Abstract
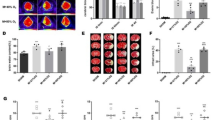
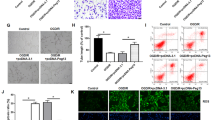
Endothelial dysfunction greatly contributes to microcirculation disorder. The role of prostaglandin E1 (PGE1) in cerebral microcirculation was explored in vitro. LPS (0.5 or 1 μg/ml) was added to induce injury in human brain microvascular endothelial cells (HCMEC/D3). CCK-8 was applied to check viabilities of HCMEC/D3 before and after LPS treatment. Western blot witnessed the changes in protein expressions of inflammatory cytokines, IL-6 and TNF-α. Caspase-3/7 activity was analyzed and so were the protein expressions of pro-apoptotic gene BAX and anti-apoptotic gene Bcl-2. mRNA expressions of eNOS and GTPCH1 were evaluated by RT-qPCR. After overexpressing eNOS or GTPCH1 in LPS-induced HCMEC/D3 cells, viabilities, inflammatory cytokines, caspase-3/7 activity, and apoptosis-related genes were detected. The modulation of PGE1 in eNOS and GTPCH1 production, viability, inflammation, and apoptosis was investigated. The inhibitor of eNOS or GTPCH1 was introduced to examine impacts of eNOS or GTPCH1 could have on the PGE1 function. LPS decreased cell viabilities, eNOS and GTPCH1 expression, and promoted inflammation and apoptosis in HCMEC/D3 cells. Overexpressed eNOS or GTPCH1 promoted cell viabilities and suppressed inflammation and apoptosis. PGE1 enhanced viability and decreased inflammation and apoptosis in cells treated by LPS. PGE1 activated eNOS and GTPCH1 and inhibition of eNOS or GTPCH1 led to the attenuation of the protective functions of PGE1 in LPS-induced cells. PGE1 protected HCMEC/D3 cells from injuries induced by LPS by activation of eNOS and GTPCH1, suggesting that PGE1 might be used to help maintain cerebral microcirculation in future.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams JH (1989) Cerebral infarction—its pathogenesis and interpretation. J Pathol 157(4):281–282
Hariharan A, Jing Y, Collie ND, Zhang H, Liu P (2019) Altered neurovascular coupling and brain arginine metabolism in endothelial nitric oxide synthase deficient mice. Nitric Oxide 87:60–72
Ritter L, Funk J, Schenkel L, Tipton A, Downey K, Wilson J, Coull B, Mcdonagh P (2008) Inflammatory and hemodynamic changes in the cerebral microcirculation of aged rats after global cerebral ischemia and reperfusion. Microcirculation 15(4):297–310
Terpolilli NA, Brem C, Bühler D, Plesnila N (2015) Are we barking up the wrong vessels? Cerebral Microcirculation After Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Stroke 46(10):3014–3019
Xiaolu D, Jing P, Fang H, Lifen Y, Liwen W, Ciliu Z, Fei Y (2011) Role of p115RhoGEF in lipopolysaccharide-induced mouse brain microvascular endothelial barrier dysfunction. Brain Res 1387:1–7
Austin SA, d'Uscio LV, Katusic ZS (2013) Supplementation of nitric oxide attenuates AβPP and BACE1 protein in cerebral microcirculation of eNOS-deficient mice. J Alzheimers Dis 33(1):29–33
Zheng Y, Wu Z, Yi F, Orange M, Yao M, Yang B, Liu J, Zhu H (2018) By activating Akt/eNOS Bilobalide B inhibits autophagy and promotes angiogenesis following focal cerebral ischemia reperfusion. Cell Physiol Biochem 47(2):604–616
Atochin DN, Huang PL (2011) Role of endothelial nitric oxide in cerebrovascular regulation. Curr Pharm Biotechnol 12(9):1334–1342
Chandra SB, Mohan S, Ford BM, Huang L, Janardhanan P, Deo KS, Cong L, Muir ER, Duong TQ (2016) Targeted overexpression of endothelial nitric oxide synthase in endothelial cells improves cerebrovascular reactivity in Ins2Akita-type-1 diabetic mice. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 36(6):1135–1142
Franscini N, Bachli EB, Blau N, Fischler M, Walter RB, Schaffner A, Schoedon G (2004) Functional tetrahydrobiopterin synthesis in human platelets. Circulation 110(2):186–192
Khoo JP, Zhao L, Alp NJ, Bendall JK, Nicoli T, Rockett K, Wilkins MR, Channon KM (2005) Pivotal role for endothelial tetrahydrobiopterin in pulmonary hypertension. Circulation 111(16):2126–2133
Korosue K, Kondoh T, Ishikawa A, Suzuki H, Nagao T, Tamaki N, Matsumoto S (1988) Clinical and hemodynamic effects of lipo PGE1 in cerebral infarction. No Shinkei Geka 16(7):819–826
Wei LY, Fu XH, Li W, Bi XL, Bai SR, Xing K, Wang YB (2015) Effect of intravenous administration of liposomal prostaglandin E1 on microcirculation in patients with ST elevation myocardial infarction undergoing primary percutaneous intervention. Chin Med J 128(9):1147–1150
Hutton I, Parratt JR, Lawrie TD (1973) Cardiovascular effects of prostaglandin E 1 in experimental myocardial infarction. Cardiovasc Res 7(2):149–155
Sheng R, Zhang LS, Han R, Gao B, Liu XQ, Qin ZH (2011) Combined prostaglandin E1 and lithium exert potent neuroprotection in a rat model of cerebral ischemia. Acta Pharmacol Sin 32(3):303–310
