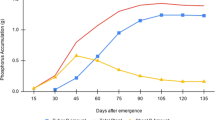
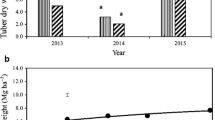
Abstract
Management of fertilizer phosphorus (P) is a critical component of potato production systems as potato has a relatively high P requirement and inefficiently uses soil P. Phosphorus promotes rapid canopy development, root cell division, tuber set, and starch synthesis. Adequate P is essential for optimizing tuber yield, solids content, nutritional quality, and resistance to some diseases. Although soil test P is the primary tool for assessing P fertilizer needs, in some areas petiole P analysis has been successfully utilized to guide in-season P applications. Potato has been shown in some studies to respond to fertilizer P at soil test levels considered very high for most other crops (100+ mg kg−1 Bray P1 or Mehlich I or III and 20+ mg kg−1 sodium bicarbonate) especially on medium- to finer-textured soils. Even on high-testing soils, fertilizer P rates for top yields sometimes exceed 150 kg P2O5 ha−1. In addition, many states/provinces continue to recommend half or more of the amount of P in the harvested portion of the crop irrespective of soil test P level. In most situations, few differences are expected among fertilizer P sources; however, high rates of diammonium phosphate (DAP) or urea-phosphate (UAP) should not be band-applied in contact or near the seed piece. Most research determined that fertilizer P was most efficiently used when band-applied at planting (e.g., 5 cm to each side of the seed piece); however, some western USA work on high-pH soils showed increased yields and petiole P levels with preplant broadcast applications. In-season applications with the irrigation water can be successful when the potato roots are sufficiently close to the soil surface; however, most research indicates that P applications are more effective when applied at planting or early in the season. Potato fertilizer phosphorus best management practices include: (1) apply the fertilizer P rate calibrated for local soils; (2) band-apply fertilizer P at least 5 cm from the seed piece, especially on very sandy soils or where DAP or UAP are used; (3) use petiole P tests to determine the need for in-season applications; (4) account for all P sources applied, including animal manures; and (5) utilize the best soil conservation practices to reduce P losses to surface waters.
Resumen
El manejo de fertilizantes fosforados (P) es un componente crítico de los sistemas de producción de papa, ya que la papa tiene un requerimiento relativamente alto de P y usa ineficientemente el P del suelo. El fósforo promueve desarrollo rápido del follaje, división celular en la raíz, tuberización y síntesis de almidón. El fósforo adecuado es esencial para optimizar rendimiento de tubérculo, contenido de sólidos, calidad nutricional y resistencia a algunas enfermedades. Aun cuando la prueba de P en el suelo es la herramienta primaria para analizar las necesidades de fertilizante de P, en algunas áreas el análisis del P en el pecíolo se ha utilizado con éxito para guiar las aplicaciones de P durante la temporada. Se ha demostrado en algunos estudios que la papa responde al fertilizante de P en pruebas a nivel del suelo considerada muy alta para la mayoría de otros cultivos (100+ mg kg−1 Bray P1 o Mehlinch I o III y 20+ mg kg−1 bicarbonato de sodio) especialmente en suelos con texturas medias o más finas. Aun en suelos de altas pruebas, los niveles de fertilizante fosforado para máximos rendimientos exceden algunas veces 150 kg P2O5 ha−1. Además, muchos estados/provincias continúan recomendando la mitad o más de la cantidad de P en la porción cosechada del cultivo independientemente del nivel de pruebas en el suelo. En la mayoría de las situaciones se esperarían pocas diferencias entre las fuentes de P en los fertilizantes; no obstante, altos niveles de fosfato diamonico (DAP) o urea-fosfato (UAP) no deberían de aplicarse en bandas en contacto o cerca de la pieza de semilla. La mayoría de las investigaciones determinaron que el fertilizante fosforado se usaba más eficientemente cuando se aplicaba en banda al momento de la siembra (por ejemplo, a 5 cm a cada lado de la pieza de la semilla); no obstante, algún trabajo al oeste de los EUA en suelos de pH alto mostró aumento de rendimientos y de niveles de P en el pecíolo en aplicaciones amplias pre-siembra. Las aplicaciones durante el ciclo de crecimiento en el agua de riego pudieran ser útiles cuando las raíces de la papa están lo suficientemente cerca a la superficie del suelo; sin embargo, la mayoría de las investigaciones indica que las aplicaciones de P son más efectivas cuando se hacen al momento de la siembra o temprano durante el ciclo. Las mejores prácticas de manejo de fertilizantes fosforados incluyen: (1) aplicar el nivel de fertilizante de P calibrado para suelos locales; (2) aplicar el fertilizante fosforado en bandas por lo menos a 5 cm de la pieza de semilla, especialmente en suelos muy arenosos o en donde se usen DAP o UAP; (3) use pruebas del P en el pecíolo para determinar la necesidad de aplicaciones en pleno ciclo del cultivo; (4) tomar en cuenta las cantidades de todas las fuentes de P aplicadas, incluyendo estiércoles; y (5) utilizar las mejores prácticas de conservación del suelo para reducir pérdidas de P en aguas superficiales.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott, J.L., and T.C. Tucker. 1973. Persistence of manure phosphorus availability in calcareous soil. Soil Science Society of America Journal 37: 60–63.
