Abstract
The impact of acute cardiac dysfunction on the gastrointestinal tract was investigated in anesthetized and instrumented pigs by sequential reductions of cardiac output (CO). Using a cardiac tamponade (n = 6) or partial inferior caval vein balloon inflation (n = 6), CO was controllably reduced for 1 h each to 75% (CO75%), 50% (CO50%), and 35% (CO35%) of the baseline value. Cardiac output in controls (n = 6) was not manipulated and maintained. Mean arterial pressure, superior mesenteric arterial blood flow, and intestinal mucosal perfusion started to decrease at CO50% in the intervention groups. The decrease in superior mesenteric arterial blood flow was non-linear and exaggerated at CO35%. Systemic, venous mesenteric, and intraperitoneal lactate concentrations increased in the intervention groups from CO50%. Global and mesenteric oxygen uptake decreased at CO35%. In conclusion, gastrointestinal metabolism became increasingly anaerobic when CO was reduced by 50%. Anaerobic gastrointestinal metabolism in low CO can be detected using intraperitoneal microdialysis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Critically ill patients and patients undergoing cardiac surgery frequently develop cardiac dysfunction with low cardiac output (CO) [1, 2]. Low CO causes impairment of splanchnic circulation, leading to loss of gastrointestinal (GI) mucosal barrier function and bacterial translocation, which may initiate, maintain, or aggravate a systemic inflammatory reaction [3]. These processes may progress to GI complications, which include GI bleeding, mesenteric ischemia, and pancreatitis [4,5,6].
From human studies, it is difficult to establish which degree of CO reduction impairs GI metabolism, and in a clinical setting, this would be difficult or even impossible to investigate in a well-regulated manner. Previous animal studies using different methods of splanchnic blood flow reduction, however not limited to low cardiac output, have found that approximately a halving or more of GI blood flow induced a GI metabolic disorder, including decreased mucosal oxygen tension, mucosal pH and mesenteric oxygen uptake, and increased jejunal mucosal-to-arterial PCO2 gradient [7,8,9]. Further metabolic consequences were increased mesenteric venous-arterial lactate difference and ß-hydroxybutyrate/acetoacetate ratio as well as increased intestinal intraluminal and intramural lactate concentrations and lactate/pyruvate ratios [7, 10]. The specific methods for detection of splanchnic anaerobic metabolism, e.g., intestinal intraluminal and intramural microdialysis, jejunal tonometry, and jejunal mucosal oxygen tension, used in these studies are predominantly applicable in experimental investigations. In contrast, percutaneous insertion of intraperitoneal microdialysis catheters is possible in non-abdominal surgical patients, e.g., in endovascular surgery of ruptured aortic aneurysm and critical care patients [11, 12]. A pilot study of intraperitoneal microdialysis with measurements of lactate, pyruvate, glucose, and glycerol showed its feasibility in cardiac surgical patients [13], whereas it has not been investigated in low cardiac output models.
Several experimental models for creating acute cardiac dysfunction and low CO by myocardial injury have been described, including percutaneous injections of microspheres [14] or ethanol in a coronary artery [15], percutaneous balloon occlusion [16], or ligation of one or several coronary arteries [17,18,19]. Although clinically relevant, one disadvantage of these models is that CO cannot easily be titrated to a preset level. Models of GI in-flow restriction are easily adjustable, but if the GI tract is the target organ of interest, the splanchnic venous outflow pressure must be increased [20]. Obstruction of right heart filling by an adjustable cardiac tamponade [7, 21] and the reduction of cardiac preload by variable inflation of an inferior caval vein balloon [22, 23] are adjustable low cardiac output models with potentially mesenteric venous congestion.
Therefore, in the current study, we used these two porcine models—cardiac tamponade and caval vein balloon inflation—and investigated the impact of low CO on the splanchnic circulation and metabolism including intraperitoneal microdialysis. We hypothesized that a 50% reduction in CO causes an impairment of the GI circulation and metabolism detectable with intraperitoneal microdialysis.
Methods
Animals
The experiments were approved by the regional animal ethics committee and were conducted in accordance with the directive of the European Union for the protection of animals used for scientific purposes [24]. In this study, 24 healthy 3-month-old domestic pigs (a crossbreed between Swedish country breed, Hampshire and Yorkshire) of both sexes and with a median body weight of 30 kg (range 25–41 kg) were used.