Serizawa F, Patterson E, Potter RF, Fraser DD, Cepinskas G (2015) Pretreatment of human cerebrovascular endothelial cells with CO-releasing molecule-3 interferes with JNK/AP-1 signaling and suppresses LPS-induced proadhesive phenotype. Microcirculation 22(1):28–36
Li J, Liu S, Cao G, Sun Y, Chen W, Dong F, Xu J, Zhang C, Zhang W (2018) Nicotine induces endothelial dysfunction and promotes atherosclerosis via GTPCH1. J Cell Mol Med 22(11):5406–5417
Corday E, Rothenberg SF, Irving DW (1963) Cerebral angiospasm. A cause of the cerebral stroke. Am J Cardiol 11:66–71
Findlay JM, Weir BKA, Kanamaru K, Espinosa F (1989) Arterial wall changes in cerebral vasospasm. Neurosurgery 25(5):736–745 discussion 745-6
Baez S (1977) Microcirculation. Annu Rev Physiol 39:391–415
Lifton RP, Gharavi AG, Geller DS (2001) Molecular mechanisms of human hypertension. Cell 104(4):545–556
Mulvany MJ (2003) Structural abnormalities of the resistance vasculature in hypertension. J Vasc Res 40(6):558–560
Schiffrin EL (1995) Remodeling of resistance arteries in human hypertension: effects of cilazapril, an angiotensin-I-converting enzyme inhibitor. Cardiology 86(Suppl 1):16–22
Christensen KL, Mulvany MJ (2001) Location of resistance arteries. J Vasc Res 38(1):1–12
Carretero OA, Oparil S (2000) Essential hypertension. Part I: definition and etiology. Circulation 101(3):329–335
Heagerty AM, Aalkjaer C, Bund SJ, Korsgaard N, Mulvany MJ (1993) Small artery structure in hypertension. Dual processes of remodeling and growth. Hypertension 21(4):391–397
Levy BI, Ambrosio G, Pries AR, Struijker-Boudier HAJ (2001) Microcirculation in hypertension: a new target for treatment? Circulation 104(6):735–740
Pervin M, Karim MR, Kuramochi M, Izawa T, Kuwamura M, Yamate J (2018) Macrophage populations and expression of regulatory inflammatory factors in hepatic macrophage-depleted rat livers under lipopolysaccharide (LPS) treatment. Toxicol Pathol 46(5):540–552
Zhang YP, Pan CS, Yan L, Liu YY, Hu BH, Chang X, Li Q, Huang DD, Sun HY, Fu G, Sun K, Fan JY, Han JY (2016) Catalpol restores LPS-elicited rat microcirculation disorder by regulation of a network of signaling involving inhibition of TLR-4 and SRC. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 311(6):G1091–g1104
Chen B, Sun K, Liu YY, Xu XS, Wang CS, Zhao KS, Huang QB, Han JY (2016) Effect of salvianolic acid B on TNF-α induced cerebral microcirculatory changes in a micro-invasive mouse model. Chin J Traumatol 19(2):85–93
Brito-Azevedo A, Perez RM, Maranhão PA, Coelho HS, Fernandes ESM, Castiglione RC, de Souza MD, Villela-Nogueira CA, Bouskela E (2019) Organ dysfunction in cirrhosis: a mechanism involving the microcirculation. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 31(5):618–625
Wang HM, Huang P, Li Q, Yan LL, Sun K, Yan L, Pan CS, Wei XH, Liu YY, Hu BH, Wang CS, Fan JY, Han JY (2019) Post-treatment with Qing-Ying-Tang, a compound Chinese medicine relives lipopolysaccharide-induced cerebral microcirculation disturbance in mice. Front Physiol 10:1320
Yasmeen S, Akram BH, Hainsworth AH, Kruuse C (2019) Cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases (PDEs) and endothelial function in ischaemic stroke. A review Cell Signal 61:108–119
Yang J, Ruan F, Zheng Z (2018) Ripasudil attenuates lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-mediated apoptosis and inflammation in pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells via ROCK2/eNOS signaling. Med Sci Monit 24:3212–3219
Watkins MT, al-Badawi H, Russo AL, Soler H, Peterson B, Patton GM (2004) Human microvascular endothelial cell prostaglandin E1 synthesis during in vitro ischemia-reperfusion. J Cell Biochem 92(3):472–480
Tang J, Hua Y, Su J, Zhang P, Zhu X, Wu L, Niu Q, Xiao H, Ding X (2009) Expression of VEGF and neural repair after alprostadil treatment in a rat model of sciatic nerve crush injury. Neurol India 57(4):387–394
Data Availability Statement
Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no new data were created or analyzed in this study.
Funding
This study was supported by Jinshan Health Commission (JSKJ-KTQN-2016-03).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
Ethical approval was obtained from IEC of the present institution.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This study was supported by Jinshan Health Commission (JSKJ-KTQN-2016-03).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, L., Zhang, H., Shi, Y. et al. Prostaglandin E1 Improves Cerebral Microcirculation Through Activation of Endothelial NOS and GRPCH1. J Mol Neurosci 70, 2041–2048 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-020-01610-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-020-01610-y