, Kang P, Park HJ, Lee YJ, Bae JW, Jang CG, Lee SY (2021a) Physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) modelling of tamsulosin related to CYP2D6*10 allele. Arch Pharm Res 44(11):1037–1049. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-021-01357-z
Cho CK, Park HJ, Kang P, Moon S, Lee YJ, Bae JW, Jang CG, Lee SY (2021b) Physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) modeling of meloxicam in different CYP2C9 genotypes. Arch Pharm Res 44(12):1076–1090. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-021-01361-3
Choi CI, Kim MJ, Jang CG, Park YS, Bae JW, Lee SY (2011) Effects of the CYP2C9*1/*13 genotype on the pharmacokinetics of lornoxicam. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 109(6):476–480. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-7843.2011.00751.x
Choi CI, Kim MJ, Chung EK, Lee HI, Jang CG, Bae JW, Lee SY (2012) CYP2C9*3 and *13 alleles significantly affect the pharmacokinetics of irbesartan in healthy Korean subjects. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 68(2):149–154. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-011-1098-0
Coppola P, Kerwash E, Cole S (2021) Physiologically based pharmacokinetics model in pregnancy: a regulatory perspective on model evaluation. Front Pediatr 9:687978. https://doi.org/10.3389/fped.2021.687978
Daly AK, Rettie AE, Fowler DM, Miners JO (2017) Pharmacogenomics of CYP2C9: functional and clinical considerations. J Pers Med 8(1):1. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm8010001
Darragh A, Gordon AJ, O’Byrne H, Hobbs D, Casey E (1985) Single-dose and steady-state pharmacokinetics of piroxicam in elderly vs young adults. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 28(3):305–309. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00543328
Dean L (2019) Piroxicam Therapy and CYP2C9 Genotype. In: Pratt VM, Scott SA, Pirmohamed M, Esquivel B, Kane MS, Kattman BL, Malheiro AJ (ed) Medical Genetics Summaries [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US) [Online] Available from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK537367/ Accessed 18 April 2022
Dessain P, Estabrooks TF, Gordon AJ (1979) Piroxicam in the treatment of osteoarthrosis: A multicentre study in general practice involving 1218 patients. J Int Med Res 7(5):335–343. https://doi.org/10.1177/030006057900700501
Dix P, Prosser DP, Streete P (2004) A pharmacokinetic study of piroxicam in children. Anaesthesia 59(10):984–987. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2044.2004.03806.x
Dixon JS, Lowe JR, Galloway DB (1984) Rapid method for the determination of either piroxicam or tenoxicam in plasma using high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr 310(2):455–459. https://doi.org/10.1016/0378-4347(84)80116-4
Dixon JS, Lacey LF, Pickup ME, Langley SJ, Page MC (1990) A lack of pharmacokinetic interaction between ranitidine and piroxicam. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 39(6):583–586. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00316100
Ferry DG, Gazeley LR, Busby WJ, Beasley DM, Edwards IR, Campbell AJ (1990) Enhanced elimination of piroxicam by administration of activated charcoal or cholestyramine. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 39(6):599–601. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00316105
Guentert TW, Defoin R, Mosberg H (1988) The influence of cholestyramine on the elimination of tenoxicam and piroxicam. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 34(3):283–289. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00540957
Hasan MM, Jilani JA, Salem MS, Najib NM, Pillai GK, Ganem E (1997) Bioequivalence of two capsule formulations of piroxicam. Acta Pharm Sci 39(3):93–97
