Abstract
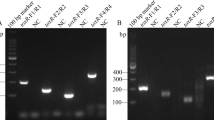
Vibrio cholerae is an important food-borne pathogenic bacterium that causes human disease, resulting in economic losses worldwide. Rapid diagnosis of cholera infection is important to avoid potential spread of disease. In this study, recombinase-aided amplification (RAA) primers labeled with biotin and fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) at 5′ end were prepared for the ctxA pathogenic gene of V. cholerae. RAA amplicons obtained at 37 °C isothermal conditions for 15 min were firstly preincubated with the antibody against FITC, subsequently with streptavidin-modified superparamagnetic nanoparticles (SA-SPMNPs), to form a DNA amplicons-FITC antibody-SA-SPMNPs complex. The complex could be captured by the secondary antibody on test line of lateral flow test strip (LFTS), and the residual streptavidin on SA-SMMNPs could be captured by the biotin-BSA on the control line of LFTS. Thus, a sensitive quantitative detection was achieved by the magnetic signal of test line of LFTS through a magnetic assay instrument. The RAA amplicons from various bacteria (n = 25) obtained by a thermostatic water bath for 15 min at 37 °C were used as samples of lateral flow assay (LFA). No positive reaction was observed besides of pathogenic V. cholerae. A total of 100 CFU/ml V. cholerae in shrimp samples could be detected by a simple naked eye observation within 50 min including the sample pretreatment. Quantitative LOD 46 CFU/ml V. cholerae in shrimp was achieved, which was more than 10 times lower than the current industry pathogenic range. The novel RAA-LFA shows a potential application in the point-of-care diagnosis or detection of V. cholerae.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Awasthi SP, Chowdhury N, Neogi SB, Hinenoya A, Hatanaka N, Chowdhury G, Ramamurthy T, Yamasaki S (2019) Development of a multiplex PCR assay for the detection of major virulence genes in Vibrio cholerae including non-O1 and non-O139 serogroups. J Microbiol Methods 157:54–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mimet
Chen W, Zhang J, Lu G, Yuan Z, Wu Q, Li J, Xu G, He A, Zheng J, Zhang J (2014) Development of an immunochromatographic lateral flow device for rapid diagnosis of Vibrio cholerae O1 serotype Ogawa. Clin Biochem 47:448–454. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2013.12.022
Chen C, Li XN, Li GX, Zhao L, Duan SX, Yan TF, Feng ZS, Ma XJ (2018) Use of a rapid reversetranscription recombinase aided amplification assay for respiratory syncytial virus detection. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 90:90–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2017.10.005
Clemens JD, Nair GB, Ahmed T, Qadri F, Holmgren J (2017) Cholera. Lancet 390:1539–1549. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(17)30559-7
Dai T, Yang X, Hu T, Jiao B, Xu Y, Zheng X, Shen D (2019) Comparative evaluation of a novel recombinase polymerase amplification-lateral flow dipstick (RPA-LFD) assay, LAMP, conventional PCR, and leaf-disc baiting methods for detection of Phytophthora sojae. Front Microbiol 10:1884. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.01884
Du XJ, Zang YX, Liu HB, Li P, Wang S (2018a) Recombinase polymerase amplification combined with lateral flow strip for Listeria monocytogenes detection in food. J Food Sci 83:1041–1047. https://doi.org/10.1111/1750-3841.14078
Du X, Zang Y, Liu H, Li P, Wang S (2018b) Rapid detection of Staphylococcus aureus via recombinase polymerase amplification combined with lateral flow strip. Food Anal Method 11:2296–2306. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-018-1200-7
Engku Nur Syafirah EAR, Nurul Najian AB, Fo PC, Mohd Ali MR, Mohamed M, Yean CY (2018) An ambient temperature stable and ready-to-use loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for detection of toxigenic Vibrio cholerae in outbreak settings. Acta Trop 182:223–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actatropica.2018.03.004
Fang B, Hu S, Wang C, Yuan M, Huang Z, Xing K, Liu D, Peng J, Lai W (2019) Lateral flow immunoassays combining enrichment and colorimetryfluorescence quantitative detection of sulfamethazine in milk based on trifunctional magnetic nanobeads. Food Control 98:268–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2018.11.039
Gao W, Huang H, Zhu P, Yan X, Fan J, Jiang J, Xu J (2018) Recombinase polymerase amplification combined with lateral flow dipstick for equipment-free detection of Salmonella in shellfish. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 41:603–611. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-018-1895-2