Allison, M.F., J.H. Fowler, and E.J. Allen. 2001. Effects of soil- and folair-applied phosphorus fertilizers on the potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) crop. Journal of Agricultural Science Cambridge 137: 379–395.
Armstrong, D.L. (editor). 1999. Phosphorus for agriculture. Better Crops with Plant Food 83(1): 1–39.
Baerug, R., and K. Steenberg. 1971. Influence of placement method and water supply on the uptake of phosphorus by early potatoes. Potato Research 14: 282–291.
Barben, S.A., B.G. Hopkins, V.D. Jolley, B.L. Webb, and B.A. Nichols. 2010. Phosphorus and zinc interactions in chelator-buffered solution grown Russet Burbank potato. Journal of Plant Nutrition 33: 587–601.
Barber, S.A. 1977. Application of phosphate fertilizers: Methods, rates and time of application in relation to the phosphorus status of soils. Phosphorus Agriculture 70: 109–115.
Barber, S.A. 1980. Soil-plant interactions in the phosphorus nutrition of plants. In The role of phosphorus in agriculture, ed. F.E. Khasawneh, E.C. Sample, and E.J. Kamprath, 591–615. Madison: American Society of Agronomy, Crop Science Society of America and Soil Science Society of America.
Barclay, G.M., H.J. Murphy, F.E. Manzer, and F.E. Hutchinson. 1973. Effects of different rates of nitrogen and phosphorus on early blight of potatoes. American Potato Journal 50: 42–48.
Benepal, P.S. 1967. Correlations among applied nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium and responses of the potato plant. American Potato Journal 44: 75–86.
Berger, K.C., P.E. Potterton, and E.L. Hobson. 1961. Yield, quality and phosphorus uptake of potatoes as influenced by placement and composition of potassium fertilizers. American Potato Journal 38: 272–285.
Birch, J.A., J.R. Devine, M.R.J. Holmes, and J.D. Whitear. 1967. Field experiments on the fertilizer requirement of maincrop potatoes. Journal of Agricultural Science Cambridge 69: 13–24.
Bishop, R.F., C.R. MacEachern, and D.C. MacKay. 1967. The relation of soil test values to fertilizer response by the potato. IV. Available phosphorus and phosphatic fertilizer requirements. Canadian Journal of Soil Science 47: 175–185.
Black, W.N., and R.R. Cairns. 1958. The effect of varying levels of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium and manure on the yield and starch content of potatoes. Canadian Journal of Soil Science 38: 1–7.
Black, W.N., and R.P. White. 1973. Effects of nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium and manure factorially applied to potatoes in a long-term study. Canadian Journal of Soil Science 53: 205–211.
Boawn, L.C., and G.E. Leggett. 1963. Zinc deficiency of the Russet Burbank potato. Soil Science 95: 137–141.
Boawn, L.C., and G.E. Leggett. 1964. Phosphorus and zinc concentrations in Russet Burbank potato tissues in relation to development of zinc deficiency symptoms. Soil Science Society of America Journal 28: 229–232.
Boyd, D.A., and W. Dermott. 1967. Fertiliser requirements of potatoes in relation to kind of soil and soil analysis. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture 18: 85–89.
Bundy, L.G., H. Tunney, and A.D. Halverson. 2005. Agronomic aspects of phosphorus management. In Phosphorus: Agriculture and the environment, ed. J.T. Sims and A.N. Sharpley, 685–727. Madison: American Society of Agronomy, Crop Science Society of America, Soil Science Society of America.
Carolus, R.L. 1937. Chemical estimations of the weekly nutrient level of a potato crop. American Potato Journal 14: 141–153.
Carpenter, P.N. 1963. Mineral accumulation in potato plants as affected by fertilizer application and potato variety. Maine Agricultural Experiment Station Bulletin 610. Orono: University of Maine.
Christenson, D.R., and E.C. Doll. 1968. Effect of phosphorus source and rate on potato yields and phosphorus content of petioles and tubers. Michigan Agricultural Experiment Station Quarterly Bulletin 50(4): 616–624.
Chu, C.-C., H. Plate, and D.L. Matthews. 1984. Fertilizer injury to potatoes as affected by fertilizer source, rate and placement. American Potato Journal 61: 591–597.
