Abstract
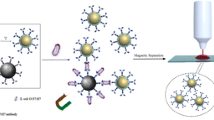
This paper investigated a new detection method for food pathogenic bacteria Vibrio parahaemolyticus based on surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS). Nanostructures consisting of Aptamer-Au nanoparticles-polydimethylsiloxane (Apt-Au-PDMS film) were firstly used as SERS substrate. Aptamers were immobilized on the functionalized PDMS film covered with Au nanoparticles (AuNPs) to act as a capture structure via the affinity binding of aptamer, and Vibrio parahaemolyticus. AuNPs were modified with the aptamer and Raman reporter molecule 4-mercaptobenzoic acid (4-MBA) to act as SERS-sensing probes that bind to the target in the same way as the Apt-Au-PDMS film. The solid sandwich structure was formed by capture structure-target-SERS-sensing probes. The concentration of Vibrio parahaemolyticus can be quantified by measurement of the SERS intensity of 4-MBA. Under optimal conditions, the signal of 4-MBA at 1590 cm−1 was linearly related to the Vibrio parahaemolyticus concentration in the range between 1.2 × 102 and 1.2 × 106 cfu·mL−1. Recoveries ranging from 97.7% to 105.3% were found when analyzing spiked prawn samples. This developed ultrasensitive aptamer-based SERS detection structure suggested that it would be a promising strategy for a variety of sensing applications.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banholzer MJ, Millstone JE, Qin L, Mirkin CA (2008) Rationally designed nanostructures for surface-enhanced Raman, spectroscopy vol 37. doi:https://doi.org/10.1039/b710915f
Chan TY, Liu TY, Wang KS, Tsai KT, Chen ZX, Chang YC, Tseng YQ, Wang CH, Wang JK, Wang YL (2017) SERS detection of biomolecules by highly sensitive and reproducible Raman-enhancing nanoparticle array. Nanoscale Res Lett 12:344. https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-017-2121-x
Chen J et al. (2015) Fabrication of SERS-active substrates using silver nanofilm-coated porous anodic aluminum oxide for detection of antibiotics: fabrication of SERS-active substrates… vol 80. doi:https://doi.org/10.1111/1750-3841.12825
Duan N, Wu S, Chen X, Huang Y, Wang Z (2012a) Selection and identification of a DNA aptamer targeted to Vibrio parahemolyticus. J Agric Food Chem 60:4034–4038. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf300395z
Duan N, Wu S, Zhu C, Ma X, Wang Z, Yu Y, Jiang Y (2012b) Dual-color upconversion fluorescence and aptamer-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles-based bioassay for the simultaneous detection of Salmonella typhimurium and Staphylococcus aureus. Anal Chim Acta 723:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2012.02.011
Duan N, Shen M, Wu S, Zhao C, Ma X, Wang Z (2017) Graphene oxide wrapped Fe3O4@au nanostructures as substrates for aptamer-based detection of Vibrio parahaemolyticus by surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Microchim Acta 184:2653–2660. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2298-9
Focsan M, Craciun AM, Potara M, Leordean C, Vulpoi A, Maniu D, Astilean S (2017) Flexible and tunable 3D gold nanocups platform as plasmonic biosensor for specific dual LSPR-SERS immuno-detection. Sci Rep 7:14240. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-14694-1
Fortuni B, Fujita Y, Ricci M, Inose T, Aubert R, Lu G, Hutchison JA, Hofkens J, Latterini L, Uji-i H (2017a) A novel method for in situ synthesis of SERS-active gold nanostars on polydimethylsiloxane film. Chem Commun 53:5121–5124. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7cc01776f
Fortuni B, Inose T, Uezono S, Toyouchi S, Umemoto K, Sekine S, Fujita Y, Ricci M, Lu G, Masuhara A, Hutchison JA, Latterini L, Uji-i H (2017b) In situ synthesis of Au-shelled Ag nanoparticles on PDMS for flexible, long-life, and broad spectrum-sensitive SERS substrates. Chem Commun 53:11298–11301. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7cc05420c
Haiss W, Thanh NT, Aveyard J, Fernig DG (2007) Determination of size and concentration of gold nanoparticles from UV-vis spectra. Anal Chem 79(11):4215–4221. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac0702084
Joshi R, Janagama H, Dwivedi HP, Senthil Kumar TM, Jaykus LA, Schefers J, Sreevatsan S (2009) Selection, characterization, and application of DNA aptamers for the capture and detection of Salmonella enterica serovars. Mol Cell Probes 23:20–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcp.2008.10.006
Kumar P, Khosla R, Soni M, Deva D, Sharma SK (2017) A highly sensitive, flexible SERS sensor for malachite green detection based on Ag decorated microstructured PDMS substrate fabricated from Taro leaf as template. Sensors Actuators B Chem 246:477–486. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.01.202
Li JF, Huang YF, Ding Y, Yang ZL, Li SB, Zhou XS, Fan FR, Zhang W, Zhou ZY, Wu DY, Ren B, Wang ZL, Tian ZQ (2010) Shell-isolated nanoparticle-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Nature 464:392–395. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature08907
Li H, Chen Q, Ouyang Q, Zhao J (2017) Fabricating a novel Raman spectroscopy-based aptasensor for rapidly sensing Salmonella typhimurium. Food Anal Methods 10:3032–3041. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-017-0864-8
Liu S, Jiang C, Yang B, Zhang Z, Han M (2014) Controlled depositing of silver nanoparticles on flexible film and its application in ultrasensitive detection. RSC Adv 4:42358–42363. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ra05735j
