Abstract
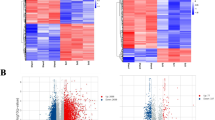
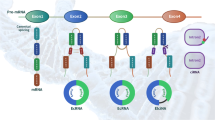
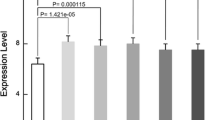
This study aimed to explore the implication of circular RNA (circRNA) expression profiles in spinal cord injury (SCI) rats at the immediate phase. CircRNA expression profiles in spinal cord samples from five SCI rats at the immediate phase (2 h post SCI) and five sham control (Ctrl) rats were assessed by microarray analysis. Subsequently, ten candidate circRNAs (obtained from microarray analysis) were validated in ten SCI rats at the immediate phase and ten Ctrl rats by the reverse transcription quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR). PCA plots and heatmap analyses revealed that circRNA expression profiles could distinguish SCI rats at the immediate phase from Ctrl rats. Furthermore, 1101 circRNAs were upregulated and 897 circRNAs were downregulated in SCI rats at the immediate phase compared with Ctrl rats. These dysregulated circRNAs distributed on all chromosomes, and most of them located on chromosome 1–10. As for circRNA types, most of these dysregulated circRNAs were exonic. Additionally, enrichment analyses displayed that these dysregulated circRNAs were enriched in multiple signaling pathways related to neuronal signal transduction, immunity, and inflammation, such as the calcium signaling pathway, JAK-STAT signaling pathway, and MAPK signaling pathway. Using RT-qPCR, eight out of ten candidate circRNAs (including rno_circRNA_011690, rno_circRNA_011494, rno_circRNA_005470, rno_circRNA_014301, rno_circRNA_009608, rno_circRNA_016031, rno_circRNA_011497, and rno_circRNA_015152) were dysregulated in SCI rats at the immediate phase compared with Ctrl rats. Our study provides a valuable reference for circRNA expression profiles in SCI rats at the immediate phase, which offers new clues for investigating mechanisms underlying the immediate phase and possible early intervention targets of SCI.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bai Y, Zhang Y, Han B et al (2018) Circular RNA DLGAP4 ameliorates ischemic stroke outcomes by targeting miR-143 to regulate endothelial-Mesenchymal transition associated with blood-brain barrier integrity. J Neurosci 38:32–50. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1348-17.2017
Ebbesen KK, Kjems J, Hansen TB (2016) Circular RNAs: identification, biogenesis and function. Biochim Biophys Acta 1859:163–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagrm.2015.07.007
Gruner JA (1992) A monitored contusion model of spinal cord injury in the rat. J Neurotrauma 9:123–126; discussion 126-128. https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.1992.9.123
Hutson TH, Di Giovanni S (2019) The translational landscape in spinal cord injury: focus on neuroplasticity and regeneration. Nat Rev Neurol 15:732–745. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41582-019-0280-3
Li F, Ma K, Sun M, Shi S (2018) Identification of the tumor-suppressive function of circular RNA ITCH in glioma cells through sponging miR-214 and promoting linear ITCH expression. Am J Transl Res 10:1373–1386
Martins D, Moreira J, Goncalves NP, Saraiva MJ (2017) MMP-14 overexpression correlates with the neurodegenerative process in familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy. Dis Model Mech 10:1253–1260. https://doi.org/10.1242/dmm.028571
Mfossa ACM, Puthenparampil HK, Inalegwu A et al (2019) Exposure to ionizing radiation triggers prolonged changes in circular RNA abundance in the embryonic mouse brain and primary neurons. Cells 8:778. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8080778
Neirinckx V, Coste C, Franzen R, Gothot A, Rogister B, Wislet S (2014) Neutrophil contribution to spinal cord injury and repair. J Neuroinflammation 11:150. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-014-0150-2
Ni S, Luo Z, Jiang L et al (2019) UTX/KDM6A deletion promotes recovery of spinal cord injury by epigenetically regulating vascular regeneration. Mol Ther: J Am Soc Gene Ther 27:2134–2146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymthe.2019.08.009
Paterniti I, Campolo M, Cordaro M et al (2017) PPAR-alpha modulates the anti-inflammatory effect of melatonin in the secondary events of spinal cord injury. Mol Neurobiol 54:5973–5987. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-0131-9
