Abstract
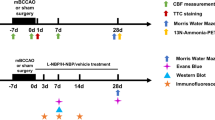
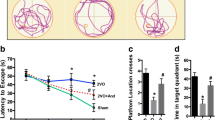
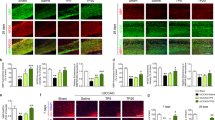
Methylene blue (MB) has a protective effect on cognitive decline caused by chronic hypoperfusion, but the specific mechanism is not clear. This article aims to determine whether MB protects vascular neurons through PI3K/Akt and plays a role in improving cognitive impairment. Molecular biological methods, the hippocampal neuronal density test, the hippocampal vascular network density test, and dynamic enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) were used to detect the blood–brain barrier permeability and Evans blue leakage rate in the hippocampus. We also observed and evaluated the changes in the above results after administration of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (Akt) pathway protein inhibitor LY294002. There were significant differences for cerebral blood flow (CBF) between the chronic cerebral hypoperfusion (CCH) + MB group (100 ml/100 g/min) and the CCH group (60 ml/100 g/min, P < 0.05). After using LY294002, the CBF of the CCH + MB + LY294002 group dropped to 82 ml/100 g/min. The vascular density in the CCH + MB group was 23%, which is significantly higher than that in the CCH group (15.1%) (P < 0.05). The vascular density (17.5%) in the CCH + MB + LY294002 group was significantly higher than that in the CCH group but lower than that in the CCH + MB group. Western blotting results showed that one week after intraperitoneal injection of MB, the expression of t-Akt and p-Akt in the CCH + MB group was increased after CCH, and LY294002 partially blocked this up-regulation effect (CCH + MB + LY294002 group). MB is a potential therapy for the relief of mild cognitive impairment associated with CCH, vascular dementia, and Alzheimer’s disease.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aberg ND, Brywe KG, Isgaard J (2008) Aspects of growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor-I related to neuroprotection regeneration and functional plasticity in the adult brain. Scientific World J 6:53–80
Arboleda G, Morales LC, Benítez B, Arboleda H (2009) Regulation of ceramide-induced neuronal death: cell metabolism meets neurodegeneration. Brain Res Rev 59:333–346
Atwal JK, Massie B, Miller FD, Kaplan DR (2000) The TrkB-Shc site signals neuronal survival and local axon growth via MEK and P13-kinase. Neuron 27:265–277
Auchter A, Williams J, Barksdale B, Monfils MH, Gonzalez-Lima F (2014) Therapeutic benefits of methylene blue on cognitive impairment during chronic cerebral hypoperfusion. J Alzheimers 42(Suppl 4):S525–S535
Barten DM, Albright CF (2008) Therapeutic strategies for Alzheimer's disease. Mol Neurobiol 37:171–186
Bousser MG, Chabriat H (2012) Vascular dementia. Bull Acad Natl Med 196:409–428
Bromley-Brits K, Deng Y, Song W (2011) Morris water maze test for learning and memory deficits in Alzheimer's disease model mice. J Vis Exp 53:2920
Brunet A, Datta SR, Greenberg ME (2001) Transcription-dependent and -independent control of neuronal survival by the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. Curr Opin Neurobiol 11:297–305
Cantley LC (2002) The phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway. Science 296:1655–1657
Castri P, Iacovelli L, De Blasi A, Giubilei F, Moretti A, Tari Capone F et al (2007) Reduced insulin-induced phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase activation in peripheral blood mononuclear leucocytes from patients with Alzheimer's disease. Eur J Neurosci 26:2469–2472
Chen C, Zhou F, Zeng L, Jiang Z, Hu Z (2019) Methylene blue offers neuroprotection after intracerebral hemorrhage in rats through the PI3K/Akt/GSK3β signaling pathway. J Cell Physiol 234(4):5304–5318
Chiang HC, Wang L, Xie Z, Yau A, Zhong Y (2010) PI3 kinase signaling is involved in Aβ-induced memory loss in drosophila. PNAS 107:7060–7065
de la Torre JC (2012) Cardiovascular risk factors promote brain hypoperfusion leading to cognitive decline and dementia. Cardiovasc Psychiatry Neurol 2012:367516
Du SQ, Wang XR, Xiao LY, Tu JF, Zhu W, He T, Liu CZ (2017) Molecular mechanisms of vascular dementia: what can be learned from animal models of chronic cerebral Hypoperfusion? Mol Neurobiol 54(5):3670–3682
Duong TQ, Kim SG (2000) In vivo MR measurements of regional arterial and venous blood volume fractions in intact rat brain. Magn Reson Med 43:393–402
Ewing JR, Knight RA, Nagaraja TN, Yee JS, Nagesh V, Whitton PA et al (2003) Patlak plots of Gd-DTPA MRI data yield blood-brain transfer constants concordant with those of 14C-sucrose in areas of blood–brain opening. Magn Reson Med 50:283–292
Gao X, Zhang H, Takahashi T, Hsieh J, Liao J, Steinberg GK et al (2008) The Akt signaling pathway contributes to postconditioning's protection against stroke; the protection is associated with the MAPK and PKC pathways. J Neurochem 105:943–955
Gong X, Ma M, Fan X, Li M, Liu Q, Liu X et al (2012) Down-regulation of IGF-1/IGF-1R in hippocampus of rats with vascular dementia. Neurosci Lett 513:20–24
Hara K, Yasuhara T, Matsukawa N, Maki M, Masuda T, Yu G et al (2007) Hippocampal CA1 cell loss in a non-human primate model of transient global ischemia: a pilot study. Brain Res Bull 74:164–171
Horwood JM, Dufour F, Laroche S, Davis S (2006) Signalling mechanisms mediated by the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt cascade in synaptic plasticity and memory in the rat. Eur J Neurosci 23:3375–3384