Heimbach T, Chen Y, Chen J, Dixit V, Parrott N, Peters SA, Poggesi I, Sharma P, Snoeys J, Shebley M, Tai G, Tse S, Upreti VV, Wang YH, Tsai A, Xia B, Zheng M, Zhu AZX, Hall S (2021) Physiologically-based pharmacokinetic modeling in renal and hepatic impairment populations: a pharmaceutical industry perspective. Clin Pharmacol Ther 110(2):297–310. https://doi.org/10.1002/cpt.2125
Helmy SA, El-Bedaiwy HM (2014) Piroxicam immediate release formulations: A fasting randomized open-label crossover bioequivalence study in healthy volunteers. Clin Pharmacol Drug Dev 3(6):466–471. https://doi.org/10.1002/cpdd.106
Hindmarsh AC, Reynolds DR, Serban R, Woodward CS, Gardner, DJ, Cohen SD, Taylor A, Peles S, Banks L, Shumaker D (2021) Open Systems Pharmacology Suite Manual version 10. [Online] Available from https://docs.open-systems-pharmacology.org/. Accessed 18 April 2022
Hobbs DC, Twomey TM (1979) Piroxicam pharmacokinetics in man: aspirin and antacid interaction studies. J Clin Pharmacol 19(5–6):270–281. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1552-4604.1979.tb02480.x
Huang W, Nakano M, Sager J, Ragueneau-Majlessi I, Isoherranen N (2017) Physiologically based pharmacokinetic model of the CYP2D6 probe atomoxetine: extrapolation to special populations and drug-drug interactions. Drug Metab Dispos 45(11):1156–1165. https://doi.org/10.1124/dmd.117.076455
Ishizaki T, Nomura T, Abe T (1979) Pharmacokinetics of piroxicam, a new nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agent, under fasting and postprandial states in man. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm 7(4):369–381. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01062535
Ito K, Hallifax D, Obach RS, Houston JB (2005) Impact of parallel pathways of drug elimination and multiple cytochrome P450 involvement on drug-drug interactions: CYP2D6 paradigm. Drug Metab Dispos 33(6):837–844. https://doi.org/10.1124/dmd.104.003715
Jeon SS, Cha HR, Park YJ, Lee BC, Kim ND (1998) Comparison of absorption rate between piroxicam-β-cyclodextrin and piroxicam in Korean healthy subjects after a single dose administration. Korean J Clin Pharm 8(2):95–100
Jung EH, Lee CM, Byeon JY, Shin HB, Oh KY, Cho CK, Lim CW, Jang CG, Lee SY (2020) Lee YJ (2020a) Relationship between plasma exposure of zolpidem and CYP2D6 genotype in healthy Korean subjects. Arch Pharm Res 43(9):976–981. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-020-01250-1
Jung EH, Lee YJ, Kim DH, Kang P, Lim CW, Cho CK, Jang CG, Lee SY, Bae JW (2020) Effects of paroxetine on the pharmacokinetics of atomoxetine and its metabolites in different CYP2D6 genotypes. Arch Pharm Res 43(12):1356–1363. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-020-01300-8
Jung EH, Cho CK, Kang P, Park HJ, Lee YJ, Bae JW, Choi CI, Jang CG, Lee SY (2021) Physiologically based pharmacokinetic modeling of candesartan related to CYP2C9 genetic polymorphism in adult and pediatric patients. Arch Pharm Res 44(12):1109–1119. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-021-01363-1
Kim SH, Kim DH, Byeon JY, Kim YH, Kim DH, Lim HJ, Lee CM, Whang SS, Choi CI, Bae JW, Lee YJ, Jang CG, Lee SY (2017) Effects of CYP2C9 genetic polymorphisms on the pharmacokinetics of celecoxib and its carboxylic acid metabolite. Arch Pharm Res 40(3):382–390. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-016-0861-2
Kim SH, Byeon JY, Kim YH, Lee CM, Lee YJ, Jang CG, Lee SY (2018) Physiologically based pharmacokinetic modelling of atomoxetine with regard to CYP2D6 genotypes. Sci Rep 8(1):12405. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-30841-8