Peng X, Jing P, Chen J, Xu L (2019) The role of circular RNA HECTD1 expression in disease risk, disease severity, inflammation, and recurrence of acute ischemic stroke. J Clin Lab Anal 33:e22954. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcla.22954
Qin C, Liu C-B, Yang D-G et al (2018) Circular RNA expression alteration and bioinformatics analysis in rats after traumatic spinal cord injury. Front Mol Neurosci 11:497. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2018.00497
Rowland JW, Hawryluk GW, Kwon B, Fehlings MG (2008) Current status of acute spinal cord injury pathophysiology and emerging therapies: promise on the horizon. Neurosurg Focus 25:E2. https://doi.org/10.3171/FOC.2008.25.11.E2
Sabirzhanov B, Matyas J, Coll-Miro M, Yu LL, Faden AI, Stoica BA, Wu J (2019) Inhibition of microRNA-711 limits angiopoietin-1 and Akt changes, tissue damage, and motor dysfunction after contusive spinal cord injury in mice. Cell Death Dis 10:839. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-019-2079-y
Salgado-Somoza A, Zhang L, Vausort M, Devaux Y (2017) The circular RNA MICRA for risk stratification after myocardial infarction. Int J Cardiol Heart Vasculature 17:33–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcha.2017.11.001
Shi J, Jiang K, Li Z (2018) MiR-145 ameliorates neuropathic pain via inhibiting inflammatory responses and mTOR signaling pathway by targeting Akt3 in a rat model. Neurosci Res 134:10–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neures.2017.11.006
Shiao R, Lee-Kubli CA (2018) Neuropathic pain after spinal cord injury: challenges and research perspectives. Neurotherapeut: J Am Soc Exp NeuroTherapeut 15:635–653. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13311-018-0633-4
Solstrand Dahlberg L, Becerra L, Borsook D, Linnman C (2018) Brain changes after spinal cord injury, a quantitative meta-analysis and review. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 90:272–293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2018.04.018
Sun X, Jones ZB, Chen XM, Zhou L, So KF, Ren Y (2016) Multiple organ dysfunction and systemic inflammation after spinal cord injury: a complex relationship. J Neuroinflammation 13:260. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-016-0736-y
Wang P, Xie Z-D, Xie C-N et al (2018) AMP-activated protein kinase-dependent induction of autophagy by erythropoietin protects against spinal cord injury in rats. CNS Neurosci Therapeut 24:1185–1195. https://doi.org/10.1111/cns.12856
Wang X, Wang R, Wu Z, Bai P (2019) Circular RNA ITCH suppressed prostate cancer progression by increasing HOXB13 expression via spongy miR-17-5p. Cancer Cell Int 19:328. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-019-0994-8
Xie BS, Wang Y-q, Zhao C-c et al (2018) Circular RNA expression profiles Alter significantly after traumatic brain injury in rats. J Neurotrauma 35:1659–1666. https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.2017.5468
Zhao Y, Zhang H, Zhang D et al (2015) Loss of microRNA-124 expression in neurons in the peri-lesion area in mice with spinal cord injury. Neural Regen Res 10:1147–1152. https://doi.org/10.4103/1673-5374.156983
Zhou H, Shi Z, Kang Y et al (2018) Investigation of candidate long noncoding RNAs and messenger RNAs in the immediate phase of spinal cord injury based on gene expression profiles. Gene 661:119–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2018.03.074
Zhou ZB, Du D, Chen KZ, Deng LF, Niu YL, Zhu L (2019) Differential expression profiles and functional predication of circular ribonucleic acid in traumatic spinal cord injury of rats. J Neurotrauma 36:2287–2297. https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.2018.6366
Funding
This study was supported by Jilin Provincial Department of Public Health (No.2017q031) and the Youth Foundation of First Hospital of Jilin University (No. JDYY92018044).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
The animal experiment protocol was approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of our hospital and conducted in line with the Guidelines for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals made by our hospital.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Liu, J. & Liu, B. Identification of Circular RNA Expression Profiles and their Implication in Spinal Cord Injury Rats at the Immediate Phase. J Mol Neurosci 70, 1894–1905 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-020-01586-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-020-01586-9