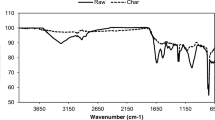
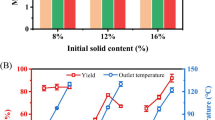
Abstract
Microalgae are one of the most potential biomass energy sources. An efficient drying method is important to development and utilization of microalgae. Microwave drying is receiving increasing attention because it is a rapid, high-efficiency, and economical method compared to conventional drying. Pyrolysis characteristics of microalgae (C. vulgaris) after conventional drying (drying at 105 °C for 20 h) and microwave drying (the microwave drying time of 20, 30, and 40 min) were investigated. The pyrolysis experiment of microalgae was carried out at the heating rates of 10, 20, and 40 °C·min−1 in a thermogravimetric analyzer (TGA). And the bio-char after pyrolysis of C. vulgaris under different heating powers (conventional power of 2500 W and microwave power of 600, 1000, 1500, and 2250 W) were analyzed. Results show that comprehensive pyrolysis characteristic index (S) of C. vulgaris after microwave drying was higher than conventional drying; however, energy consumption and activation energy (E) after microwave drying were lower. For microwave drying, as microwave drying time increases, ignition temperature (Ti), final temperature detected as mass stabilization (Tf), reaction rate at the second peaks (Rp2), residual mass (Mr), and energy consumption increased, while average reaction rate (Rv) decreased. As the heating rate (β) increased, the Ti, Tf, Rp2, Rv, and S of C. vulgaris increased, while Mr decreased, and E firstly decreased and then increased. And except for microwave power of 600 W, as microwave power increased, the volatile content and the fixed carbon content of C. vulgaris bio-char decreased, and the ash was increased.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bilandzija N, Voca N, Jelcic B, Jurisic V, Matin A, Grubor M, Kricka T (2018) Evaluation of Croatian agricultural solid biomass energy potential. Renew Sust Energ Rev 93:225–230
Mao G, Huang N, Chen L, Wang H (2018) Research on biomass energy and environment from the past to the future: a bibliometric analysis. Sci Total Environ 635:1081–1090
Kadir WNA, Lam MK, Uemura Y, Lim JW, Lee KT (2018) Harvesting and pre-treatment of microalgae cultivated in wastewater for biodiesel production: a review. Energy Convers Manag 171:1416–1429
Rizwan M, Mujtaba G, Memon SA, Lee K, Rashid N (2018) Exploring the potential of microalgae for new biotechnology applications and beyond: a review. Renew Sust Energ Rev 92:394–404
Miranda MT, Sepúlveda FJ, Arranz JI, Montero I, Rojas CV (2018) Physical-energy characterization of microalgae Scenedesmus and experimental pellets. Fuel 226:121–126
Xu K, Li Y, Zou X, Wen H, Shen Z, Ren X (2018) Investigating microalgae cell-microsphere interactions during microalgae harvesting by ballasted dissolved air flotation through XDLVO theory. Biochem Eng J 137:294–304
Singh G, Patidar SK (2018) Microalgae harvesting techniques: a review. J Environ Manag 217:499–508
Santos NO, Oliveira SM, Alves LC, Cammarota MC (2014) Methane production from marine microalgae Isochrysis galbana. Bioresour Technol 157:60–67
Chen J, Li J, Dong W, Zhang X, Tyagi RD, Drogui P, Surampalli RY (2018) The potential of microalgae in biodiesel production. Renew Sust Energ Rev 90:336–346
Sukiran MA, Abnisa F, Wan Daud WMA, Abu Bakar N, Loh SK (2017) A review of torrefaction of oil palm solid wastes for biofuel production. Energy Convers Manag 149:101–120
Cao X, Zhang M, Fang Z, Mujumdar AS, Jiang H, Qian H, Ai H (2017) Drying kinetics and product quality of green soybean under different microwave drying methods. Dry Technol 35:240–248
Song Z, Yao L, Jing C, Zhao X, Wang W, Ma C (2017) Drying behavior of lignite under microwave heating. Dry Technol 35:433–443
Lv W, Fan G, Lv X, Lv X, Hu M, Zhang S, Qiu G, Bai C (2018) Drying kinetics of Philippine nickel laterite by microwave heating. Dry Technol 36:849–858
Wang X, Chen H, Luo K, Shao J, Yang H (2008) The influence of microwave drying on biomass pyrolysis. Energy Fuel 22:67–74
Fennell LP, Boldor D (2014) Continuous microwave drying of sweet sorghum bagasse biomass. Biomass Bioenergy 70:542–552
Ho S, Zhang C, Chen W, Shen Y, Chang J (2018) Characterization of biomass waste torrefaction under conventional and microwave heating. Bioresour Technol 264:7–16
Iraola-Arregui I, Van Der Gryp P, Görgens JF (2018) A review on the demineralisation of pre- and post-pyrolysis biomass and tyre wastes. Waste Manag 79:667–688
Dhyani V, Bhaskar T (2018) A comprehensive review on the pyrolysis of lignocellulosic biomass. Renew Energy 129:695–716