Kilkenny C, Browne W, Cuthill IC, Emerson M, Altman DG (2010) Animal research: reporting in vivo experiments: the ARRIVE guidelines. NC3Rs reporting guidelines working group. Br J Pharmacol 160(7):1577–1579
Kim YH, Choi KH, Park JW, Kwon TK (2005) LY294002 inhibits LPS-induced NO production through a inhibition of NF-κB activation: independent mechanism of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. Immunol Lett 99:45–50
Lee HK, Kumar P, Fu Q, Rosen KM, Querfurth HW (2009) The insulin/Akt signaling pathway is targeted by intracellular beta-amyloid. Mol Biol Cell 20:1533–1544
Li Y, He Y, Guan Q, Liu W, Han H, Nie Z (2012) Disrupted iron metabolism and ensuing oxidative stress may mediate cognitive dysfunction induced by chronic cerebral hypoperfusion. Biol Trace Elem Res 150:242–248
Li Y, Shen Q, Huang S, Li W, Muir ER, Long JA et al (2015) Cerebral angiography, blood flow and vascular reactivity in progressive hypertension. Neuroimage 111:329–337
Maeda S, Nakajima K, Tohyama Y, Kohsaka S (2009) Characteristic response of astrocytes to plasminogen/plasmin to upregulate transforming growth factor beta 3 (TGFβ3) production/secretion through proteinase-activated receptor-1 (PAR-1) and the downstream phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)-Akt/PKB signaling cascade. Brain Res 11:1–13
Maira SM, Stauffer F, Schnell C, García-Echeverría C (2009) PI3K inhibitors for cancer treatment: where do we stand? Biochem Soc Trans 37:265–272
Manning BD, Toker A (2017) AKT/PKB signaling: navigating the network. Cell 169(3):381–405
Nadam J, Navarro F, Sanchez P, Moulin C, Georges B, Laglaine A et al (2007) Neuroprotective effects of erythropoietin in the rat hippocampus after pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus. Neurobiol Dis 25:412–426
Roy Choudhury G, Winters A, Rich RM, Ryou MG, Gryczynski Z, Yuan F et al (2015) Methylene blue protects astrocytes against glucose oxygen deprivation by improving cellular respiration. PLoS One 10:e0123096
Ryou MG, Choudhury GR, Li W, Winters A, Yuan F, Liu R et al (2015) Methylene blue-induced neuronal protective mechanism against hypoxia-reoxygenation stress. Neuroscience 301:193–203
Schäbitz WR, Krüger C, Pitzer C, Weber D, Laage R, Gassler N et al (2008) A neuroprotective function for the hematopoietic protein granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor (GM-CSF). J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 28:29–43
Shen Q, Meng X, Fisher M, Sotak CH, Duong TQ (2003) Pixel-by-pixel spatiotemporal progression of focal ischemia derived using quantitative perfusion and diffusion imaging. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 23:1479–1488
Shu Y, Zhang H, Kang T, Zhang JJ, Yang Y, Liu H, Zhang L (2013) PI3K/Akt signal pathway involved in the cognitive impairment caused by chronic cerebral hypoperfusion in rats. PLoS One 8:e81901
Stewart CA, Morris RGM (1993) The watermaze. In: Sahgal A (ed) Behavioural neuroscience, volume I, a practical approach. IRL Press at Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 107–122
Tsai PS, Kaufhold JP, Blinder P, Friedman B, Drew PJ, Karten HJ et al (2009) Correlations of neuronal and microvascular densities in murine cortex revealed by direct counting and colocalization of nuclei and vessels. J Neurosci 29:14553–14570
Uyama O, Okamura N, Yanase M, Narita M, Kawabata K, Sugita M (1988) Quantitative evaluation of vascular permeability in the gerbil brain after transient ischemia using Evans blue fluorescence. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 8:282–284
Vasconcellos AP, Zugno AI, Dos Santos AH (2005) Na+ K+-ATPase activity is reduced in hippocampus of rats submitted to an experimental model of depression: effect of chronic lithium treatment and possible involvement in learning deficits. Neurobiol Learn Mem 84:102–110
Vlahos CJ, Matter WF, Hui KY, Brown RF (1994) A specific inhibitor of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, 2-(4-morpholinyl)-8-phenyl-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one (LY294002). J Biol Chem 269:5241–5248
Wu X, Jeong EK, Emerson L, Hoffman J, Parker DL, Lu ZR (2010) Noninvasive evaluation of antiangiogenic effect in a mouse tumor model by DCE-MRI with Gd-DTPA cystamine copolymers. Mol Pharm 7:41–48
Yao BC, Yuan H, Huang X (2004) Aberrant neuronal expression of cyclin a in the rat brain after injection of Aβ1-40 into the hippocampi. Yunyang Yixueyuan Xuebao 23:193–196 (In Chinese)
Zhao Y, Gu JH, Dai CL, Liu Q, Iqbal K, Liu F, Gong CX (2014) Chronic cerebral hypoperfusion causes decrease of O-GlcNAcylation, hyperphosphorylation of tau and behavioral deficits in mice. Front Aging Neurosci 6:10
Funding
The present study was supported by a grant from the National Natural Science Foundation of China [No.81671307] and Priority of Shanghai key discipline of medicine [2017ZZ02020].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethics approval
All animal procedures were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee and followed the ARRIVE guidelines. Male SD rats (Charles River) were studied with IACUC approval.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Wang, X., Liu, M. et al. Effect of Methylene Blue and PI3K-Akt Pathway Inhibitors on the Neurovascular System after Chronic Cerebral Hypoperfusion in Rats. J Mol Neurosci 70, 1797–1807 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-020-01572-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-020-01572-1