Hao M, Zhang P, Li B, Liu X, Zhao Y, Tan H, Sun C, Wang X, Wang X, Qiu H, Wang D, Diao B, Jing H, Yang R, Kan B, Zhou L (2017) Development and evaluation of an up-converting phosphor technology-based lateral flow assay for the rapid, simultaneous detection of Vibrio cholerae serogroups O1 and O139. PLoS One 12:e0179937. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0179937
Hong L, Wang K, Yan W, Xu H, Chen Q, Zhang Y, Cui D, Jin Q, He J (2018) High performance immunochromatographic assay for simultaneous quantitative detection of multiplex cardiac markers based on magnetic nanobeads. Theranostics 8:6121–6131. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.29070
Hu S, Zhong H, Huang W, Zhan W, Yang X, Tang B, Chen K, Wang J, Hu T, Zhang C, Zhou Z, Luo M (2019) Rapid and visual detection of Group B streptococcus using recombinase polymerase amplification combined with lateral flow strips. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 93:9–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2018.07.011
Izumiya H, Morita M, Arakawa E, Ngo TC, Nguyen HT, Nguyen DT, Ohnishi M (2019) Development of a loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for Vibrio cholerae O1 and O139. Mol Cell Probes 45:65–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcp.2019.05.001
Jaroenram W, Owens L (2014) Recombinase polymerase amplification combined with a lateral flow dipstick for discriminating between infectious Penaeus stylirostris densovirus and virus-related sequences in shrimp genome. J Virological Methods 208:144–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jviromet.2014.08.006
Lalitha P, Siti Suraiya MN, Lim KL, Lee SY, Nur Haslindawaty AR, Chan YY, Ismail A, Zainuddin ZF, Ravichandran M (2008) Analysis of lolB gene sequence and its use in the development of a PCR assay for the detection of Vibrio cholerae. J Microbiol Methods 75:142–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mimet.2008.05.001
Li J, Ma B, Fang J et al (2020) Recombinase Polymerase Amplification (RPA) Combined with Lateral Flow Immunoassay for Rapid Detection of Salmonella in Food. Foods 9:27. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9010027
Liu Y, Zhang Z, Wang Y, Zhao Y, Lu Y, Xu X, Yan J, Pan Y (2015) A highly sensitive and flexible magnetic nanoprobe labeled immunochromatographic assay platform for pathogen Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Int J Food Microbiol 211:109–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2015.07.005
Liu F, Zhang H, Wu Z, Dong H, Zhou L, Yang D, Ge Y, Jia C, Liu H, Jin Q, Zhao J, Zhang Q, Mao H (2016) Highly sensitive and selective lateral flow immunoassay based on magnetic nanoparticles for quantitative detection of carcinoembryonic antigen. Talanta 161:205–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2016.08.048
Liu HB, Zang YX, Du XJ, Li P, Wang S (2017) Development of an isothermal amplification-based assay for the rapid visual detection of Salmonella bacteria. J Dairy Sci 100:7016–7025. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2017-12566
Ma Q, Liu H, Ye F, Xiang G, Shan W, Xing W (2017) Rapid and visual detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex using recombinase polymerase amplification combined with lateral flow strips. Mol Cell Probes 36:43–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcp.2017.08.004
Ma Q, Yao J, Yuan S, Liu H, Wei N, Zhang J, Shan W (2019) Development of a lateral flow recombinase polymerase amplification assay for rapid and visual detection of Cryptococcus neoformans/C. gattii in cerebral spinal fluid. BMC Infect Dis 19:108. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12879-019-3744-6
Mehrabadi JF, Morsali P, Nejad HR, Imani Fooladi AA (2012) Detection of toxigenic Vibrio cholerae with new multiplex PCR. J Infect Public Heal 5:263–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiph.2012.02.004
Noguera P, Posthuma-Trumpie GA, van Tuil M, van der Wal FJ, de Boer A, Moers AP, van Amerongen A (2011) Carbon nanoparticles in lateral flow methods to detect genes encoding virulence factors of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli. Anal Bioanal Chem 399:831–838. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-010-4334-z
Okada K, Chantaroj S, Taniguchi T, Suzuki Y, Roobthaisong A, Puiprom O, Honda T, Sawanpanyalert P (2010) A rapid, simple, and sensitive loop-mediated isothermal amplification method to detect toxigenic Vibrio cholerae in rectal swab samples. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 66:135–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2009.09.004