Anesthesia, Fluid Administration, Ventilation, and Euthanasia
On the farm, the animals were given azaperone (200 mg, i.m.; Elanco, Herlev, Denmark). On arrival at the research facility, anesthesia was induced by tiletamine (6 mg kg−1, i.m.; Virbac, Kolding, Denmark), zolazepam (6 mg kg−1, i.m.; Virbac), and azaperone i.m. (4 mg kg−1). Atropine (1.5 mg, i.m.; Mylan, Stockholm, Sweden) was given. Two peripheral catheters (1.1 mm, Venflon™ Pro Safety, BD, Helsingborg, Sweden) were inserted in auricular veins. Propofol (1–2 mg kg−1, i.v.; Fresenius Kabi, Uppsala, Sweden) was given if needed. The pigs were orally intubated with a 6-mm endotracheal tube (Covidien, Tullamore, Ireland). Anesthesia was maintained with propofol (10–15 mg kg−1 h−1, i.v.) and fentanyl (5–20 μg kg−1 h−1, i.v; Meda, Solna, Sweden) given by motorized syringe pumps (Alaris CC, Cardinal Health, Rulle, Switzerland). The depth of anesthesia was intermittently checked by pain response. Cefuroxim (750 mg, i.v.; GSK, Solna, Sweden) was given before, and heparin (5000 IU, i.v.; LEO Pharma, Malmö, Sweden) after instrumentation. Ringer’s acetate (10 ml kg−1 h−1, i.v.; Fresenius Kabi) and 10% glucose with 40 mM sodium and 20 mM potassium (0.5 ml kg−1 h−1, i.v.; Fresenius Kabi) were administered, by volume pumps (Alaris GP, CareFusion). The pigs were ventilated in volume control ventilation mode (PV 501, Breas Medical AB, Sweden) to achieve arterial PCO2 of 4.8–5.5 kPa, and the fraction of inspired O2 was adjusted to maintain arterial PO2 at 11–18 kPa. The positive-end expiratory pressure was set at 4–6 cm H2O. Respiratory variables and gases were measured at the endotracheal tube (AS/3, Datex, Helsinki, Finland). The body temperature was kept at 37.5–38.5 °C by using a thermal mattress and a forced-air warming blanket. At the end of the experiment, the anesthetized animals were euthanized by a rapid i.v. injection of 40 mmol potassium chloride (B. Braun, Danderyd, Sweden), and asystole and circulatory arrest were confirmed by ECG and blood pressure recordings.
Surgical Preparation and Measurements
In the left external jugular vein, a 7-Fr triple-lumen central line (Arrow/Vingmed, Järfälla, Sweden) was inserted for fluid and drug administration. In the right carotid artery, a 4-Fr introducer (Cordis Corporation, Miami Lakes, FL, USA) was positioned for measurement of systemic blood pressure and heart rate and also for blood sampling. In the right external jugular vein, an 8-Fr introducer was inserted (Cordis Corporation). Through this, a pulmonary artery catheter (Swan-Ganz CCOmbo, 7.5 Fr, Edwards Lifesciences, Irvine, CA, USA) was positioned, with its tip in a branch of the pulmonary artery, under the guidance of the pressure curve. In addition, correct placement was confirmed by fluoroscopy (Philips BV 300, Stockholm, Sweden). The pulmonary artery catheter was used for blood sampling and measurements of pulmonary capillary wedge pressure (PCWP), central venous pressure (CVP), and CO using the semi-continuous thermodilution technique (Vigilance, Edwards Lifesciences).
A midline abdominal incision was performed. A 14-Fr Foley catheter (Unomedical, Flintshire, UK) was inserted in the bladder and fixed with a purse string suture. A laser Doppler probe (Probe 427, Perimed, Järfälla, Sweden), connected to a laser Doppler device (Periflux System 5000, Perimed), was placed intraluminally, pointing toward the intestinal mucosa in a mid-jejunal intestinal loop approximately 30 cm distal to the Treitz ligament for estimation of local mucosal perfusion [25]. An ultrasonic transit-time flowmeter (Vascular TTFM Probe 6 mm, Medistim ASA, Oslo, Norway) was placed around the superior mesenteric artery (SMA). A 6-Fr catheter (Nutrisafe 2, Vygon, Ecouen, France) was inserted in a distal branch and advanced to the superior mesenteric vein for pressure measurement and blood sampling. The blood samples were analyzed for pH, blood gases, electrolytes, lactate, hemoglobin, and glucose, using either i-STAT (Abbott Scandinavia, Solna, Sweden) or GEM Premier 4000 (Instrumentation Laboratory, Lexington, MA, USA), at 37 °C. Blood pressures were measured by a pressure transducer (Codan, Forstinnigen, Germany) connected to the AS/3 (Datex). A free-floating microdialysis catheter (62 Gastrointestinal Microdialysis Catheter, membrane length 30 mm, cut-off 20 kDa, M Dialysis, Stockholm, Sweden) was placed intraperitoneally in the left lower quadrant [26]. A syringe pump (107 Microdialysis Pump, M Dialysis) was used to propel a solution (Perfusion fluid T1, M Dialysis) at 2 μL min−1 through the microdialysis catheter. The microdialysate was analyzed for glucose, glycerol, lactate, and pyruvate (CMA 600, M Dialysis).
Specific Preparation of Animals in the Cardiac Tamponade and Control Groups
In the control and the tamponade groups, a 12-Fr Foley catheter (Unomedical) was inserted into the pericardial space via a small incision through a diaphragmatic window and sutured in place. Subcutaneous fat was used as pledgets to reduce the risk of leakage. Approximately 5 ml of physiological sodium chloride solution (B. Braun) was instilled in the balloon of the Foley catheter.
