Abstract
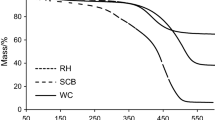
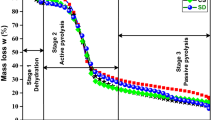
The present investigation deals with the thermogravimetric analysis of bamboo and bamboo biochar in an inert environment at 10, 20, and 30 °C/min. In addition, vacuum pyrolysis was used for the bamboo biochar. The FWO (Flynn–Wall–Ozawa) and KAS (Kissinger–Akahira–Sunose) methods were used to determine thermodynamic and kinetic parameters within the active pyrolysis zone. Thermal degradation of bamboo biomass undergoes several steps of loss of mass, including moisture loss, and passive and active pyrolysis. Between 180 and 395 °C, the active pyrolysis zone accounted for 50 to 55% of the mass loss. Furthermore, in both FWO and KAS models, bamboo biochar had lower activation energy values (99.23 and 96.07 kJ/mol) than bamboo biomass (262.5303 and 266.62 kJ/mol). The study’s study on bamboo and its biochar revealed a significant opportunity in the agro-industry for designing and building pyrolysis reactors for long-term biofuel generation.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rehman A, Ma H, Chishti MZ et al (2021) Asymmetric investigation to track the effect of urbanization, energy utilization, fossil fuel energy and CO2 emission on economic efficiency in China: another outlook. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:17319–17330. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-12186-w
Hosseini SE, Wahid MA, Aghili N (2013) The scenario of greenhouse gases reduction in Malaysia. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 28:400–409. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2013.08.045
York R, Bell SE (2019) Energy transitions or additions?: why a transition from fossil fuels requires more than the growth of renewable energy. Energy Res Soc Sci 51:40–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.erss.2019.01.008
Kumar A, Anushree KJ, Bhaskar T (2020) Utilization of lignin: a sustainable and eco-friendly approach. J Energy Inst 93:235–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joei.2019.03.005
Variny M, Varga A, Rimár M et al (2021) Advances in biomass co-combustion with fossil fuels in the European context: a review. Processes 9:1–34. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9010100
Bilandzija N, Voca N, Jelcic B et al (2018) Evaluation of Croatian agricultural solid biomass energy potential. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 93:225–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2018.05.040
Ghosh U, Das D, Banerjee D et al (2021) Biomass energy potential in India: a review. Int J Eng Res Technol Nceter 9:42–45. https://doi.org/10.17577/IJERTCONV9IS11012
Rathore NS, Panwar NL (2021) Biomass production and efficient utilization for energy generation, 1st edn. CRC Press, London
Hoang AT, Ong HC, Fattah IMR et al (2021) Progress on the lignocellulosic biomass pyrolysis for biofuel production toward environmental sustainability. Fuel Process Technol 223:106997. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2021.106997
Panwar NL, Pawar A (2022) Influence of activation conditions on the physicochemical properties of activated biochar: a review. Biomass Conv Bioref 12:925–947. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-020-00870-3
Cai J, Wu W, Liu R, Huber GW (2013) A distributed activation energy model for the pyrolysis of lignocellulosic biomass. Green Chem 15:1331–1340. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3gc36958g
Panwar NL, Gajera B, Jain S, Salvi BL (2020) Thermogravimetric studies on co-pyrolysis of raw/torrefied biomass and coal blends. Waste Manag Res 38: https://doi.org/10.1177/0734242X19896624
Slopiecka K, Bartocci P, Fantozzi F (2012) Thermogravimetric analysis and kinetic study of poplar wood pyrolysis. Appl Energy 97:491–497. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2011.12.056
Burnham AK, Dinh LN (2007) A comparison of isoconversional and model-fitting approaches to kinetic parameter estimation and application predictions. J Therm Anal Calorim 89:479–490. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-006-8486-1
Mishra RK, Mohanty K (2018) Pyrolysis characteristics and kinetic parameters assessment of three waste biomass. J Renew Sustain Energy 10:013102. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5000879
Jiang Z, Liu Z, Fei B et al (2012) The pyrolysis characteristics of moso bamboo. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis 94:48–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2011.10.010
Chen D, Zhou J, Zhang Q (2014) Effects of heating rate on slow pyrolysis behavior, kinetic parameters and products properties of moso bamboo. Bioresour Technol 169:313–319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.07.009
Mallick D, Baruah D, Mahanta P, Moholkar VS (2019) A comprehensive kinetic analysis of bamboo waste using thermogravimetric analysis. In: 2nd International Conference on Energy, Power and Environment: Towards Smart Technology, ICEPE 2018
Poletto M, Zattera AJ, Santana RMC (2012) Thermal decomposition of wood: kinetics and degradation mechanisms. Bioresour Technol 126:7–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.08.133
Zakikhani P, Zahari R, Sultan MTH, Majid DL (2016) Thermal degradation of four bamboo species. BioResources 11:414–425. https://doi.org/10.15376/biores.11.1.414-425
Rathore NS, Pawar A, Panwar NL (2021) Kinetic analysis and thermal degradation study on wheat straw and its biochar from vacuum pyrolysis under non-isothermal condition. Biomass Convers Biorefinery. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-021-01360-w
Wongsiriamnuay T, Tippayawong N (2010) Non-isothermal pyrolysis characteristics of giant sensitive plants using thermogravimetric analysis. Bioresour Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.02.037
Brown ME (1988) Reaction kinetics from thermal analysis. Introd to Therm Anal 127–151. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-009-1219-9_13
Jiang G, Nowakowski DJ, Bridgwater AV (2010) A systematic study of the kinetics of lignin pyrolysis. Thermochim Acta 498:61–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tca.2009.10.003