Qi Y, Yin Q, Shao Y, Cao M, Li S, Chen H, Shen W, Rao J, Li J, Li X, Sun Y, Lin Y, Deng Y, Zeng W, Zheng S, Liu S, Li Y (2018) Development of a rapid and visual nucleotide detection method for a Chinese epidemic strain of Orientia tsutsugamushi based on recombinase polymerase amplification assay and lateral flow test. Int J Infect Dis 70:42–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijid.2018.03.003
Ramamurthy T, Bhattacharya SK, Uesaka Y, Horigome K, Paul M, Sen D, Pal SC, Takeda T, Takeda Y, Nair GB (1992) Evaluation of the bead enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of cholera toxin directly from stool specimens. J Clin Microbiol 30:1783–1786
Sayeed MA, Islam K, Hossain M, Akter NJ, Alam MN, Sultana N, Khanam F, Kelly M, Charles RC, Kováč P, Xu P, Andrews JR, Calderwood SB, Amin J, Ryan ET, Qadri F (2018) Development of a new dipstick (Cholkit) for rapid detection of Vibrio cholerae O1 in acute watery diarrheal stools. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 12:e0006286. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0006286
Shen XX, Qiu FZ, Shen LP, Yan TF, Zhao MC, Qi JJ, Chen C, Zhao L, Wang L, Feng ZS, Ma XJ (2019) A rapid and sensitive recombinase aided amplification assay to detect hepatitis B virus without DNA extraction. BMC Infect Dis 19:229. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12879-019-3814-9
Sun N, Wang W, Wang J, Yao X, Chen F, Li X, Yinglei Y, Chen B (2018) Reverse transcription recombinase polymerase amplification with lateral flow dipsticks for detection of influenza A virus and subtyping of H1 and H3. Mol Cell Probes 42:25–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcp.2018.10.004
Villicaña C, Amarillas L, Soto-Castro L, Gómez-Gil B, Lizárraga-Partida ML, León-Félix J (2019) Occurrence and abundance of pathogenic Vibrio species in raw oysters at retail seafood markets in northwestern Mexico. J Food Prot 82:2094–2099. https://doi.org/10.4315/0362-028X.JFP-19-237
Wang W, Wang C, Zhang P, Yao S, Liu J, Zhai X, Zhang T (2019) Reverse transcription recombinase-aided amplification assay combined with a lateral flow dipstick for detection of avian infectious bronchitis virus. Poult Sci 20:pez559. https://doi.org/10.3382/ps/pez559
Wu L, Ye L, Wang Z, Cui Y, Wang J (2019) Utilization of recombinase polymerase amplification combined with a lateral flow strip for detection of Perkinsus beihaiensis in the oyster Crassostrea hongkongensis. Parasit Vectors 12:360. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-019-3624-3
Yan TF, Li XN, Wang L, Chen C, Duan SX, Qi JJ, Li LX, Ma XJ (2018) Development of a reverse transcription recombinase-aided amplification assay for the detection of coxsackievirus A10 and coxsackievirus A6 RNA. Arch Virol 163:1455–1461. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-018-3734-3739
Zhang X, Guo L, Ma R, Cong L, Wu Z, Wei Y, Xue S, Zheng W, Tang S (2017) Rapid detection of salmonella with recombinase aided amplification. J Microbiol Methods 139:202–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mimet.2017.06.011
Zhang RQ, Li GX, Li XN, Shen XX, Gao Y, Wang L, Fan T, Duan QX, Wang YK, Wang J, Feng ZS, Ma XJ (2019) A rapid and sensitive recombinase aided amplification assay incorporating competitive internal control to detect Bordetella pertussis using the DNA obtained by boiling. Int J Infect Dis 86:108–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijid.2019.06.028
Funding
This work was supported by the National Science and Technology Major Project of China (No. 2018ZX10101003), the State Key Laboratory of Pathogen and Biosecurity (Academy of Military Medical Science) (No. SKLPBS1832).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Weiwei Fang declares that she has no conflict of interest. Yangyang Cai declares that he has no conflict of interest. Li Zhu declares that he has no conflict of interest. Hengliang Wang declares that he has no conflict of interest. Ying Lu declares that she has no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in this article.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fang, W., Cai, Y., Zhu, L. et al. Rapid and Highly Sensitive Detection of Toxigenic Vibrio cholerae Based on Recombinase-Aided Amplification Combining with Lateral Flow Assay. Food Anal. Methods 14, 687–696 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-020-01909-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-020-01909-x