Cox, F.R. 1992. Range in soil phosphorus critical levels with time. Soil Science Society of America Journal 56: 1504–1509.
Curless, M.A., K.A. Kelling, and P.E. Speth. 2005. Nitrogen and phosphorus availability from liquid dairy manure to potatoes. American Journal of Potato Research 82: 287–297.
Davis, J.R., R.E. McDole, and R.H. Callihan. 1976. Fertilizer effects on common scab of potato and the relation of calcium and phosphate-phosphorus. Phytopathology 66: 1236–1241.
Davis, J.R., L.H. Sorenson, J.C. Stark, and D.T. Westermann. 1990. Fertility and management practices on control of verticillium wilt of the Russet Burbank potato. American Potato Journal 67: 55–65.
Davis, J.R., J.C. Stark, L.H. Sorenson, and A.T. Schneider. 1994. Interactive effects of nitrogen and phosphorus on Verticillium wilt of Russet Burbank potato. American Potato Journal 71: 467–481.
Dubetz, S., and J.B. Bole. 1975. Effects of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium on yield components and specific gravity of potatoes. American Potato Journal 52: 399–405.
Dyson, P.W., and D.J. Watson. 1971. An analysis of the effects of nutrient supply on the growth of potato crops. Annals of Applied Biology 69: 47–63.
Elias-Azar, K., A.E. Lang, and P.F. Pratt. 1980. Bicarbonate-extractable phosphorus in fresh and composted dairy manures. Soil Science Society of America Journal 44: 435–437.
Engelstad, O.P., and G.L. Terman. 1980. Agronomic effectiveness of phosphate fertilizers. In The role of phosphorus in agriculture, ed. F.E. Khasawneh, E.C. Sample, and E.J. Kamprath, 311–332. Madison: American Society of Agronomy, Crop Science Society of America, Soil Science Society of America.
Fitzgerald, C.B. 1998. Soil phosphorus in Aroostock County (Maine) potato cropping systems: organic matter effects and residual phosphorus contribution. Master of Science thesis, University of Maine, Orono, Maine. 124 pp.
Fixen, P.E., E.A. Liegel, C.R. Simson, L.M. Walsh, and R.P. Wolkowski. 1979–1981. Effect of phosphorus source and rate on potatoes. Unpublished research reports, Department of Soil Science, University of Wisconsin-Madison.
Freeman, K.L., P.R. Franz, and R.W. de Jong. 1998. Effect of phosphorus on the yield, quality and petiolar phosphorus concentrations of potatoes (cvv. Russet Burbank and Kennebec) grown in the krasnozem and duplex soils of Victoria. Australian Journal of Experimental Agriculture 38: 83–93.
Gale, P.M., M.D. Mullen, C. Cieslik, D.D. Tyler, B.N. Deuk, M. Kirchner, and J. McClure. 2000. Phosphorus distribution and availability in response to dairy manure applications. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis 31: 553–565.
Giroux, M., A. Dube, and G.M. Barnett. 1984. Effet de la fertilisation phosphatee sur la pomme de terre en relation avec l’analyse du sol et al. source de phosphore utilisee. Canadian Journal of Soil Science 64: 369–381.
Gracey, H.I. 1984. Availability of phosphorus in organic manures compared with monoammonium phosphate. Agricultural Wastes 11: 133–141.
Grant, C.A., D.N. Flaten, D.J. Tomasiewicz, and S.C. Sheppard. 2001. The importance of early season phosphorus nutrition. Canadian Journal of Plant Science 81: 211–224.
Hammes, J.K. 1961–1962. Influence of fertilizer placement on the cumulative uptake of fertilizer phosphorus by Early Gem potatoes. Unpublished research reports, Department of Soil Science, University of Wisconsin-Madison.
Hang, Z. 1993. Influence of chloride on the uptake and transport of phosphorus in potato. Journal of Plant Nutrition 16(9): 1733–1737.
Hawkins, A. 1954. Time, method of application and placement of fertilizer for efficient production of potatoes in New England. American Potato Journal 31: 106–113.
Hegney, M.A., and I.R. McPharlin. 1999. Broadcasting phosphate fertiliser produces higher yields of potatoes (Solanum tuberosum L.) than band placement on coastal sands. Australian Journal of Experimental Agriculture 39: 495–503.
Herlihy, M. 1970. Contrasting effects of nitrogen and phosphorus on potato tuber blight. Plant Pathology 19: 69–71.
Herlihy, M., and P.J. Carroll. 1969. Effects of N, P and K and their interactions on yield, tuber blight and quality of potatoes. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture 20: 513–517.
Hooker, M.L., G.A. Peterson, D.H. Sander, and L.A. Daigger. 1980. Phosphate fractions in calcareous soils as altered by time and amounts of added phosphate. Soil Science Society of America Journal 44: 269–277.