Specific Preparation of Animals in the Inferior Caval Vein Balloon Group
In the animals allocated to the caval vein balloon group, an additional 11-Fr introducer (Cordis Corporation) was inserted in the right external jugular vein. A balloon catheter (Cordis PTA Dilatation Catheter, large diameter balloon, 7 Fr, 80 cm, Cordis Corporation) was advanced to the diaphragmatic part of the inferior caval vein under fluoroscopic guidance.
Protocol
After an intervention-free period of 1 h to achieve stable baseline conditions, the animals were divided into three groups: (1) the tamponade group, (2) the caval vein balloon group, and (3) the control group. In the tamponade group, CO was reduced by instillation of a colloid fluid (at 38 °C; 6% hydroxyethyl starch, Fresenius Kabi) via the pericardial Foley catheter into the closed pericardium. Cardiac tamponade was confirmed by transthoracic echocardiography (SonoSite Titan™, L52/10–5 MHz Transducer, Askim, Sweden). In the caval vein balloon group, CO was decreased by partial inflation of the balloon. Inflation of the balloon was confirmed by fluoroscopy. After collecting baseline values, blood samples, and microdialysate, CO was stepwise lowered in these groups to 75% (CO75%), 50% (CO50%), and 35% (CO35%) of baseline value for 1 h each, at which point respiratory and hemodynamic variables as well as blood samples were collected. The microdialysate was gathered during the last 30 min at each CO level. In the control group, no intervention was made to affect CO, but data collection was identical to that of the two other groups.
Calculations
Cardiac output and SMA blood flow were divided by body surface area, according to the formula: body surface area (m2) = 0.0734 × weight (kg)0.656, to obtain the cardiac index (CI) and the SMA blood flow index [27]. Oxygen saturation was calculated as PO22.94/(PO22.94 + P502.94). 4.76 kPa was used as the porcine partial pressure of oxygen (PO2), where hemoglobin is half-saturated (P50), and the value was adjusted with the fixed acid Bohr coefficient [28]. Oxygen content was calculated as saturation (fraction) × Hb (g/l) × 1.34 + 0.225 × PO2 (kPa) [29]. Oxygen extraction was calculated as arterial oxygen content subtracted by venous oxygen content. Oxygen delivery (DO2) was acquired as the blood flow index times arterial oxygen content, and oxygen uptake (VO2) was calculated as oxygen extraction times the blood flow index.
Statistical Analysis
Data are presented as medians with interquartile ranges. In the statistical analysis, the absolute value was used at baseline, and thereafter, the difference or percentage change from baseline was used. The Bonferroni corrected Kruskal-Wallis tests were performed to identify statistical differences between groups at each CO level, and, if significant, they were followed by pairwise comparisons between groups using the Bonferroni corrected Mann-Whitney U tests. Least-squares linear and logarithmic regressions were made. A P value of less than 0.05 was regarded as statistically significant. Statistical analysis was performed using IBM SPSS Statistics version 22.0 for Windows (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA).
Results
Animal Inclusion
Of the 24 animals used in the study, one pig was excluded due to circulatory instability after instrumentation, and one died suddenly during instrumentation. Nine animals were allocated to the tamponade group; two were excluded because of leakage from the pericardial sutures that could not be repaired, and one was excluded due to failure to collect microdialysate. Four of the six animals in the tamponade group died at CO35% and were only included in the statistical analyses until CO50% (Fig. 1b). Seven pigs were allocated to the caval vein balloon group; one died of an arrhythmia at CO75% and was excluded. Six pigs were included in the control group.
Cardiac output (CO, panel a, data are presented as medians and interquartile ranges) and survival (panel b) in anesthetized and mechanically ventilated pigs subjected to a graded reduction of CO to 75% (CO75%), 50% (CO50%), and 35% (CO35%) of the baseline value by either cardiac tamponade (n = 6) or partial inflation of an inferior caval vein balloon (n = 6). In one group, no intervention was made (control, n = 6)
Cardiac Output
At baseline, CI values were 6.4 (5.5–7.5), 5.9 (4.8–6.6), and 6.7 (6.0–7.5) l min−1 m−2 in the control (n = 6), tamponade (n = 6), and caval vein balloon (n = 6) groups, respectively. Both inflation of the caval vein balloon and induction of the cardiac tamponade caused a controllable and steady lowering of CO to the targeted level, whereas the controls maintained their CO level throughout the study (Fig. 1a). After the desired level of CO was reached, no major adjustments of the pericardial volume or caval vein balloon inflation were required (data not presented).