Liu D, Han Y, Zhu L, Chen W, Zhou Y, Chen J, Jiang Z, Cao X, Dou Z (2016a) Quantitative detection of Isofenphos-methyl in corns using surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) with chemometric methods. Food Anal Methods 10:1202–1208. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-016-0677-1
Liu X, Guan Y, Cheng S, Huang Y, Yan Q, Zhang J, Huang G, Zheng J, Liu T (2016b) Development of a highly sensitive lateral immunochromatographic assay for rapid detection of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. J Microbiol Methods 131:78–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mimet.2016.10.007
Liu Y, Zhao C, Fu K, Song X, Xu K, Wang J, Li J (2017) Selective turn-on fluorescence detection of Vibrio parahaemolyticus in food based on charge-transfer between CdSe/ZnS quantum dots and gold nanoparticles. Food Control 80:380–387. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2017.05.032
Lu G, Li H, Zhang H (2012) Gold-nanoparticle-embedded polydimethylsiloxane elastomers for highly sensitive Raman detection. Small 8:1336–1340. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201102258
Maji D, Lahiri SK, Das S (2012) Study of hydrophilicity and stability of chemically modified PDMS surface using piranha and KOH solution vol 44. doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/sia.3770
Sha Y, Zhang X, Li W, Wu W, Wang S, Guo Z, Zhou J, Su X (2016) A label-free multi-functionalized graphene oxide based electrochemiluminscence immunosensor for ultrasensitive and rapid detection of Vibrio parahaemolyticus in seawater and seafood. Talanta 147:220–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2015.09.058
Shiohara A, Langer J, Polavarapu L, Liz-Marzan LM (2014) Solution processed polydimethylsiloxane/gold nanostar flexible substrates for plasmonic sensing. Nanoscale 6:9817–9823. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4nr02648a
Teng J, Ye Y, Yao L, Yan C, Cheng K, Xue F, Pan D, Li B, Chen W (2017) Rolling circle amplification based amperometric aptamer/immuno hybrid biosensor for ultrasensitive detection of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Microchim Acta 184:3477–3485. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2383-0
Tombelli S, Minunni M, Mascini M (2005) Analytical applications of aptamers. Biosens Bioelectron 20:2424–2434. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2004.11.006
Wu W-Y, Bian Z-P, Wang W, Wang W, Zhu J-J (2010) PDMS gold nanoparticle composite film-based silver enhanced colorimetric detection of cardiac troponin I. Sensors Actuators B Chem 147:298–303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2010.03.027
Xu KX, Guo MH, Huang YP, Li XD, Sun JJ (2018) Rapid and sensitive detection of malachite green in aquaculture water by electrochemical preconcentration and surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Talanta 180:383–388. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2017.12.079
Yan W, Yang L, Zhuang H, Wu H, Zhang J (2016) Engineered “hot” core-shell nanostructures for patterned detection of chloramphenicol. Biosens Bioelectron 78:67–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2015.11.011
Yao L, Ye Y, Teng J, Xue F, Pan D, Li B, Chen W (2017) In vitro isothermal nucleic acid amplification assisted surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopic for ultrasensitive detection of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Anal Chem 89:9775–9780. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.7b01717
Zhang R, Zhang Y, Dong ZC, Jiang S, Zhang C, Chen LG, Zhang L, Liao Y, Aizpurua J, Luo Y, Yang JL, Hou JG (2013) Chemical mapping of a single molecule by plasmon-enhanced Raman scattering. Nature 498:82–86. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12151
Zhang Q, Dong X, Chen B, Zhang Y, Zu Y, Li W (2016) Zebrafish as a useful model for zoonotic Vibrio parahaemolyticus pathogenicity in fish and human. Dev Comp Immunol 55:159–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dci.2015.10.021
Zhu D, Yang RX, Tang YP, Li W, Miao ZY, Hu Y, Chen J, Yu S, Wang J, Xu CY (2016) Robust nanoplasmonic substrates for aptamer macroarrays with single-step detection of PDGF-BB. Biosens Bioelectron 85:429–436. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2016.05.039
Ziegler C, Eychmüller A (2011) Seeded growth synthesis of uniform gold nanoparticles with diameters of 15−300 nm. J Phys Chem C 115:4502–4506. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp1106982
Funding
This work was partially supported by Jiangsu Agriculture Science and Technology Innovation Fund CX(18)2025-01, National Natural Science Fund of China (NSFC 31871721), Project funded by China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2017M610299, 2018T110443), Jiangsu Planned Projects for Postdoctoral Research Funds (1601087B), and Young Elite Scientists Sponsorship Program by CAST (2017QNRC001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Mofei Shen declares that he has no conflict of interest. Nuo Duan declares that she has no conflict of interest. Shijia Wu declares that he has no conflict of interest. Ying Zou declares that she has no conflict of interest. Zhouping Wang declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed Consent
Not applicable.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, M., Duan, N., Wu, S. et al. Polydimethylsiloxane Gold Nanoparticle Composite Film as Structure for Aptamer-Based Detection of Vibrio parahaemolyticus by Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy. Food Anal. Methods 12, 595–603 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-018-1389-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-018-1389-5