Abstract
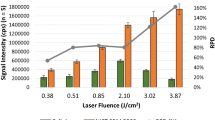
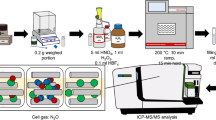
The quality and safety of food samples always require strict control. From an analytical perspective, many techniques can be used for this type of monitoring, one of which involves the application of laser pulses in laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS). LA-ICP-MS has great advantages such as simplicity of operation, versatility, and high analytical capability for multielement determinations. One of the difficulties and challenges associated with this technique involves quantitative analyses because of problems in the process of ablation, plasma formation and/or matrix effects. In this case, calibration strategies combining internal standards, standard addition methods, and chemometric tools can help improve the results. Food samples are among the most variable samples in terms of their matrix and composition, which can further complicate analysis by laser ablation and require the development of ablation strategies. This study describes the use of calibration strategies and the determination of Ca, Cd, Cr, Cu, Fe, Mg, Pb and Zn in food samples, including liquid (i.e., orange juice) and solid (i.e., dietary supplements) samples. The calibration curve for the solid samples was constructed using microcrystalline cellulose and a proportional mixture of solid samples chosen according to their higher and lower concentrations of metals. The liquid samples were immobilized in a polymer film with the help of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA). Using these calibration strategies, it was possible to obtain accuracy values between 60 and 120 % for almost all samples, except for Ca, Mg, and Zn. These exceptions could be a reflection of unresolved matrix interferences. Carbon was used as the internal standard but did not show promising results.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Austin C, Fryer F, Lear J et al (2011) Factors affecting internal standard selection for quantitative elemental bio-imaging of soft tissues by LA-ICP-MS. J Anal At Spectrom 26:1494–1501. doi:10.1039/C0JA00267D
Castro JP, Pereira-filho ER (2016) Proposition of classification , univariate and analyses of alloys by laser-induced breakdown. J Anal At Spectrom 31:2005–2014. doi:10.1039/C6JA00224B
Darke SA, Tyson JF (1994) Review of solid sample introduction for plasma spectrometry and a comparison of results for laser ablation, electrothermal vaporization, and slurry nebulization. Microchem J 50:310–336
Food supplements: list of vitamins and minerals which may be used in the manufacture of food supplements in the EU (2012). https://www.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/204324/Supplements_SI_guidance__Jan_2012__DH_FINAL.pdf. Accessed 26 August 2016
Frick DA, Günther D (2012) Fundamental studies on the ablation behaviour of carbon in LA-ICP-MS with respect to the suitability as internal standard. J Anal At Spectrom 27:1294–1303. doi:10.1039/c2ja30072a
Günther D, Hattendorf B (2005) Solid sample analysis using laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. TrAC - Trends Anal Chem 24:255–265. doi:10.1016/j.trac.2004.11.017
Kopriva S, Calderwood A, Weckopp SC, Koprivova A (2015) Plant sulfur and big data. Plant Sci 241:1–10. doi:10.1016/j.plantsci.2015.09.014
Lei WQ, El Haddad J, Motto-Ros V et al (2011) Comparative measurements of mineral elements in milk powders with laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy and inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectroscopy. Anal Bioanal Chem 400:3303–3313. doi:10.1007/s00216-011-4813-x
Lin Q, Han X, Wang J et al (2016) Ultra-trace metallic element detection in liquid samples using laser induced breakdown spectroscopy based on matrix conversion and crosslinked PVA polymer membrane. J Anal At Spectrom 31:1622–1630. doi:10.1039/C6JA00177G
Miliszkiewicz N, Walas S, Tobiasz A (2015) Current approaches to calibration of LA-ICP-MS analysis. J Anal At Spectrom 30:327–338. doi:10.1039/C4JA00325J
Nunes MAG, Voss M, Corazza G et al (2016) External calibration strategy for trace element quantification in botanical samples by LA-ICP-MS using filter paper. Anal Chim Acta 905:51–57. doi:10.1016/j.aca.2015.11.049
Thomas R (2013) Practical guide to ICP-MS: a tutorial for beginners. Taylor & Francis, New York
Ohata M, Yasuda H, Namai Y, Furuta N (2002) Laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS): comparison of different internal standardization methods using laser-induced plasma (LIP) emission and LA-ICP-MS signals. Anal Sci 18:1105–1110. doi:10.2116/analsci.18.1105
Russo RE, Mao X, Liu H et al (2002) Laser ablation in analytical chemistry-a review. Talanta 57:425–451. doi:10.1016/S0039-9140(02)00053-X
Sarkar A, Mao X, Russo RE (2014) Advancing the analytical capabilities of laser ablation molecular isotopic spectrometry for boron isotopic analysis. Spectrochim Acta - Part B At Spectrosc 92:42–50. doi:10.1016/j.sab.2013.12.001
Schiavo D, Trevizan LC, Pereira-filho ER, Nóbrega JA (2009) Evaluation of the use of multiple lines for determination of metals in water by inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry with axial viewing. Spectrochim Acta Part B At Spectrosc 64:544–548. doi:10.1016/j.sab.2009.05.009
Szymczycha-Madeja A, Welna M, Jedryczko D, Pohl P (2014) Developments and strategies in the spectrochemical elemental analysis of fruit juices. TrAC - Trends Anal Chem 55:68–80. doi:10.1016/j.trac.2013.12.005
Wolle MM, Rahman GMM, Kingston HMS, Pamuku M (2014) Speciation analysis of arsenic in prenatal and children’s dietary supplements using microwave-enhanced extraction and ion chromatography-inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Anal Chim Acta 818:23–31. doi:10.1016/j.aca.2014.01.060
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Sao Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP), 2015/14488-0, 2014/11415-0 PhD grant to ASA, and Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq, 401074/2014-5, 160152/2015-1 and 305637/2015-0). The authors are grateful to Analítica and Thermo Scientific for the instrument loan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Amanda dos Santos Augusto declares that she has no conflict of interest. Marco Aurélio Sperança declares that he has no conflict of interest. Daniel Fernandes de Andrade declares that he has no conflict of interest. Edenir Rodrigues Pereira-Filho declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Augusto, A.d.S., Sperança, M.A., Andrade, D.F. et al. Nutrient and Contaminant Quantification in Solid and Liquid Food Samples Using Laser-Ablation Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS): Discussion of Calibration Strategies. Food Anal. Methods 10, 1515–1522 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-016-0703-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-016-0703-3