Central Hemodynamic Variables
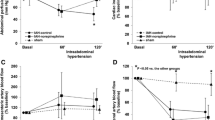
At CO75%, the mean arterial pressure (MAP) was unchanged in the tamponade and caval vein groups, compared to the control group (Fig. 2a). In both intervention groups, MAP decreased significantly when CO was further reduced (P < 0.05 compared to the control group, Fig. 2a). Heart rate followed a biphasic response in both intervention groups (Fig. 2b). CVP increased in the tamponade group and decreased in the caval vein group (P < 0.05 in both groups compared to the control group), while the mesenteric venous pressure (MVP) tended to increase in both intervention groups (Fig. 2c, d).
Mean arterial pressure (MAP, panel a), heart rate (HR, panel b), central venous pressure (CVP, panel c), mesenteric venous pressure (MVP, panel d), superior mesenteric arterial blood flow (SMA, panel e), and intestinal mucosal perfusion (Muc. perf., panel f) in anesthetized and mechanically ventilated pigs subjected to a graded reduction of cardiac output to 75% (CO75%), 50% (CO50%), and 35% (CO35%) of the baseline value by either cardiac tamponade (n = 6) or partial inflation of an inferior caval vein balloon (n = 6). In one group, no intervention was made (control, n = 6). Data are presented as medians and interquartile ranges. Asterisk, number, and currency symbols indicate a statistical difference (P < 0.05) between the caval vein balloon group and the control group, the cardiac tamponade group and the control group, and the caval vein balloon and cardiac tamponade groups, respectively
Gastrointestinal Circulation
At baseline, SMA flow index values were 1.03 (0.90–1.42), 0.85 (0.60–1.29) and 1.04 (0.92–1.40) l min−1 m−2 in the control, tamponade, and caval vein balloon groups, respectively. SMA blood flow decreased significantly in both intervention groups as CI decreased (P < 0.05 compared to the control group, Fig. 2e). Intestinal mucosal perfusion was decreased at CO35% (P < 0.05 for caval vein balloon versus controls, Fig. 2f).
Relationship Between Cardiac Index and Blood Flow in the Superior Mesenteric Artery
The decrease in SMA flow in the intervention groups followed the decrease in CI, but the SMA flow was higher than predicted at CO50% (61% [48–73] and 60% [53–70]) in the tamponade and caval vein groups, respectively) and lower at CO35% (17% and 24% [19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36] in the tamponade and caval vein groups, respectively; Figs. 2e and 3). To further explore the relationship between CI and SMA flow, linear and logarithmic regressions were carried out. Using SMA flow (percentage of baseline) as the dependent variable and CI (percentage of baseline) as the independent variable, regression analysis resulted in a better fit when using a natural logarithmic rather than a linear equation (Fig. 3).
Respiratory Variables
Arterial PO2 and PCO2 and also minute ventilation and fraction of inspired O2 were normal, stable, and similar in all groups throughout the study (Table 1).
Oxygen Indices
At baseline, systemic DO2 values were 550 (490–690), 690 (590–820), and 730 (590–810) ml O2 min−1 m−2 in the control, tamponade, and caval vein balloon groups, respectively, while mesenteric DO2 were 92 (75–138), 108 (62–170), and 116 (103–131) ml O2 min−1 m−2 in the respective groups. Systemic respective mesenteric VO2 were 300 (260–300) and 38 (27–59) ml O2 min−1 m−2 in the control group, 350 (250–430) and 47 (34–61) ml O2 min−1 m−2 in the tamponade group, and 360 (330–390) and 50 (46–68) ml O2 min−1 m−2 in the caval vein balloon group. Systemic and mesenteric DO2 decreased significantly when CO was reduced (P < 0.05 compared to control, Fig. 4a, b). In parallel, the mixed venous and mesenteric venous SO2 decreased significantly to very low values at CO35% (P < 0.05 compared to controls, Fig. 4c, d). Significant decrements in systemic and mesenteric VO2 developed at CO35% (P < 0.05, compared to controls, Fig. 4e, f).
Global and mesenteric oxygen deliveries (DO2, panela a and b, respectively), mixed-venous saturation (Mix.-ven. SO2, panel c), mesenteric venous saturation (Mes. ven. SO2, panel d), global and mesenteric oxygen uptakes (VO2, panels e and f, respectively), and also systemic and mesenteric venous lactate concentrations (panels g and h, respectively) in anesthetized and mechanically ventilated pigs subjected to a graded reduction of cardiac output to 75% (CO75%), 50% (CO50%), and 35% (CO35%) of the baseline value by either cardiac tamponade (n = 6) or partial inflation of an inferior caval vein balloon (n = 6). In one group, no intervention was made (control, n = 6). Data are presented as medians and interquartile ranges. Asterisk, number, and currency symbols indicate a statistical difference (P < 0.05) between the caval vein balloon group and the control group, the cardiac tamponade group and the control group, and the caval vein balloon and cardiac tamponade groups, respectively
Metabolic Variables
Arterial pH decreased in the intervention groups and was significantly lower compared to the control group (P < 0.05) at CO50% and CO35% (Table 1). Arterial and mesenteric lactate levels increased significantly from CO75% and CO50% in the tamponade and caval vein balloon groups, respectively (P < 0.05 compared to the control group, Fig. 4g, h). The arterial-mesenteric venous differences of lactate tended to become more negative as CO was progressively reduced (Table 1). Intraperitoneal lactate concentrations increased significantly in both intervention groups and were significantly higher compared to the control group from CO50% (P < 0.05, Table 1). Intraperitoneal lactate/pyruvate ratios increased from CO50% and CO35% in the tamponade and caval vein balloon groups, respectively (P < 0.05 compared to the control group, Table 1). Intraperitoneal glycerol levels increased at CO35% in the caval vein group (P < 0.05 compared to the control group, Table 1). Intraperitoneal pyruvate and glucose concentrations and plasma glucose concentrations did not change significantly (Table 1).