Kim YH, Kang P, Cho CK, Jung EH, Park HJ, Lee YJ, Bae JW, Jang CG, Lee SY (2021) Physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) modeling for prediction of celecoxib pharmacokinetics according to CYP2C9 genetic polymorphism. Arch Pharm Res 44(7):713–724. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-021-01346-2
Kim NT, Cho CK, Kang P, Park H-J, Lee YJ, Bae JW, Jang C-G, Lee S-Y (2022) Effects of CYP2C9*3 and *13 alleles on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of glipizide in healthy Korean subjects. Arch Pharm Res 45(2):114–121. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-021-01366-y
Kirchheiner J, Tsahuridu M, Jabrane W, Roots I, Brockmöller J (2004) The CYP2C9 polymorphism: from enzyme kinetics to clinical dose recommendations. Per Med 1(1):63–84. https://doi.org/10.1517/17410541.1.1.63
Lee HI, Bae JW, Choi CI, Lee YJ, Byeon JY, Jang CG, Lee SY (2014) Strongly increased exposure of meloxicam in CYP2C9*3/*3 individuals. Pharmacogenet Genomics 24(2):113–117. https://doi.org/10.1097/fpc.0000000000000025
Lee YJ, Byeon JY, Kim YH, Kim SH, Choi CI, Bae JW, Sohn UD, Jang CG, Lee J, Lee SY (2015) Effects of CYP2C9*1/*3 genotype on the pharmacokinetics of flurbiprofen in Korean subjects. Arch Pharm Res 38(6):1232–1237. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-015-0580-0
Lee CM, Jung EH, Byeon JY, Kim SH, Jang CG, Lee YJ, Lee SY (2019) Effects of steady-state clarithromycin on the pharmacokinetics of zolpidem in healthy subjects. Arch Pharm Res 42(12):1101–1106. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-019-01201-5
Li X, Yang Y, Zhang Y, Wu C, Jiang Q, Wang W, Li H, Li J, Luo C, Wu W, Wang Y, Zhang T (2019) Justification of biowaiver and dissolution rate specifications for piroxicam immediate release products based on physiologically based pharmacokinetic modeling: an in-depth analysis. Mol Pharm 16(9):3780–3790. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.9b00350
Li X, Frechen S, Moj D, Lehr T, Taubert M, Hsin C-h, Mikus G, Neuvonen PJ, Olkkola KT, Saari TI, Fuhr U (2020) A physiologically based pharmacokinetic model of voriconazole integrating time-dependent inhibition of CYP3A4, genetic polymorphisms of CYP2C19 and predictions of drug–drug Interactions. Clin Pharmacokinet 59(6):781–808. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40262-019-00856-z
Loisios-Konstantinidis I, Cristofoletti R, Jamei M, Turner D, Dressman J (2020) Physiologically based pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic modeling to predict the impact of CYP2C9 genetic polymorphisms, co-medication and formulation on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of flurbiprofen. Pharmaceutics 12(11):1049. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12111049
Macek J, Vácha J (1987) Rapid and sensitive method for determination of piroxicam in human plasma by high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr 420(2):445–449. https://doi.org/10.1016/0378-4347(87)80203-7
Mäkelä AL, Olkkola KT, Mattila MJ (1991) Steady state pharmacokinetics of piroxicam in children with heumatic diseases. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 41(1):79–81. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00280114
Milligan PA, McGill PE, Howden CW, Kelman AW, Whiting B (1993) The consequences of H2 receptor antagonist—piroxicam coadministration in patients with joint disorders. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 45(6):507–512. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00315306
Nishimura M, Naito S (2005) Tissue-specific mRNA expression profiles of human ATP-binding cassette and solute carrier transporter superfamilies. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 20(6):452–477. https://doi.org/10.2133/dmpk.20.452
