Abstract
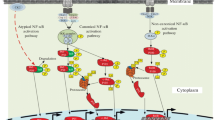
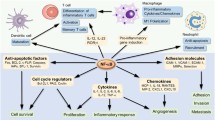
NF-κB family is a kind of nuclear factors in B lymphocyte that can bind to the immunoglobulin κ-chain enhancer and enhance transcriptional activity. NF-κB/Rel proteins, as a dimeric transcription factor, control the expression of genes that regulate a broad range of biological processes through canonical and non-canonical pathways. In the central nervous system, NF-κB controls inflammatory reactions and the apoptotic cell death following nerve injury. It also contributes to the infarction and cell death in stroke models and patients. However, NF-κB is essential for neurosurvival as well. NF-κB activation is a part of recovery process that may protect neurons against oxidative-stresses or brain ischemia-induced apoptosis and neurodegeneration. Inhibition of NF-κB may reduce its neuroprotection activity. Hence the dual opposite effects of NF-κB on cells. The ultimate survival or death of neurons depends on which, where and when the NF-κB factors are activated.
摘要
细胞核因子-κB(nuclear factor kappa B, NF-κB) 家族是 B 淋巴细胞核因子, 它能够与免疫球蛋白 κ 链增强子结合并增加各种基因的表达活性。 NF-κB 通过典型和非典型途径的激活来控制和调节各种生理病理过程。 在中枢神经系统, NF-κB 调控炎症反应、 神经损伤后的神经细胞凋亡等, 它可以促进中风等缺血性脑损伤的脑梗死面积和神经元死亡, 同时又对神经元的存活有重要影响。 NF-κB 激活是神经康复的重要组成部分, 它能够保护神经元免于由氧化应激和脑缺血诱导的神经元凋亡和变性, 阻滞 NF-κB 活性将影响它的神经保护机制。 NF-κB 这种对神经元存活和死亡的双重效应取决于 NF-κB 激活的亚单位类型、激活所处的损伤位置以及损伤后修复的时程。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gilmore TD. Introduction to NF-κB: players, pathways, perspectives. Oncogene 2006, 25: 6680–6684.
Vernon DO, Garbuzova-Davis S, Desjarlais T, Singh Rasile R, Sanberg PR, Willing AE, et al. Reduced Nuclear Factor kappa B activation in dentate gyrus after active avoidance training. Brain Res 2006, 1104: 39–44.
Kaltschmidt B, Widera D, Kaltschmidt C. Signaling via NF-κB in the nervous system. Biochim Biophys Acta 2005, 1745:287–299.
Mattson MP, Meffert MK. Roles for NF-kappaB in nerve cell survival, plasticity, and disease. Cell Death Differ 2006, 13:852–860.
Zhang W, Stanimirovic D. Current and future therapeutic strategies to target inflammation in stroke. Curr Drug Targets Inflamm Allergy 2002, 1: 151–166.
Daily D, Vlamis-Gardikas A, Offen D, Mittelman L, Melamed E, Holmgren A, et al. Glutaredoxin protects cerebellar granule neurons from dopamine-induced apoptosis by dual activation of the ras-phosphoinositide 3-kinase and jun n-terminal kinase pathways. J Biol Chem 2001, 276: 21618–21626.
Saito N, Courtois G, Chiba A, Yamamoto N, Nitta T, Hironaka N, et al. Two carboxyl-terminal activation regions of Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 activate NF-κB through distinct signaling pathways in fibroblast cell lines. J Biol Chem 2003, 278: 46565–46575.
Nurmi A, Lindsberg PJ, Koistinaho M, Zhang W, Juettler E, Karjalainen-Lindsberg ML, et al. Nuclear factor-kappaB contributes to infarction after permanent focal ischemia. Stroke 2004, 35: 987–991.
Zhang W, Potrovita I, Tarabin V, Herrmann O, Beer V, Weih F, et al. Neuronal activation of NF-κB contributes to cell death in cerebral ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2005, 25: 30–40.
Domanska-Janik K, Bronisz-Kowalczyk A, Zajac H, Zablocka B. Interrelations between nuclear-factor kappa B activation, glial response and neuronal apoptosis in gerbil hippocampus after ischemia. Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars) 2001, 61: 45–51.
Pennypacker KR, Kassed CA, Eidizadeh S, Saporta S, Sanberg PR, Willing AE. NF-κB p50 is increased in neurons surviving hippocampal injury. Exp Neurol 2001, 172: 307–319.
Duckworth EA, Butler T, Collier L, Collier S, Pennypacker KR. NF-κB protects neurons from ischemic injury after middle cerebral artery occlusion in mice. Brain Res 2006, 1088: 167–175.
Hang CH, Shi JX, Li JS, Wu W, Yin HX. Concomitant up regulation of nuclear factor-kB activity, proinflammatory cytokines and ICAM-1 in the injured brain after cortical contusion trauma in a rat model. Neurol India 2005, 53: 312–317.
Tao L, Chen X, Qin Z, Bian S. Could NF-κB and caspase-3 be markers for estimation of post-interval of human traumatic brain injury? Forensic Sci Int 2006, 162: 174–177.