Discussion
In this study, two different methods to induce low CO states were used with the aim of simulating acute cardiac dysfunction. Important features of the present methods include a high degree of adjustability to a predetermined level of CO and the ability to maintain a stable CO after reaching target values. During the conduct of the experiments, the authors found the cardiac tamponade model more surgically demanding and that the responses to the titrations of CO in that model were less predictable. A noteworthy difference between the models was that only a minority of the animals in the cardiac tamponade group survived 1 h at the lowest CO level, which is in line with a previous study [7]. Both models compromise ventricular filling but with different cardiac pathology. Both methods induce preload-dependent systolic dysfunction, while cardiac tamponade also deteriorates diastolic function. The diastolic dysfunction composes an early diastolic collapse of the right ventricle, a late diastolic collapse of the right atrium, and an abnormal septal motion [30]. The increased pericardial pressure and the decreased MAP in cardiac tamponade may lower the myocardial blood flow resulting in myocardial ischemia [31]. The distinctive effects on cardiac function by the cardiac tamponade could explain the higher mortality at the very low CO levels. These differences in features between the models favor the use of the caval vein balloon model in future work aimed at studying distal organ function in low CO conditions.
In contrast to models of low CO induced by cardiac ischemia [14, 16, 17, 19, 32], neither of the presented models mirrors cardiac dysfunction with load-independent decreased contractility, which would have been a disadvantage if the cardiac function per se was the subject matter. However, from the perspective of the intestines, both mimic a combined backward and forward cardiac failure, which makes the models highly clinically relevant for gastrointestinal consequences of cardiac dysfunction.
Backward failure was indicated by raised MVP in both conditions. Forward failure caused decreases in SMA flow and also global and mesenteric DO2. MAP and intestinal mucosal perfusion were maintained at CO75% and decreased thereafter. An effect on the metabolism was apparent first at CO50% and was clearly pronounced at CO35%. VO2 decreased at CO35% possibly due to reaching the limit of oxygen extraction capability when mesenteric venous SO2 entered the lower flat part of the hemoglobin oxygen dissociation curve.
In the present models, a global anaerobic state was induced. The GI tract contributed partly to this response, since the arterial-mesenteric venous lactate difference tended to become gradually more negative when reducing CO in parallel with increments in intraperitoneal lactate and glycerol concentrations. This is further supported by the decrease in intestinal VO2 at CO35%.
The present data indicate that the GI tract can withstand only a mild compromised circulation with major metabolic derangements evident at CO50%. These findings are in accordance with several other studies using various methods of splanchnic hypoperfusion. Using cardiopulmonary bypass in a porcine model, Thomassen et al. [10] showed that the pump flow had to be reduced to approximately 50% of the normal CO value to increase the colonic intramural lactate level and lactate/pyruvate ratio. In a canine model with selective restriction of aortic blood flow, a reduction in splanchnic blood flow to approximately 50% affected the intestinal CO2 gradient measured with tonometry [8]. In a study with selective flow reduction of SMA, the jejunal intraluminal pH started to decrease when the flow was reduced to around 50% of baseline [9]. Furthermore, a porcine study using cardiac tamponade found that anaerobic metabolism in jejunal mucosa was initiated in an interval of an aortic flow reduction between 40 and 60% of the baseline value [7].
Both methods used in the present study had a physiological component of mesenteric venous congestion, which is highly relevant when investigating the effects of cardiac dysfunction and low CO on the GI tract. Pure arterial occlusive models or models with hypovolemia do not include mesenteric venous congestion [8, 9]. Venous congestion is of importance for the circulation of the GI tract, since occlusion of the mesenteric vein produced earlier and larger effects on the systemic and regional hemodynamic and metabolism than an occlusion of the SMA [33].
There might be concerns about whether the most vulnerable part of the large GI tract has been found when detecting effects of low CO. Using intraluminal laser Doppler in postoperative cardiac surgical patients, Thorén et al. [34] showed a possible mismatch between the total splanchnic blood flow and the local mucosal perfusion. However, intraperitoneal microdialysis, with measurements of glucose, lactate, pyruvate, lactate/pyruvate ratio, and glycerol, reflects the overall intraabdominal balance between aerobic and anaerobic metabolism [35,36,37,38,39]. Intraluminal microdialysis detected anaerobic GI metabolism in low cardiac output, but small intestinal intraluminal insertion is not easily done in patients with closed abdomen [7]. Intraperitoneal microdialysis may be as sensitive as local intraluminal measurements in detecting regional occlusive intestinal ischemia [40], and the present data show that intraperitoneal lactate and lactate/pyruvate ratio responded with gradual increments to low CO. Thus, further exploration of intraperitoneal microdialysis in patients susceptible to low CO, and therefore GI injury, is warranted.