Nishimura M, Naito S (2006) Tissue-specific mRNA expression profiles of human phase I metabolizing enzymes except for cytochrome P450 and phase II metabolizing enzymes. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 21(5):357–374. https://doi.org/10.2133/dmpk.21.357
Nishimura M, Yaguti H, Yoshitsugu H, Naito S, Satoh T (2003) Tissue Distribution of mRNA expression of human cytochrome p450 isoforms assessedby high-sensitivity real-time reverse transcription PCR. Yakugaku Zasshi 123(5):369–375. https://doi.org/10.1248/yakushi.123.369
Ochoa D, Prieto-Pérez R, Román M, Talegón M, Rivas A, Galicia I, Abad-Santos F, Cabaleiro T (2015) Effect of gender and CYP2C9 and CYP2C8 polymorphisms on the pharmacokinetics of ibuprofen enantiomers. Pharmacogenomics 16(9):939–948. https://doi.org/10.2217/pgs.15.40
Palma-Aguirre JA, Lopez-Gamboa M, Cariño L, Burke-Fraga V, González-de la Parra M (2010) Relative bioavailability of two oral formulations of piroxicam 20 mg: a single-dose, randomized-sequence, open-label, two-period crossover comparison in healthy Mexican adult volunteers. Clin Ther 32(2):357–364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinthera.2010.02.002
Perini JA, Suarez-Kurtz G (2006) Impact of CYP2C9*3/*3 genotype on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of piroxicam. Clin Pharmacol Ther 80(5):549–551. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clpt.2006.08.003
Perini JA, Vianna-Jorge R, Brogliato AR, Suarez-Kurtz G (2005) Influence of CYP2C9 genotypes on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of piroxicam. Clin Pharmacol Ther 78(4):362–369. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clpt.2005.06.014
Pfizer (2016) FELDENE® (piroxicam) Prescribing information. [Online] Available from https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2016/018147s044lbl.pdf. Accessed 18 April 2022
Piscitelli DA, Bigora S, Propst C, Goskonda S, Schwartz P, Lesko LJ, Augsburger L, Young D (1998) The impact of formulation and process changes on in vitro dissolution and the bioequivalence of piroxicam capsules. Pharm Dev Technol 3(4):443–452. https://doi.org/10.3109/10837459809028625
Rahman NU, Ahamd M, Akhtar N (2004) Bioequivalence of a generic piroxicam capsule formulation. J Pure Appl Sci 23(2):52–61
Rasetti-Escargueil C, Grangé V (2005) Pharmacokinetic profiles of two tablet formulations of piroxicam. Int J Pharm 295(1–2):129–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2005.02.006
Rettie AE, Korzekwa KR, Kunze KL, Lawrence RF, Eddy AC, Aoyama T, Gelboin HV, Gonzalez FJ, Trager WF (1992) Hydroxylation of warfarin by human cDNA-expressed cytochrome P-450: a role for P-4502C9 in the etiology of (S)-warfarin-drug interactions. Chem Res Toxicol 5(1):54–59. https://doi.org/10.1021/tx00025a009
Richardson CJ, Blocka KL, Ross SG, Verbeeck RK (1985) Effects of age and sex on piroxicam disposition. Clin Pharmacol Ther 37(1):13–18. https://doi.org/10.1038/clpt.1985.4
Richardson C, Blocka K, Ross S, Verbeeck R (1987) Piroxicam and 5’-hydroxypiroxicam kinetics following multiple dose administration of piroxicam. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 32(1):89–91. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00609964
Riedel KD, Laufen H (1983) High-performance thin-layer chromatographic assay for the routine determination of piroxicam in plasma, urine and tissue. J Chromatogr 276:243–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0378-4347(00)85090-2
Rodrigues AD (1999) Integrated cytochrome P450 reaction phenotyping: attempting to bridge the gap between cDNA-expressed cytochromes P450 and native human liver microsomes. Biocheml Pharmacol 57(5):465–480. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0006-2952(98)00268-8
