Abstract
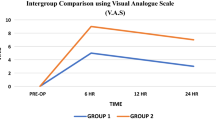
Tonsillectomy is one of the most common surgical procedures carried out in ENT since ancient time, is associated with several morbidities in which the pain and bleeding being the commonest and can cause considerable delay in starting oral intake and discharge from the hospital. Different methods have been used to reduce posttonsillectomy pain including use of opioids, sucralfate and local anaesthetics. Local anaesthetics in the form of pre-incisional or post-incisional peritonsillar infiltration and also topical post-incisional spray or packing are some of the most effective methods for post-tonsillectomy pain management. In our hospital, a study was carried out for preincisional peritonsillar infiltration of 0.5% bupivacaine in tonsillectomy patients for post operative pain relief. Written informed valid consent was taken, all routine investigations were done. Pre anaesthetic check up was done and bupivacaine test dose was given, none of the patients showed allergic reactions. Our study showed that this is effective method of controlling post operative pain. Patients receiving bupivacaine showed lower pain scores 6 h post operatively. The mean pain scores for Bupivacaine group were 2.85, 5.52 and 7.04 versus 5.04, 7.04 and 7.61 in saline group at 2, 4, and 6 h post operatively (t value significant). Pre incisional peritonsillar infiltration of 0.5% bupivacaine significantly reduces postoperative pain till 6 h, thereby reducing the need of analgesics intraoperatively and post operatively. Oral intake was also earlier without any adverse effects in our study.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hydri AS, Nawaid M, Afridi J, Shabbir G (2012) Comparison of local application versus infiltration of bupivacaine for post tonsillectomy pain in adults. Ann Pak Inst Med Sci 8(1):3–5
Ozkiris M, Kapusuz Z, Sayadam L (2012) Comparison of ropivacaine, bupivacaine and lidocaine in management of post tonsillectomy pain. Int J Paediatr Otorhinolaryngol 76(12):1831–1834
Nikandish R, Maghsoodi B, Khadei S, Kaboodkhani R (2008) Peritonsillar infiltration with bupivacaine and pethidine for relief of post tonsillectomy pain randomised double bind study. Anaesthesia 63(1):20–25
Akoglu E, Akkurt BCO, Inanoglu K, Okuyucu S, Dagli S (2006) Ropivacaine compared to bupivacaine for post tonsillectomy pain relief in children: a randomised controlled study. Int J Paediatr Otorhinolaryngol 70(7):1169–1173
Coté CJ, Lerman J, Todres ID (2009) A practice of anesthesia for infants and children. Elsevier Health Sciences, Amsterdam. ISBN 978-1-4160-3134-5
Hockenberry MJ, Wilson D (2015) Pain assessment and management in children. In: Hockenberry MJ, Wilson D (eds) Wong’s nursing care of infants and children. Mosby, Elsevier, St. Louis, p 155
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rajput, S.D., Patel, A.V., Prajapati, M.B. et al. Role of Preincisional Peritonsillar Infiltration of Bupivacaine in Postoperative Pain Relief in Tonsillectomy Patients. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 71 (Suppl 1), 610–613 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-018-1436-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-018-1436-y