The present data were used to find a relationship between the reduction in CO and the blood flow in SMA. The logarithmic equation showed that CO is not proportionally distributed to SMA throughout the various levels of CO reduction. From normal CO to a reduction of 58% of the baseline value, the decrease in SMA flow is less than expected. Thereafter, a further CO reduction causes the flow in SMA to drop more steeply. This gives an indication of how the physiological regulation of the GI tract is executed in low CO states. A similar non-linear relationship between aortic and mesenteric blood flow has been shown in conscious dogs during cardiac tamponade [41]. From a physiological point of view, a combined flow and pressure threshold for preserved intestinal perfusion and metabolism would be expected, although the exact levels to target in an individual patient with various comorbidities in a clinical setting cannot be inferred from this study.
In conclusion, both cardiac tamponade and caval vein balloon inflation caused a reproducible lowering of CO and mesenteric congestion with similar GI circulatory and metabolic effects. Gastrointestinal metabolism became increasingly anaerobic when CO was reduced to 50% of the baseline value, which is considered a moderate reduction, demonstrating the potential hazard of cardiac dysfunction on the gastrointestinal tract. Anaerobic GI metabolism in low CO can be detected using intraperitoneal microdialysis, suggesting a potential use in risk patients.
Abbreviations
- CI:
-
Cardiac index
- CO:
-
Cardiac output
- CVP:
-
Central venous pressure
- DO2 :
-
Oxygen delivery
- GI:
-
Gastrointestinal
- MAP:
-
Mean arterial pressure
- MVP:
-
Mesenteric venous pressure
- PCWP:
-
Pulmonary capillary wedge pressure
- SMA:
-
Superior mesenteric artery
- SO2 :
-
Oxygen saturation
- VO2 :
-
Oxygen uptake
References
Lomivorotov, V. V., Efremov, S. M., Kirov, M. Y., Fominskiy, E. V., & Karaskov, A. M. (2017). Low-cardiac-output syndrome after cardiac surgery. Journal of Cardiothoracic and Vascular Anesthesia, 31(1), 291–308. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.jvca.2016.05.029.
Mebazaa, A., Pitsis, A. A., Rudiger, A., Toller, W., Longrois, D., Ricksten, S. E., et al. (2010). Clinical review: practical recommendations on the management of perioperative heart failure in cardiac surgery. Critical Care (London, England), 14(2), 201. https://doi.org/10.1186/cc8153.
Hassoun, H. T., Kone, B. C., Mercer, D. W., Moody, F. G., Weisbrodt, N. W., & Moore, F. A. (2001). Post-injury multiple organ failure: the role of the gut. Shock, 15(1), 1–10.
Chaudhry, R., Zaki, J., Wegner, R., Pednekar, G., Tse, A., Sheinbaum, R., et al. (2017). Gastrointestinal complications after cardiac surgery: a nationwide population-based analysis of morbidity and mortality predictors. Journal of Cardiothoracic and Vascular Anesthesia, 31(4), 1268–1274. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.jvca.2017.04.013.
Rodriguez, R., Robich, M. P., Plate, J. F., Trooskin, S. Z., & Sellke, F. W. (2010). Gastrointestinal complications following cardiac surgery: a comprehensive review. Journal of Cardiac Surgery, 25(2), 188–197. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1540-8191.2009.00985.x.
Mutlu, G. M., Mutlu, E. A., & Factor, P. (2001). GI complications in patients receiving mechanical ventilation. Chest, 119(4), 1222–1241.
Tenhunen, J. J., Jakob, S., Ruokonen, E., & Takala, J. (2002). Jejunal luminal microdialysate lactate in cardiac tamponade--effect of low systemic blood flow on gut mucosa. Intensive Care Medicine, 28(7), 953–962. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-002-1314-6.
Cruz Jr., R. J., Garrido, A. G., de Natale Caly, D., & Rocha-e-Silva, M. (2011). Hepatosplanchnic vasoregulation and oxygen consumption during selective aortic blood flow reduction and reperfusion. Journal of Surgical Research, 171(2), 532–539. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jss.2010.05.037.
Pargger, H., Staender, S., Studer, W., Schellscheidt, O., Mihatsch, M. J., Scheidegger, D., et al. (1997). Occlusive mesenteric ischemia and its effects on jejunal intramucosal pH, mesenteric oxygen consumption and oxygen tensions from surfaces of the jejunum in anesthetized pigs. Intensive Care Medicine, 23(1), 91–99.