Hopkins, B., and J. Ellsworth. 2003. Phosphorus nutrition in potato production. In Proceedings of the University of Idaho Winter Commodity Schools 35: 75–85.
Hopkins, B.G., J.W. Ellsworth, T.R. Bowen, A.G. Cook, S.C. Stephens, V.D. Jolley, A.K. Shiffler, and D. Eggett. 2010a. Phosphorus fertilizer timing for Russet Burbank potato grown in calcareous soil. Journal of Plant Nutrition 33: 529–540.
Hopkins, B.G., J.W. Ellsworth, A.K. Shiffler, T.R. Bowen, and A.G. Cook. 2010b. Pre-plant versus in-season application of phosphorus fertilizer for Russet Burbank potato grown in calcareous soil. Journal of Plant Nutrition 33: 1026–1039.
Hoskins, B. 2012. Personal communication. Orono ME: Plant, Soil and Environmental Sciences Department, University of Maine.
Horneck, D., and C. Rosen. 2008. Measuring nutrient accumulation rates of potatoes—tools for better management. Better Crops 92(1): 4–6.
Hoveland, C.S., K.C. Berger, and H.M. Darling. 1954. The effect of mineral nutrition on the expression of potato leaf roll virus symptoms. Soil Science Society of America Journal 18: 53–55.
Jackson, T.L., and G.E. Carter. 1976. Nutrient uptake by Russet Burbank potatoes as influenced by fertilization. Agronomy Journal 68: 9–12.
Jacob, W.C., C.H. vanMiddelem, W.L. Nelson, C.D. Welch, and N.S. Hall. 1949. Utilization of phosphorus by potatoes. Soil Science 68: 113–120.
James, D.W., W.H. Weaver, and R.L. Rader. 1970. Chloride uptake by potatoes and the effects of potassium chloride, nitrogen and phosphorus fertilization. Soil Science 109: 48–52.
Jenkins, P.D., and H. Ali. 1999. Growth of potato cultivars in response to application of phosphate fertiliser. Annals of Applied Biology 135: 431–438.
Jenkins, P.D., and H. Ali. 2000. Phosphate supply and progeny tuber numbers in potato crops. Annals of Applied Biology 136: 41–46.
Johnston, A.E., P.W. Lane, G.E.G. Mattingly, P.R. Poulton, and M.V. Hewitt. 1986. Effects of soil and fertilizer P on yields of potatoes, sugar beet, barley and winter wheat on a sandy clay loam soil at Saxmundham, Suffolk. Journal of Agriculture Science (Cambridge) 106: 155–167.
Kalifa, A., N.N. Barthakur, and D.J. Donnelly. 2000. Phosphorus reduces salinity stress in micro-propated potato. American Journal of Potato Research 77: 179–182.
Kalkafi, U., B. Bar-Yosef, and A. Hadas. 1978. Fertilization decision model—A synthesis of soil and plant parameters in a computerized program. Soil Science 125: 261–268.
Kelling, K.A., and P.E. Speth. 1997. Influence of phosphorus rate and timing on Wisconsin potatoes. Proceedings of the Wisconsin Annual Potato Meetings 10: 33–41.
Kelling, K.A., R.P. Wolkowski, J.G. Iyer, R.B. Corey, and W.R. Stevenson. 1992. Potato responses to phosphorus application and using petiole analysis in determining P status. Proceedings of the Wisconsin Annual Potato Meetings 5: 39–50.
Kelling, K.A., S.A. Wilner, R.F. Hensler, and L.M. Massie. 1998. Placement and irrigation effects on nitrogen fertilizer use efficiency. Proceedings of the Wisconsin Annual Potato Meetings 11: 79–88.
Khiari, L., L.E. Parent, A. Pellerin, A.R.A. Alimi, C. Tremblay, R.R. Simard, and J. Fortin. 2000. An agri-environmental phosphorus saturation index for acid coarse-textured soils. Journal of Environmental Quality 29: 1561–1567.
Kingston, B.D., and R.W. Jones. 1980. Response of potatoes to phosphorus rate and placement on the Texas rolling plains. Texas Agricultural Research Station Report PR3680, College Station: Texas A&M University.
Klein, L.B., S. Chandra, and N.I. Mondy. 1980. The effect of phosphorus fertilization on the chemical quality of Katahdin potatoes. American Potato Journal 57: 259–266.
Kleinkopf, G.E., D.T. Westermann, and R.B. Dwelle. 1981. Dry matter production and nitrogen utilization by six potato cultivars. Agronomy Journal 73: 799–802.
Kovar, J.L., and S.A. Barber. 1987. Placing phosphorus and potassium for greatest recovery. Journal of Fertilizer Issues 4: 1–6.