Apaydin-Varol E, Polat S, Putun AE (2014) Pyrolysis kinetics and thermal decomposition behavior of polycarbonate - a TGA-FTIR study. Therm Sci 18:833–842. https://doi.org/10.2298/TSCI1403833A
Vyazovkin S (2006) Model-free kinetics: staying free of multiplying entities without necessity. J Therm Anal Calorim 83:45–51. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-005-7044-6
Flynn J, Wall L (1966) A quick, direct method for the determination of activation energy from thermogravimetric data. J Polym Sci Part B Polym Lett 4:323–328. https://doi.org/10.1002/pol.1966.110040504
Kissinger HE (1957) Reaction kinetics in differential thermal analysis. Anal Chem. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac60131a045
Starink MJ (2003) The determination of activation energy from linear heating rate experiments: a comparison of the accuracy of isoconversion methods. Thermochim Acta. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0040-6031(03)00144-8
Xu Y, Chen B (2013) Investigation of thermodynamic parameters in the pyrolysis conversion of biomass and manure to biochars using thermogravimetric analysis. Bioresour Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.07.086
Ahmad MS, Mehmood MA, Al Ayed OS et al (2017) Kinetic analyses and pyrolytic behavior of Para grass (Urochloa mutica) for its bioenergy potential. Bioresour Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.10.090
Gupta GK, Mondal MK (2019) Kinetics and thermodynamic analysis of maize cob pyrolysis for its bioenergy potential using thermogravimetric analyzer. J Therm Anal Calorim. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08053-7
Zhao R, Wang X, Liu L et al (2019) Slow pyrolysis characteristics of bamboo subfamily evaluated through kinetics and evolved gases analysis. Bioresour Technol 289:121674. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.121674
Ferrara F, Orsini A, Plaisant A, Pettinau A (2014) Pyrolysis of coal, biomass and their blends: performance assessment by thermogravimetric analysis. Bioresour Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.08.104
Wiktorsson LP, Wanzl W (2000) Kinetic parameters for coal pyrolysis at low and high heating rates - a comparison of data from different laboratory equipment. Fuel 79:701–716. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0016-2361(99)00138-6
Díez D, Urueña A, Piñero R et al (2020) and lignin content in different types of biomasses by thermogravimetric analysis and pseudocomponent kinetic model. Processes 8:1–21
Gajera B, Panwar NL (2019) Pyrolysis and kinetic behaviour of black gram straw using thermogravimetric analysis. Energy Sources, Part A Recover Util Environ Eff. https://doi.org/10.1080/15567036.2019.1662138
Kim KH, Kim JY, Cho TS, Choi JW (2012) Influence of pyrolysis temperature on physicochemical properties of biochar obtained from the fast pyrolysis of pitch pine (Pinus rigida). Bioresour Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.04.094
Hamza UD, Nasri NS, Amin NAS et al (2016) Characteristics of oil palm shell biochar and activated carbon prepared at different carbonization times. Desalin Water Treat. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2015.1042068
Pawar A, Panwar NL (2022) A comparative study on morphology, composition, kinetics, thermal behaviour and thermodynamic parameters of Prosopis Juliflora and its biochar derived from vacuum pyrolysis. Bioresour Technol Reports 18:101053. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biteb.2022.101053
Lopez-Velazquez MA, Santes V, Balmaseda J, Torres-Garcia E (2013) Pyrolysis of orange waste: a thermo-kinetic study. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2012.09.016
Cavinato CD, Poletto M (2021) Kinetic analysis of thermal degradation of Cedrela odorata, Marmaroxylon racemosum and Tectona grandis from timber industry. Maderas Cienc y Tecnol 23:1–10
Ornaghi HL, Ornaghi FG, Neves RM et al (2020) Mechanisms involved in thermal degradation of lignocellulosic fibers: a survey based on chemical composition. Cellulose 27:4949–4961. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03132-7
Havilah PR, Sharma PK, Sharma AK (2021) Characterization, thermal and kinetic analysis of Pinusroxburghii. Environ Dev Sustain 23:8872–8894. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-020-01001-8
Narnaware SL, Panwar NL (2022) Kinetic study on pyrolysis of mustard stalk using thermogravimetric analysis. Bioresour Technol Reports 17:100942. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biteb.2021.100942
Balogun AO, Lasode OA, McDonald AG (2014) Devolatilisation kinetics and pyrolytic analyses of Tectona grandis (teak). Bioresour Technol 156:57–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.01.007
Chen D, Shuang E, Liu L (2018) Analysis of pyrolysis characteristics and kinetics of sweet sorghum bagasse and cotton stalk. J Therm Anal Calorim 131:1899–1909. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-017-6585-9
Acknowledgements
Priti Jagnade sincerely acknowledged Chhatrapati Shahu Maharaj Research Training and Human Development Institute (SARTHI), Pune, for providing Research Fellowship. In addition, the authors are sincerely acknowledged the Indian Council of Agriculture Research Government of India for conducting a study under the Consortium Research Platform (CRP) on Energy from Agriculture.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Priti Jagnade conducted an experimental study, prepared a draft manuscript, and analyzed the constructive discussion data. Narayan Lal Panwar and Chitranjan Agarwal contributed to writing the manuscript and interpreting the data. All authors read and approved the final paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jagnade, P., Panwar, N.L. & Agarwal, C. Experimental Investigation of Kinetic Parameters of Bamboo and Bamboo Biochar Using Thermogravimetric Analysis Under Non-isothermal Conditions. Bioenerg. Res. 16, 1143–1155 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12155-022-10497-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12155-022-10497-z