Thomassen, S. A., Kjaergaard, B., Sorensen, P., Andreasen, J. J., Larsson, A., & Rasmussen, B. S. (2017). Regional muscle tissue saturation is an indicator of global inadequate circulation during cardiopulmonary bypass: a randomized porcine study using muscle, intestinal and brain tissue metabolomics. Perfusion, 32(3), 192–199. https://doi.org/10.1177/0267659116674271.
Horer, T. M., Skoog, P., Norgren, L., Magnuson, A., Berggren, L., Jansson, K., et al. (2013). Intra-peritoneal microdialysis and intra-abdominal pressure after endovascular repair of ruptured aortic aneurysms. European Journal of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery, 45(6), 596–606. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejvs.2013.03.002.
Konstantinos, T., Apostolos, K., Georgios, P., & Konstantinos, T. (2014). Intraperitoneal microdialysis as a monitoring method in the intensive care unit. International Surgery, 99(6), 729–733. https://doi.org/10.9738/INTSURG-D-13-00139.1.
Adluri, R. K., Singh, A. V., Skoyles, J., Baker, M., & Mitchell, I. M. (2011). Measurement of intraperitoneal metabolites during hypothermic cardiopulmonary bypass using microdialysis. Scandinavian Cardiovascular Journal, 45(4), 229–235. https://doi.org/10.3109/14017431.2011.572995.
Kolseth, S. M., Wahba, A., Kirkeby-Garstad, I., Aro, S., Nordgaard, H., Hoydal, M., et al. (2012). A dose-response study of levosimendan in a porcine model of acute ischaemic heart failure. European Journal of Cardio-Thoracic Surgery, 41(6), 1377–1383. https://doi.org/10.1093/ejcts/ezr201.
Shi, W., McIver, B. V., Kalra, K., Sarin, E. L., Schmarkey, S., Duggan, M., et al. (2017). A swine model of percutaneous intracoronary ethanol induced acute myocardial infarction and ischemic mitral regurgitation. Journal of Cardiovascular Translational Research, 10(4), 391–400. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12265-017-9751-3.
Axelsson, B., Haggmark, S., Svenmarker, S., Johansson, G., Gupta, A., Tyden, H., et al. (2016). Effects of combined milrinone and levosimendan treatment on systolic and diastolic function during postischemic myocardial dysfunction in a porcine model. Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 21(5), 495–503. https://doi.org/10.1177/1074248416628675.
Lie, R. H., Hasenkam, J. M., Nielsen, T. T., Poulsen, R., & Sloth, E. (2008). Post-conditioning reduces infarct size in an open-chest porcine acute ischemia-reperfusion model. Acta Anaesthesiologica Scandinavica, 52(9), 1188–1193. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-6576.2008.01756.x.
Malliaras, K., Charitos, E., Diakos, N., Pozios, I., Papalois, A., Terrovitis, J., et al. (2014). Effects of intra-aortic balloon pump counterpulsation on left ventricular mechanoenergetics in a porcine model of acute ischemic heart failure. Journal of Cardiovascular Translational Research, 7(9), 810–820. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12265-014-9600-6.
Haraldsen, P., Lindstedt, S., Metzsch, C., Algotsson, L., & Ingemansson, R. (2014). A porcine model for acute ischaemic right ventricular dysfunction. Interactive Cardiovascular and Thoracic Surgery, 18(1), 43–48. https://doi.org/10.1093/icvts/ivt418.
De Backer, D., Zhang, H., & Vincent, J. L. (1995). Models to study the relation between oxygen consumption and oxygen delivery during an acute reduction in blood flow: comparison of balloon filling in the inferior vena cava, tamponade, and hemorrhage. Shock, 4(2), 107–112.
Aneman, A., Treggiari, M. M., Burgener, D., Laesser, M., Strasser, S., & Hadengue, A. (2009). Tezosentan normalizes hepatomesenteric perfusion in a porcine model of cardiac tamponade. Acta Anaesthesiologica Scandinavica, 53(2), 203–209. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-6576.2008.01834.x.
Haney, M. F., A’Roch, R., Johansson, G., Poelaert, J., & Biber, B. (2007). Beat-to-beat change in “myocardial performance index” related to load. Acta Anaesthesiologica Scandinavica, 51(5), 545–552. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-6576.2007.01287.x.
Fagerberg, A., Stenqvist, O., & Aneman, A. (2009). Electrical impedance tomography applied to assess matching of pulmonary ventilation and perfusion in a porcine experimental model. Critical Care (London, England), 13(2), R34. https://doi.org/10.1186/cc7741.
Directive 2010/63/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council of 22 September 2010 on the protection of animals used for scientific purposes. http://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:32010L0063&rid=1. Accessed 30 Nov 2016.
Leahy, M. J., de Mul, F. F., Nilsson, G. E., & Maniewski, R. (1999). Principles and practice of the laser-Doppler perfusion technique. Technology and Health Care, 7(2–3), 143–162.