Kunkel, R., N. Holstad, and T.S. Russell. 1973. Mineral element content of potato plants and tubers vs. yields. American Potato Journal 50: 275–282.
Laboski, C.A.M. 2006. Potato response to phosphorus fertilizer. Proceedings of the Wisconsin Annual Potato Meetings 19: 81–89.
Laboski, C.A.M., and T.W. Andraski. 2009. Potato response to phosphorus fertilizers: 2008 results. Proceedings of the Wisconsin Annual Potato Meetings 22: 139–154.
Laboski, C.A.M., and J. B. Peters. 2012. Nutrient application guidelines for field, vegetable and fruit crops in Wisconsin. Publication A2809, Madison: University of Wisconsin-Extension.
Laboski, C.A.M., and K.A. Kelling. 2007. Influence of fertilizer management and soil fertility on tuber specific gravity: A review. American Journal of Potato Research 84: 283–290.
Laboski, C.A.M., and J.A. Lamb. 2003. Changes in soil test phosphorus concentration after application of manure or fertilizer. Soil Science Society of America Journal 67: 544–554.
Laboski, C.A.M., J. B. Peters, and L.G. Bundy. 2006. Nutrient application guidelines for field, vegetable and fruit crops in Wisconsin. Publication A2809, Madison: University of Wisconsin-Extension.
Laboski, C.A.M., M.J. Repking, and T.W. Andraski. 2007. Potato responses to phosphorus fertilizer: 2006 results. Proceedings of the Wisconsin Annual Potato Meetings 20: 177–195.
Lambert, D.H., M.L. Powelson, and W.R. Stevenson. 2005. Nutritional interactions influencing diseases of potato. American Journal of Potato Research 82: 309–319.
Lang, N.S., R.G. Stevens, R.E. Thornton, W.L. Pan, and S. Victory. 1999. Potato nutrient management for central Washington. Extension Bulletin 871. Pullman: Washington State University.
Laughlin, W.M. 1962. Influence of soil and spray application of phosphorus on potato yield, dry matter content and chemical composition. American Potato Journal 39: 343–347.
Laughlin, W.M. 1968. Effect of calcium metaphosphate and treble-superphosphate on yield and chemical composition of Kennebec potatoes. American Potato Journal 45: 45–50.
Laughlin, W.M., P.F. Martin, and G.R. Smith. 1974. Lime and phosphorus influence Kennebec potato yield and chemical composition. American Potato Journal 51: 393–402.
Lesczynski, D.B., and C.B. Tanner. 1976. Seasonal variation of root distribution of irrigated, field-grown Russet Burbank potato. American Potato Journal 53: 69–78.
Liegel, E.A., C.R. Simson, P.E. Fixen, R.E. Rand, and G.G. Weis. 1981. Potato responses to phosphorus and potassium and recommendations for P-K fertilization. Potato Manual 81EL. Madison: University of Wisconsin.
Locasio, S.J., and R.D. Rhue. 1990. Phosphorus and micronutrient sources for potato. American Potato Journal 67: 217–226.
Logan, C., M. Hossain, and G. Little. 1987. The effect of various levels of nitrogen, phosphate and potash and climatic factors on the incidence of potato black leg and gangrene. Record of Agricultural Research 1987: 17–22.
Lorenz, O.A. 1947. Studies on potato nutrition: III. Chemical composition and uptake of nutrients by Kern County potatoes. American Potato Journal 24: 281–293.
MacKay, D.C., J.M. Carefoot, and T. Entz. 1988. Detection and correction of midseason P deficiency in irrigated potatoes. Canadian Journal of Plant Science 68: 523–534.
MacLean, A.A. 1983. Source of fertilizer nitrogen and phosphorus for potatoes in Atlantic Canada. American Potato Journal 60: 913–918.
Maier, N.A., K.A. Potocky-Pacay, A.P. Dahlenburg, and C.M.J. Williams. 1989a. Effect of phosphorus on the specific gravity of potato tubers (Solanum tuberosum L.) of cultivars Kennebec and Coliban. Australian Journal of Experimental Agriculture 29: 869–874.
Maier, N.A., K.A. Potocky-Pacay, J.M. Jacka, and C.M.J. Williams. 1989b. Effect of phosphorus fertiliser on the yield of potato tubers (Solanum tuberosum L.) and the prediction of tuber yield response by soil analysis. Australian Journal of Experimental Agriculture 29: 419–432.
Mallarino, A.P. 1997. Interpretation of soil phosphorus tests for corn in soils with varying pH and calcium carbonate content. Journal of Production Agriculture 10: 163–167.
Mallarino, A.P., J.R. Webb, and A.M. Blackmer. 1991. Corn and soybean yields during 11 years of phosphorus and potassium fertilization on a high-testing soil. Journal of Production Agriculture 4: 312–317.