Rogers HJ, Spector RG, Morrison PJ, Bradbrook ID (1981) Comparative steady state pharmacokinetic study of piroxicam and flurbiprofen in normal subjects. Eur J Rheumatol Inflamm 4(3):303–308
Rüdesheim S, Wojtyniak JG, Selzer D, Hanke N, Mahfoud F, Schwab M, Lehr T (2020) Physiologically based pharmacokinetic modeling of metoprolol enantiomers and α-Hydroxymetoprolol to Describe CYP2D6 drug-gene interactions. Pharmaceutics 12(12):1200. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12121200
Rudy AC, Figueroa NL, Hall SD, Brater DC (1994) The pharmacokinetics of piroxicam in elderly persons with and without renal impairment. Br J Clin Pharmacol 37(1):1–5. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2125.1994.tb04230.x
Said SA, Foda AM (1989) Influence of cimetidine on the pharmacokinetics of piroxicam in rat and man. Arzneimittelforschung 39(7):790–792
Schmitt W (2008) General approach for the calculation of tissue to plasma partition coefficients. Toxicol in Vitro 22(2):457–467. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tiv.2007.09.010
Shahbaz N, Iqbal Z, Nasir F, Khan FU, Hassan AM, Khan SI (2018) Simultaneous determination of piroxicam and 5-hydroxypiroxicam: HPLC/UV method development, validation and application for pharmacokinetic evaluation in Pakistani population. J Chem Soc Pak 40(05):856–865
Shin HB, Jung EH, Kang P, Lim CW, Oh KY, Cho CK, Lee YJ, Choi CI, Jang CG, Lee SY, Bae JW (2020) ABCB1 c.2677G>T/c.3435C>T diplotype increases the early-phase oral absorption of losartan. Arch Pharm Res 43(11):1187–1196. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-020-01294-3
Smith DM, Stevenson JM, Ho TT, Formea CM, Gammal RS, Cavallari LH (2022) Pharmacogenetics: A precision medicine approach to combatting the opioid epidemic. J Am Coll Clin Pharm 5(2):239–250. https://doi.org/10.1002/jac5.1582
Song HH, Choi KS, Kim CW, Kwon YE (2009) Pharmacokinetic profiles of two branded formulations of piroxicam 20mg in healthy Korean volunteers by a rapid isocratic HPLC method. J Bioequiv Availab 1(3):74–79
Suri A, Chapel S, Lu C, Venkatakrishnan K (2015) Physiologically based and population PK modeling in optimizing drug development: A predict–learn–confirm analysis. Clin Pharmacol Ther 98(3):336–344. https://doi.org/10.1002/cpt.155
Tang C, Shou M, Rushmore TH, Mei Q, Sandhu P, Woolf EJ, Rose MJ, Gelmann A, Greenberg HE, De Lepeleire I, Van Hecken A, De Schepper PJ, Ebel DL, Schwartz JI, Rodrigues AD (2001) In-vitro metabolism of celecoxib, a cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor, by allelic variant forms of human liver microsomal cytochrome P450 2C9: correlation with CYP2C9 genotype and in-vivo pharmacokinetics. Pharmacogenet Genomics 11(3):223–235
Theken KN, Lee CR, Gong L, Caudle KE, Formea CM, Gaedigk A, Klein TE, Agúndez JAG, Grosser T (2020) Clinical pharmacogenetics implementation consortium guideline (CPIC) for CYP2C9 and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Clin Pharmacol Ther 108(2):191–200. https://doi.org/10.1002/cpt.1830
Thelen K, Coboeken K, Willmann S, Burghaus R, Dressman JB, Lippert J (2011) Evolution of a detailed physiological model to simulate the gastrointestinal transit and absorption process in humans, part 1: oral solutions. J Pharm Sci 100(12):5324–5345. https://doi.org/10.1002/jps.22726
Thelen K, Coboeken K, Willmann S, Dressman JB, Lippert J (2012) Evolution of a detailed physiological model to simulate the gastrointestinal transit and absorption process in humans, part II: extension to describe performance of solid dosage forms. J Pharm Sci 101(3):1267–1280. https://doi.org/10.1002/jps.22825
Tilstone WJ, Lawson DH, Omara F, Cunningham F (1981) The steady-state pharmacokinetics of piroxicam: effect of food and iron. Eur J Rheumatol Inflamm 4(3):309–313