Ungerstedt, U. (1991). Microdialysis--principles and applications for studies in animals and man. Journal of Internal Medicine, 230(4), 365–373.
Kelley, K. W., Curtis, S. E., Marzan, G. T., Karara, H. M., & Anderson, C. R. (1973). Body surface area of female swine. Journal of Animal Science, 36(5), 927–930.
Willford, D. C., & Hill, E. P. (1986). Modest effect of temperature on the porcine oxygen dissociation curve. Respiration Physiology, 64(2), 113–123.
Grimm, K. A., Lumb, W. V., & Jones, E. W. (2015). Veterinary anesthesia and analgesia : the fifth edition of Lumb and Jones. Ames: Wiley.
Kearns, M. J., & Walley, K. R. (2018). Tamponade: hemodynamic and echocardiographic diagnosis. Chest, 153(5), 1266–1275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chest.2017.11.003.
Taichman, G. C., Byrne, P., Forester, G. V., & Keon, W. J. (1984). Regional myocardial blood flow during pericardial tamponade. Canadian Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology, 62(5), 539–543.
Korvald, C., Elvenes, O. P., Aghajani, E., Myhre, E. S., & Myrmel, T. (2001). Postischemic mechanoenergetic inefficiency is related to contractile dysfunction and not altered metabolism. American Journal of Physiology: Heart and Circulatory Physiology, 281(6), H2645–H2653.
Cruz Jr., R. J., Garrido, A. G., Ribeiro, C. M., Harada, T., & Rocha-e-Silva, M. (2010). Regional blood flow distribution and oxygen metabolism during mesenteric ischemia and congestion. Journal of Surgical Research, 161(1), 54–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jss.2008.12.005.
Thoren, A., Jakob, S. M., Pradl, R., Elam, M., Ricksten, S. E., & Takala, J. (2000). Jejunal and gastric mucosal perfusion versus splanchnic blood flow and metabolism: an observational study on postcardiac surgical patients. Critical Care Medicine, 28(11), 3649–3654.
Jansson, K., Ungerstedt, J., Jonsson, T., Redler, B., Andersson, M., Ungerstedt, U., et al. (2003). Human intraperitoneal microdialysis: Increased lactate/pyruvate ratio suggests early visceral ischaemia. A pilot study. Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology, 38(9), 1007–1011.
Skoog, P., Horer, T., Nilsson, K. F., Agren, G., Norgren, L., & Jansson, K. (2015). Intra-abdominal hypertension--an experimental study of early effects on intra-abdominal metabolism. Annals of Vascular Surgery, 29(1), 128–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.avsg.2014.08.004.
Horer, T. M., Skoog, P., Nilsson, K. F., Oikonomakis, I., Larzon, T., Norgren, L., et al. (2014). Intraperitoneal metabolic consequences of supraceliac aortic balloon occlusion in an experimental animal study using microdialysis. Annals of Vascular Surgery, 28(5), 1286–1295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.avsg.2014.01.005.
Verdant, C. L., Chierego, M., De Moor, V., Chamlou, R., Creteur, J., de Dieu Mutijima, J., et al. (2006). Prediction of postoperative complications after urgent laparotomy by intraperitoneal microdialysis: a pilot study. Annals of Surgery, 244(6), 994–1002. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.sla.0000225092.45734.e6.
Horer, T. M., Norgren, L., & Jansson, K. (2011). Intraperitoneal glycerol levels and lactate/pyruvate ratio: early markers of postoperative complications. Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology, 46(7–8), 913–919. https://doi.org/10.3109/00365521.2011.568519.
Sommer, T., & Larsen, J. F. (2004). Intraperitoneal and intraluminal microdialysis in the detection of experimental regional intestinal ischaemia. British Journal of Surgery, 91(7), 855–861. https://doi.org/10.1002/bjs.4586.
Bernath, G. A., Cogswell, T. L., Hoffman, R. G., & Klopfenstein, H. S. (1987). Influences on the distribution of blood flow during cardiac tamponade in the conscious dog. Circulation Research, 60(1), 72–81.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Ms. Nina Adolfsson, RN, and Ms. Monica Clomén, RN, for the outstanding laboratory assistance, and also Mr. Jonathan Kimber for the language revision.
Funding
This study received funding from the Research Committee of Region Örebro County, Nyckelfonden at Örebro University Hospital, ALF Grants (Agreement concerning research and education of doctors) at Region Örebro County and the Swedish Society for Medical Research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. The experiments were approved by the regional animal ethics committee (Linköpings djurförsöksetiska nämnd, Linköping, Sweden: reference number 49-13) and were conducted in accordance with the directive of the European Union for the protection of animals used for scientific purposes.
Additional information
Associate Editor Junjie Xiao oversaw the review of this article
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Seilitz, J., Hörer, T.M., Skoog, P. et al. Splanchnic Circulation and Intraabdominal Metabolism in Two Porcine Models of Low Cardiac Output. J. of Cardiovasc. Trans. Res. 12, 240–249 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12265-018-9845-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12265-018-9845-6