McCollum, R.E. 1978a. Analysis of potato growth under differing P regimes. I. Tuber yields and allocation of dry matter and P. Agronomy Journal 70: 51–57.
McCollum, R.E. 1978b. Analysis of potato growth under differing P regimes. II. Time by P-status interactions for growth and leaf efficiency. Agronomy Journal 70: 58–66.
Meek, B.D., L.E. Graham, T.J. Donovan, and K.S. Mayberry. 1979. Phosphorus availability in a calcareous soil after high loading rates of animal manure. Soil Science Society of America Journal 43: 741–743.
Meisinger, J.J., D.R. Bouldin, and E.D. Jones. 1978. Potato yield reductions associated with certain fertilizer mixtures. American Potato Journal 55: 227–234.
Mohr, R.M., and D.J. Tomasiewicz. 2011. Effect of phosphorus fertilizer rate on irrigated Russet Burbank potato. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis 42: 2284–2298.
Moorby, J. 1978. The physiology of growth and tuber yield. In The potato crop―The scientific basis for improvement, ed. P.M. Harris, 153–194. London: Chapman and Hill.
Mortvedt, J.J., L.S. Murphy, and R.H. Follett. 1999. Fertilizer technology and application. Willoughby: Meister Publishing Company.
Motavalli, P.P., K.A. Kelling, and J.C. Converse. 1989. First-year nutrient availability from injected dairy manure. Journal of Environmental Quality 18: 180–185.
Mullins, G.L., and C.E. Evans. 1990. Field evaluation of commercial triple superphosphate fertilizers. Fertilizer Research 25: 101–106.
Murphy, H.J., P.N. Carpenter, and M.J. Goven. 1967. Effect of differential rates of phosphorus, potassium and lime on yield, specific gravity and nutrient uptake of the Katahdin and Russet Burbank. Maine Agricultural Experiment Station Bulletin 652. Orono: University of Maine.
National Agricultural Statistics Service (NASS). 2010. Agricultural practices-Maine. Washington, DC: USDA.
Nelson, W.L., and A. Hawkins. 1947. Response of Irish potatoes to phosphorus and potassium on soils having different levels of these nutrients in Maine and North Carolina. Journal of the American Society of Agronomy 39: 1053–1067.
Ohms, R.E., C.G. Painter, and J.P. Jones. 1977. Comparison of nitrogen and phosphorus requirements between PVX free and regular Russet Burbank seed stocks. American Potato Journal 54: 425–432.
Opena, G.B., and G.A. Porter. 1999. Soil management and supplemental irrigation effects on potato: II. Root growth. Agronomy Journal 91: 426–431.
Overdahl, C.J., and C.P. Klint. 1969. Soil fertility trials on potatoes irrigated (loamy sands and sandy loams). Soil Series no. 85. St. Paul: University of Minnesota.
Ozanne, P.G. 1980. Phosphate nutrition of plants―A general treatise. In The role of phosphorus in agriculture, ed. F.E. Khasawneh, E.C. Sample, and E.K. Kamprath, 559–589. Madison: American Society of Agronomy, Crop Science Society of America, Soil Science Society of America.
Panique, E., K.A. Kelling, E.E. Schulte, D.E. Hero, W.R. Stevenson, and R.V. James. 1997. Potassium rate and source effects on potato yield, quality and disease interaction. American Potato Journal 74: 379–398.
Payton, F.V., R.D. Rhue, and D.R. Hensel. 1989. Mitscherlich-Bray equation used to correlate soil phosphorus and potato yields. Agronomy Journal 81: 571–576.
Peterson, L.A., G.G. Weis, and L.M. Walsh. 1971. Potato response to varying levels of soil test P and K. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis 2: 267–274.
Platt, H.W., and W.J. Arsenault. 2001. Management of nitrogen and phosphorus rates does not suppress Verticillium wilt in Yukon Gold. American Journal of Potato Research 78: 215–219.
Porter, G.A. 2012. Personal communication. Orono ME: Plant, Soil and Environmental Sciences Department, University of Maine.
Powell, J.M., Z. Wu, and L.D. Satter. 2001. Dairy diet effects on phosphorus cycles of cropland. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation 56: 22–26.
Pursglove, J.D., and F.E. Sanders. 1981. The growth and phosphorus economy of the early potato (Solanum tuberosum). Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis 12: 1105–1121.
Randall, G.W., T.K. Iragavarapu, and S.D. Evans. 1997. Long-term P and K applications: 1. Effect on soil test incline and decline rates and critical soil test levels. Journal of Production Agriculture 10: 565–571.