Tracy TS, Hutzler JM, Haining RL, Rettie AE, Hummel MA, Dickmann LJ (2002) Polymorphic variants (CYP2C9*3 and CYP2C9*5) and the F114L active site mutation of CYP2C9: effect on atypical kinetic metabolism profiles. Drug Metab Dispos 30(4):385–390. https://doi.org/10.1124/dmd.30.4.385
Trnavská Z, Trnavský K (1984) Plasma protein binding and interaction studies with piroxicam. Naunyn Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol 327(1):81–85. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00504996
Tvrdonova M, Dedik L, Mircioiu C, Miklovicova D, Durisova M (2009) Physiologically motivated time-delay model to account for mechanisms underlying enterohepatic circulation of piroxicam in human beings. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 104(1):35–42. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-7843.2008.00304.x
Verscheijden LFM, Koenderink JB, Johnson TN, de Wildt SN, Russel FGM (2020) Physiologically-based pharmacokinetic models for children: Starting to reach maturation? Pharmacol Ther 211:107541. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2020.107541
Wang D, Miller R, Zheng J, Hu C (2000) Comparative population pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic analysis for piroxicam-beta-cyclodextrin and piroxicam. J Clin Pharmacol 40(11):1257–1266
Wang L, Bao SH, Pan PP, Xia MM, Chen MC, Liang BQ, Dai DP, Cai JP, Hu GX (2015) Effect of CYP2C9 genetic polymorphism on the metabolism of flurbiprofen in vitro. Drug Dev Ind Pharm 41(8):1363–1367. https://doi.org/10.3109/03639045.2014.950274
Wanwimolruk S, Wanwimolruk SZ, Zoest A (1991) A simple and sensitive HPLC assay for piroxicam in plasma and its application to bioavailability study. J Liq Chromatogr 14(12):2373–2381. https://doi.org/10.1080/01483919108049697
Weintraub M, Jacox RF, Angevine CD, Atwater EC (1977) Piroxicam (CP 16171) in rheumatoid arthritis: a controlled clinical trial with novel assessment techniques. J Rheumatol 4(4):393–404
Wojtyniak JG, Britz H, Selzer D, Schwab M, Lehr T (2020) Data digitizing: accurate and precise data extraction for quantitative systems pharmacology and physiologically-based pharmacokinetic modeling. CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol 9(6):322–331. https://doi.org/10.1002/psp4.12511
Wojtyniak JG, Selzer D, Schwab M, Lehr T (2021) Physiologically based precision dosing approach for drug-drug-gene interactions: a simvastatin network analysis. Clin Pharmacol Ther 109(1):201–211. https://doi.org/10.1002/cpt.2111
Xu M, Zheng L, Zeng J, Xu W, Jiang X, Wang L (2021) Physiologically based pharmacokinetic modeling of tramadol to inform dose adjustment and drug-drug interactions according to CYP2D6 phenotypes. Pharmacotherapy 41(3):277–290. https://doi.org/10.1002/phar.2494
Yellepeddi V, Rower J, Liu X, Kumar S, Rashid J, Sherwin CMT (2019) State-of-the-art review on physiologically based pharmacokinetic modeling in pediatric drug development. Clin Pharmacokinet 58(1):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40262-018-0677-y
Zhuang X, Lu C (2016) PBPK modeling and simulation in drug research and development. Acta Pharm Sin B 6(5):430–440. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsb.2016.04.004
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT, and Future Planning (NRF-2019R1A2C1004582).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cho, C., Kang, P., Park, HJ. et al. Physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) modeling of piroxicam with regard to CYP2C9 genetic polymorphism. Arch. Pharm. Res. 45, 352–366 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-022-01388-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-022-01388-0