Mallick D, Poddar MK, Mahanta P, Moholkar VS (2018) Discernment of synergism in pyrolysis of biomass blends using thermogravimetric analysis. Bioresour Technol 261:294–305
Al Arni S (2018) Comparison of slow and fast pyrolysis for converting biomass into fuel. Renew Energy 124:197–201
Zhao B, Wang X, Yang X (2015) Co-pyrolysis characteristics of microalgae Isochrysis and Chlorella: kinetics, biocrude yield and interaction. Bioresour Technol 198:332–339
Hu Z, Ma X, Li L (2016) The synergistic effect of co-pyrolysis of oil shale and microalgae to produce syngas. J Energy Inst 89:447–455
Azizi K, Keshavarz Moraveji M, Abedini Najafabadi H (2017) Characteristics and kinetics study of simultaneous pyrolysis of microalgae Chlorella vulgaris, wood and polypropylene through TGA. Bioresour Technol 243:481–491
Chen C, Ma X, He Y (2012) Co-pyrolysis characteristics of microalgae Chlorella vulgaris and coal through TGA. Bioresour Technol 117:264–273
Wu Z, Yang W, Yang B (2018) Thermal characteristics and surface morphology of char during co-pyrolysis of low-rank coal blended with microalgal biomass: effects of Nannochloropsis and Chlorella. Bioresour Technol 249:501–509
Hu Z, Ma X, Chen C (2012) A study on experimental characteristic of microwave-assisted pyrolysis of microalgae. Bioresour Technol 107:487–493
Hu Z, Jiang E, Ma X (2018) Microwave pretreatment on microalgae: effect on thermo-gravimetric analysis and kinetic characteristics in chemical looping gasification. Energy Convers Manag 160:375–383
Liu H, E J, Ma X, Xie C (2016) Influence of microwave drying on the combustion characteristics of food waste. Dry Technol 34:1397–1405
Gao Z, Zheng M, Zhang D, Zhang W (2016) Low temperature pyrolysis properties and kinetics of non-coking coal in Chinese western coals. J Energy Inst 89:544–559
Agrawal A, Chakraborty S (2013) A kinetic study of pyrolysis and combustion of microalgae Chlorella vulgaris using thermo-gravimetric analysis. Bioresour Technol 128:72–80
Wu K, Liu J, Wu Y, Chen Y, Li Q, Xiao X, Yang M (2014) Pyrolysis characteristics and kinetics of aquatic biomass using thermogravimetric analyzer. Bioresour Technol 163:18–25
Ceylan S, Kazan D (2015) Pyrolysis kinetics and thermal characteristics of microalgae Nannochloropsis oculata and Tetraselmis sp. Bioresour Technol 187:1–5
Sanchez-Silva L, López-González D, Garcia-Minguillan AM, Valverde JL (2013) Pyrolysis, combustion and gasification characteristics of Nannochloropsis gaditana microalgae. Bioresour Technol 130:321–331
Wang S, Jiang XM, Wang N, Yu LJ, Li Z, He PM (2007) Research on pyrolysis characteristics of seaweed. Energy Fuel 21:3723–3729
Vo TK, Ly HV, Lee OK, Lee EY, Kim CH, Seo J, Kim J, Kim S (2017) Pyrolysis characteristics and kinetics of microalgal Aurantiochytrium sp. KRS101. Energy 118:369–376
Kim S, Ly HV, Kim J, Lee EY, Woo HC (2015) Pyrolysis of microalgae residual biomass derived from Dunaliella tertiolecta after lipid extraction and carbohydrate saccharification. Chem Eng J 263:194–199
Li D, Chen L, Zhang X, Ye N, Xing F (2011) Pyrolytic characteristics and kinetic studies of three kinds of red algae. Biomass Bioenergy 35:1765–1772
Jeguirim M, Trouvé G (2009) Pyrolysis characteristics and kinetics of Arundo donax using thermogravimetric analysis. Bioresour Technol 100:4026–4031
Chahbani A, Fakhfakh N, Balti MA, Mabrouk M, El-Hatmi H, Zouari N, Kechaou N (2018) Microwave drying effects on drying kinetics, bioactive compounds and antioxidant activity of green peas (Pisum sativum L.). Food Biosci 25:32–38
Li L, Jiang X, Bian Z, Wang J, Wang F, Song Z, Zhao X, Ma C (2018) Microwave drying performance of lignite with the assistance of biomass-derived char. Dry Technol 1–13
Chaiwong K, Kiatsiriroat T, Vorayos N, Thararax C (2013) Study of bio-oil and bio-char production from algae by slow pyrolysis. Biomass Bioenergy 56:600–606
Bird MI, Wurster CM, de Paula Silva PH, Bass AM, de Nys R (2011) Algal biochar-production and properties. Bioresour Technol 102:1886–1891
Funding
This work was supported by the Guangxi Natural Science Foundation (2014GXNSFBA118252), the Guangxi Scientific Research and Technology Development Project (Gui Kegong 1598008-17), and the University Scientific Research Key Project of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region Education Department (ZD2014008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, C., Yang, S. & Bu, X. Microwave Drying Effect on Pyrolysis Characteristics and Kinetics of Microalgae. Bioenerg. Res. 12, 400–408 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12155-019-09970-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12155-019-09970-z