Recke, H., H.F. Schnier, S. Nabwile, and J.N. Qureshi. 1997. Responses of Irish potatoes (Solanum tuberosum L.) to mineral and organic fertilizer in various agro-ecological environments in Kenya. Experimental Agriculture 33: 91–102.
Redulla, C.A., J.R. Davenport, R.G. Evans, M.J. Hattendorf, A.K. Alva, and R.A. Boydston. 2002. Relating potato yield and quality to field scale variability in soil characteristics. American Journal of Potato Research 79: 317–323.
Repking, M.J., C.A.M. Laboski, and T.W. Andraski. 2008. Potato response to phosphorus fertilizers: 2007 results. Proceedings of the Wisconsin Annual Potato Meetings 21: 139–156.
Rhue, R.D., D.R. Hensel, T.L. Yuan, and W.K. Robertson. 1981. Ammonium orthophosphate and ammonium polyphosphate as sources of phosphorus for potatoes. Soil Science Society of America Journal 45: 1229–1233.
Roberts, S., and J.D. Beaton. 1988. Potato use of phosphorus and potassium in sandy soils. Research Bulletin XB1004. Pullman: Washington State University.
Roberts, S., and A.I. Dow. 1982. Critical nutrient ranges for petiole phosphorus levels of sprinkler-irrigated Russet Burbank potatoes. Agronomy Journal 74: 583–585.
Roberts, S., A.I. Dow, and T.A. Cline. 1984. Slow release nitrogen evaluations and phosphorus and potassium requirements for potatoes on sandy soil. Research Bulletin XB0943. Pullman: Washington State University.
Roberts, S., H.H. Cheng, and F.O. Farrow. 1991. Potato uptake and recovery of nitrogen-15-enriched ammonium nitrate from periodic applications. Agronomy Journal 83: 378–381.
Rosen, C.J., and P.M. Bierman. 2008. Potato yield and tuber set as affected by phosphorus fertilization. American Journal of Potato Research 85: 110–120.
Rosen, C., and D. Birong. 1995. Potato response to phosphorus on high phosphorus testing sandy soils: On-farm trials. 28–31. Field Research in Soil Science Miscellaneous Publication 88–1995, St. Paul: University of Minnesota.
Rosen, C., and D. Birong. 1996. Potato response to phosphorus on high phosphorus testing sandy soils: On-farm trials. 17–20. Field Research in Soil Science Miscellaneous Publication 90–1996, St. Paul: University of Minnesota.
Rosen, C., D. Birong, and G. Titrud 1991. Phosphorus requirements for irrigated potatoes. 41–43. Field Research in Soil Science Miscellaneous Publication 71–1991, St. Paul: University of Minnesota.
Rosen, C., D. Birong, and G. Titrud. 1993. Phosphorus requirements for irrigated potatoes. 34–38. Field Research in Soil Science Miscellaneous Publication 79–1993, St. Paul: University of Minnesota.
Rosen, C., D. Birong, and G. Titrud. 1994. Phosphorus requirements for irrigated potatoes. 21–27. Field Research in Soil Science Miscellaneous Publication 79–1994, St. Paul: University of Minnesota.
Rosen, C., P. Bierman, and M. McNearney. 2006–2008. Effects of liquid fertilizer sources on potato yield and quality. Department of Soil, Water and Climate, University of Minnesota. Unpublished research reports.
Rosen, C., M. McNearney, and P. Bierman. 2007–2009. Evaluation of specialty phosphorus fertilizer formulations for potatoes. Department of Soil, Water and Climate, University of Minnesota. Unpublished research reports.
Ruark, M.D., K.A. Kelling, and L.W. Good. 2013. Environmental concersn of phosphorus management in potto production. American Journal of Potato Research 90: (this issue).
Rykbost, K.A., N.W. Christensen, and J. Maxwell. 1993. Fertilization of Russet Burbank in short-season environment. American Potato Journal 70: 699–710.
Sale, P.J.M. 1973. Productivity of vegetable crops in a region of high solar input. I. Growth and development of the potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). Australian Journal of Agricultural Research 24: 733–749.
Sanderson, J.B., J.A. MacLeod, B. Douglas, R. Coffin, and T. Bruulsema. 2003. Phosphorus research on potato in PEI. Acta Horticulturae 619: 409–417.
Sharma, U.C., and B.R. Arora. 1987. Effect of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium application on yield of potato tubers (Solanum tuberosum L.). Journal of Agricultural Science Cambridge 108: 321–329.
Sharma, U.C., and B.R. Arora. 1988. Effect of nutrients on starch, proteins and sugars in potatoes. Food Chemistry 30: 313–317.
Simpson, K., R.D. Verma, and J. Dainty. 1959. The effect of rate of application of superphosphate on growth and yield of potatoes. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture 10: 588–596.