Nomoto Y, Yamamoto M, Fukushima T, Kimura H, Ohshima K, Tomonaga M. Expression of nuclear factor kappa B and tumor necrosis factor alpha in the mouse brain after experimental thermal ablation injury. Neurosurgery 2001, 48: 158–166.
Uberti D, Grilli M, Memo M. Contribution of NF-κB and p53 in the glutamate-induced apoptosis. Int J Dev Neurosci 2000, 18: 447–454.
Juravleva E, Barbakadze T, Mikeladze D, Kekelidze T. Creatine enhances survival of glutamate-treated neuronal/glial cells, modulates Ras/NF-κB signaling, and increases the generation of reactive oxygen species. J Neurosci Res 2005, 79: 224–230.
Dhandapani KM, Wade FM, Wakade C, Mahesh VB, Brann DW. Neuroprotection by stem cell factor in rat cortical neurons involves AKT and NFkappaB. J Neurochem 2005, 95: 9–19.
Marini AM, Jiang X, Wu X, Tian F, Zhu D, Okagaki P, et al. Role of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and NF-κB in neuronal plasticity and survival: From genes to phenotype. Restor Neurol Neurosci 2004, 22: 121–130.
Zhu Y, Culmsee C, Klumpp S, Krieglstein J. Neuroprotection by transforming growth factor-beta1 involves activation of nuclear factor-kappaB through phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase/Akt and mitogen-activated protein kinase-extracellular-signal regulated kinase1,2 signaling pathways. Neuroscience 2004, 123: 897–906.
Keel M, Mica L, Stover J, Stocker R, Trentz O, Harter L. Thiopental-induced apoptosis in lymphocytes is independent of CD95 activation. Anesthesiology 2005, 103: 576–584.
Toliver-Kinsky T, Rassin D, Perez-Polo JR. NF-kappaB activity decreases in basal forebrain of young and aged rats after hyperoxia. Neurobiol Aging 2002, 23: 899–905.
Gu Z, Wortwein G, Yu J, Perez-Polo JR. Model for aging in the basal forebrain cholinergic system. Antioxid Redox Signal 2000, 2: 437–447.
Gu Z, Cain L, Werrbach-Perez K, Perez-Polo JR. Differential alterations of NF-κB to oxidative stress in primary basal forebrain cultures. Int J Dev Neurosci 2000, 18: 185–192.
Chau CH, Clavijo CA, Deng HT, Zhang Q, Kim KJ, Qiu Y, et al. Etk/Bmx mediates expression of stress-induced adaptive genes VEGF, PAI-1, and iNOS via multiple signaling cascades in different cell systems. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 2005, 289: C444–C554.
Ravati A, Ahlemeyer B, Becker A, Klumpp S, Krieglstein J. Preconditioning-induced neuroprotection is mediated by reactive oxygen species and activation of the transcription factor nuclear factor-κB. J Neurochem 2001, 78: 909–919.
Caccamo D, Campisi A, Marini H, Adamo EB, Li Volti G, Squadrito F, et al. Glutamate promotes NF-κB pathway in primary astrocytes: protective effects of IRFI 016, a synthetic vitamin E analogue. Exp Neurol 2005, 193: 377–383.
Mattson MP, Goodman Y, Luo H, Fu W, Furukawa K. Activation of NF-κB protects hippocampal neurons against oxidative stress-induced apoptosis: evidence for induction of manganese superoxide dismutase and suppression of peroxynitrite production and protein tyrosine nitration. J Neurosci Res 1997, 49: 681–697.
Memet S. NF-κB functions in the nervous system: from development to disease. Biochem Pharmacol 2006, 72: 1180–1195.
Henn IH, Bouman L, Schlehe JS, Schlierf A, Schramm JE, Wegener E, et al. Parkin mediates neuroprotection through activation of IêB kinase/nuclear factor-κB signaling. J Neurosci 2007, 27: 1868–1878.
Pizzi M, Sarnico I, Boroni F, Benarese M, Steimberg N, Mazzoleni G, et al. NF-κB factor c-Rel mediates neuroprotection elicited by mGlu5 receptor agonists against amyloid β-peptide toxicity. Cell Death Differ 2005, 12: 761–772.
Ramesh V, Thatte HS, McCarley RW, Basheer R. Adenosine and sleep deprivation promote NF-κB nuclear translocation in cholinergic basal forebrain. J Neurochem 2007, 100: 1351–1363.
Schneider A, Martin-Villalba A, Weih F, Vogel J, Wirth T, Schwaninger M. NF-κB is activated and promotes cell death in focal cerebral ischemia. Nat Med 1999, 5: 554–559.
Kaltschmidt C, Kaltschmidt B, Neumann H, Wekerle H, Baeuerle PA. Constitutive NF-κB activity in neurons. Mol Cell Biol 1994, 14: 3981–3992.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, L., Tao, LY. & Chen, XP. Roles of NF-κB in central nervous system damage and repair. Neurosci. Bull. 23, 307–313 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-007-0046-6
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-007-0046-6