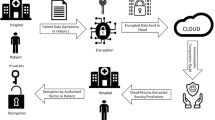
Abstract
Certificateless proxy signcryption (CLPSc) is one of the most efficient security primitives for secure data transmission. The entrustment of signing rights to a proxy signcrypter at the behest of an original signcrypter imparts its utility in various fields such as an online proxy auction, healthcare industry, cloud computing, mobile-agents, ubiquitous computing, etc. Unlike the traditional sign-then-encrypt approach, signcryption primitive saves computational costs and bandwidth load. Recently, a pairing-free CLPSc scheme has been proposed which claims to be secure against forgery under adaptive chosen-message attacks. This paper unveils that the aforementioned scheme has failed to provide unforgeability. As an improvement of their scheme, a novel pairing-free certificateless proxy signcryption scheme using elliptic curve cryptography (ECC) has been proposed for e-prescription system in mobile cloud computing. The proposed scheme is proven to be secure against indistinguishability under adaptive chosen-ciphertext attack and existential forgery under adaptive chosen-message attack in the random oracle model against Type 1 and Type 2 adversaries through formal analysis. The proposed scheme outperforms the existing schemes in terms of computational efficiency making it suitable for futuristic mobile cloud computing applications.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Xia Z, Wang X, Sun X, Wang Q (2016) A secure and dynamic multi-keyword ranked search scheme over encrypted cloud data. IEEE Trans Parallel Distrib Syst 27(2):340–352
Mambo M, Usuda K, Okamoto E (1996) Proxy signature for delegating signature operation. In: Proceedings of the 3rd ACM conference on computer and communications security, New Delhi, India, pp. 48–57
Shamir A (1984) Identity-based cryptosystems and signature schemes. In: Workshop on the theory and application of cryptographic techniques, Santa Barbara, CA, USA, pp. 47–53
Li J, Li J et al (2015) Identity-based encryption with outsourced revocation in cloud computing. IEEE Trans Comput 64(2):425–437
Hwang MS, Tzeng SF, Tsai CS (2004) Generalization of proxy signature based on elliptic curves. Comput Stand Interfaces 26(2):73–84
Hu, X., Wang, J., Xu, H., Yang, Y., & Xu, X. (2015). An improved efficient identity-based proxy signature in the standard model. Int J Comput Math, 1–18. doi: 10.1080/00207160.2015.1086759.
El-Kamchouchi H, Gaber H, Ahmed F, El-Kamchouchi DH (2016) An efficient proxy signature scheme over a secure communications network. World Acad Sci Eng Technol, Int J Comput Electr Autom Control Inf Eng 10(7):1226–1229
Al-Riyami SS, Paterson KG (2003) Certificateless public key cryptography. In international conference on the theory and application of cryptology and information security, Taipei, Taiwan, China, pp. 452–473
Zheng Y (1997) Digital signcryption or how to achieve cost (signature & encryption)≪ cost (signature)+ cost (encryption). In annual international cryptology conference, Santa Barbara, California, USA, (pp. 165–179)
Barbosa, M., &Farshim, P. (2008) Certificateless signcryption. In Proceedings of the 2008 ACM symposium on information, computer and communications security, New York, USA, pp. 369–372
Yin A, Liang H (2015) Certificateless hybrid Signcryption scheme for secure communication of wireless sensor networks. Wirel Pers Commun 80(3):1049–1062
Islam SH, Li F (2015) Leakage-free and provably secure certificateless signcryption scheme using bilinear pairings. Comput J 58(10):2636–2648
Debiao H, Jianhua C, Jin H (2011) An ID-based proxy signature schemes without bilinear pairings. Ann Telecommun 66(11–12):657–662
Jing, X. (2011). Provably secure certificateless signcryption scheme without pairing. In electronic and mechanical engineering and information technology (EMEIT), 2011 international conference on, 9, Harbin, Heilongjiang, China, pp. 4753–4756
Selvi SSD, Vivek SS, Rangan CP (2009) Cryptanalysis of certificateless signcryption schemes and an efficient construction without pairing. In F. Bao (Ed.), International conference on information security and cryptology, (pp. 75–92). Beijing, China
Xie W, Zhang Z (2010) Certificateless Signcryption without pairing. IACR Cryptol ePrint Arch 187
Shi W, Kumar N, Gong P, Zhang Z (2014) Cryptanalysis and improvement of a certificateless signcryption scheme without bilinear pairing. Front Comput Sci 8(4):656–666
Gamage C, Leiwo J, Zheng Y (1999) An efficient scheme for secure message transmission using proxy-signcryption. In Proceedings of the 22nd Australasian computer science conference, Sydney, Australia, pp. 420–431
Jung HY, Lee DH, Lim JI, Chang KS (2001) Signcryption schemes with forward secrecy, proceedings of information security application (WISA’01), Seoul, Korea, pp. 403–475
Elkamchouchi HM, Abouelseoud Y (2008) A new proxy identity-based Signcryption scheme for partial delegation of signing rights. IACR Cryptol ePrint Arch 2008:41
Wang C, Han Y, Li F (2009) A secure mobile agent protocol for m-commerce using self-certified proxy signcryption. In 2009 second international symposium on information science and engineering (ISISE’09), Washington, DC, USA, pp. 376–380
Lin HY, Wu TS, Huang SK, Yeh YS (2010) Efficient proxy signcryption scheme with provable CCA and CMA security. Comput Math Appl 60(7):1850–1858
Lo NW, Tsai JL (2014) A provably secure proxy signcryption scheme using bilinear pairings. J Appl Math. doi:10.1155/2014/454393.
Yanfeng Q, Chunming T, Yu L, Maozhi X, Baoan G (2013) Certificateless proxy identity-based signcryption scheme without bilinear pairings. China Commun 10(11):37–41
Ming Y, Wang Y (2015) Proxy signcryption scheme in the standard model. Secur Commun Netw 8(8):1431–1446
Zhou CX (2016) Identity based generalized proxy signcryption scheme. Inf Technol Control 45(1):13–26
Yeh JH (2014) The insecurity of two proxy signcryption schemes: proxy credential forgery attack and how to prevent it. J Supercomput 70(3):1100–1119
Shamus Software Ltd., Miracl library, https://certivox.org/display/EXT/MIRACL. Accessed on 20 September, 2016
The Certicom Corporation, SEC 2: Recommended Elliptic Curve Domain Parameters, http://www.secg.org/SEC2-Ver-1.0.pdf. Accessed on Accessed on 20 September, 2016
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhatia, T., Verma, A.K. Cryptanalysis and improvement of certificateless proxy signcryption scheme for e-prescription system in mobile cloud computing. Ann. Telecommun. 72, 563–576 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12243-017-0595-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12243-017-0595-2