Smith, J.A., and R.W. Sheard. 1957. Evaluation and calibration of phosphorus soil test methods for predicting fertilizer requirements of potatoes. Canadian Journal of Soil Science 37: 134–142.
Soltanpour, P.N. 1969a. Accumulation of dry matter and N, P, K by Russet Burbank, Oromonte, and Red McClure potatoes. American Potato Journal 46: 111–119.
Soltanpour, P.N. 1969b. Effect of nitrogen, phosphorus and zinc placement on yield and composition of potatoes. Agronomy Journal 61: 288–289.
Sommerfeldt, T.G., and K.W. Knutson. 1965. Effects of nitrogen and phosphorus on the growth and development of Russet Burbank potatoes grown in southeastern Idaho. American Potato Journal 42: 351–360.
Sparrow, L.A., K.S.R. Chapman, D. Parsley, P.R. Hardman, and B. Cullen. 1992. Response of potatoes (Solanum tuberosum cv. Russet Burbank) to band-placed and broadcast high cadmium phosphorus fertiliser on heavily cropped Kzasnozems in north-western Tasmania. Australian Journal of Experimental Agriculture 32: 113–119.
Stark, J.C., and S.L. Love. 2003. Tuber quality. In Potato production systems, ed. J.C. Stark and S.L. Love, 329–343. Moscow: University of Idaho Extension.
Stark, J.C., and J.C. Ojala. 1989. Comparison of banded ammonium polyphosphate and acid urea phosphate as P sources for potatoes. HortScience 24: 282–284.
Stark, J., D. Westermann, and B. Hopkins. 2004. Nutrient management guidelines for Russet Burbank potatoes. Bulletin 840. Moscow: University of Idaho.
Teich, A.H., and J.A. Menzies. 1964. The effect of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium on the specific gravity, ascorbic acid content and chipping quality of potato tubers. American Potato Journal 41: 169–173.
Terman, G.L., A. Hawkins, C.E. Cunningham, and P.N. Carpenter. 1952. Rate, placement and source of phosphorus fertilizers for potatoes in Maine. Maine Agricultural Experiment Station Bulletin no. 506, Orono: University of Maine.
Thornton, R.E., and H. Timm. 1990. Influence of fertilizer and irrigation management on tuber bruising. American Potato Journal 67: 45–54.
Tindall, T.A., D.T. Westermann, and J.C. Stark. 1993. Phosphorus nutrition in Idaho potatoes. Better Crops 77(1): 23–25.
van Lierop, W., P.S. Tran, G. Banville, and S. Morisette. 1982. Effect of liming on potato yields as related to soil pH, Al, Mn, and Ca. Agronomy Journal 74: 1050–1055.
Vander Zaag, P., and C. Kagenzi. 1986. The phosphorus requirements of five consecutive potato crops on andept in Rwanda. American Potato Journal 63: 121–129.
Vitosh, M.L. 1979. Fertilizer correlation study. 73–76. Montcalm Experimental Station Research Report, East Lansing: Michigan State University.
Vitosh, M.L. 1980. Phosphorus study with Russet Burbanks. 34–39, Montcalm Experimental Station Research Report, East Lansing: Michigan State University.
Vitosh, M.L. 1987. Personal communication. East Lansing MI: Department of Soil and Crop Science, Michigan State University.
Walworth, J.L., and J.E. Muniz. 1993. A compendium of tissue nutrient concentrations for field-grown potatoes. American Potato Journal 70: 579–597.
Webb, J.R., A.P. Mallarino, and A.M. Blackmer. 1992. Effects of residual and annually applied phosphorus on soil test values and yields of corn and soybean. Journal of Production Agriculture 5: 148–152.
Westermann, D.T. 1984. Mid-season P fertilization effects on potatoes. 1–9. Proceedings of the 35th Northwest Fertilizer Conference: Pasco, Washington.
Westermann, D.T. 1992. Lime effects on phosphorus availability in a calcareous soil. Soil Science Society of America Journal 56: 489–494.
Westermann, D.T. 2005. Nutritional requirements of potatoes. American Journal of Potato Research 82: 301–307.
Westermann, D.T., and G.E. Kleinkopf. 1983. Phosphorus dynamics in potato plants. 89–97. Proceedings of the 34th Northwest Fertilizer Conference: Portland, Oregon.
Westermann, D.T., and G.E. Kleinkopf. 1985. Phosphorus relationships in potato plants. Agronomy Journal 77: 490–494.
Zhong, H. 1993. Influence of chloride on the uptake and translocation of phosphorus in potato. Journal of Plant Nutrition 16: 1733–1737.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rosen, C.J., Kelling, K.A., Stark, J.C. et al. Optimizing Phosphorus Fertilizer Management in Potato Production. Am. J. Potato Res. 91, 145–160 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12230-014-9371-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12230-014-9371-2