Abstract
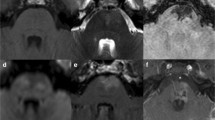
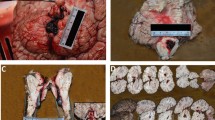
Cerebral capillary telangiectasia (CCT) is a type of vascular malformation that is incidentally encountered in clinical practice. Diseased vessels are small and usually clinically benign over the course of a patient’s life. Although most CCT patients are asymptomatic, the situation becomes complicated when trauma is encountered. A case of sudden death due to an epileptic episode after very mild head trauma is reported, including a retrospective study of 12 cases, to remind peers to pay close attention to CCT especially when located in important functional regions of the brain. After immunohistochemical staining and pathological examination, we speculated that the epileptogenic mechanism of CCT may be similar to that of hippocampal sclerosis. As the definite epileptogenic mechanism of CCT in the hippocampus is still elusive, we suggest that more research should be conducted on CCT.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tang SC, Jeng JS, Liu HM, et al. Diffuse capillary telangiectasia of the brain manifested as a slowly progressive course. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2003;15:140–2.
Lee RR, Becher MW, Benson ML, et al. Brain capillary telangiectasia: MR imaging appearance and clinicohistopathologic findings. Radiology. 1997;205:797–805.
Economou A, Zhang GX, Katsetos CD. Psychiatric disturbance and mild intellectual disability in the context of a vascular malformation (capillary telangiectasia) of the posterior hippocampus and subiculum. J Neuropsychiatr Clin Neurosci. 2013;25:E23–4.
Huddle DC, Chaloupka JC, Sehgal V. Clinically aggressive diffuse capillary telangiectasia of the brain stem: a clinical radiologic-pathologic case study. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1999;20:1674–7.
Graber D, Delisle MB, Sevely A, et al. Multiple cerebral telangiectasias. Apropos of an anatoma-radioclinical case. J Radiol. 1996;77:41–4.
Kuzma B, Goodman J M, Britt P. Capillary telangiectasia of the pons. Surg Neurol. 1997;48:93–4
De Gennaro A, Manzo G, Serino A, et al. Large capillary telangiectasia and developmental venous anomaly of the basal ganglia: an unusual finding. Neuroradiol J. 2012;25:744–9.
Bland LI, Lapham LW, Ketonen L, et al. Acute cerebellar hemorrhage secondary to capillary telangiectasia in an infant. A case report. Arch Neurol. 1994;51:1151–4.
Pozzati E, Gaist G, Galassi E, et al. Giant cerebral capillary telangiectasis in an infant. Childs Brain. 1982;9:114–20.
Chang SD, Steinberg GK, Rosario M, et al. Mixed arteriovenous malformation and capillary telangiectasia: a rare subset of mixed vascular malformations. J Neurosurg. 1997;86:699–703.
Bonneville F, Cattin F, Bonneville JF. The juxtaposition of a capillary telangiectasia, cavernous malformation, and developmental venous anomaly in the brainstem of a single patient: case report. Neurosurgery. 2002;51:850–1 author reply 1.
Goyal MK, Kumar G, Sahota PK. Reversible sensorineural hearing loss with normal brainstem auditory evoked potentials in pontine hemorrhage due to capillary telangiectasia. J Clin Neurosci. 2010;17:1198–201.
McCormick PW, Spetzler RF, Johnson PC, et al. Cerebellar hemorrhage associated with capillary telangiectasia and venous angioma: a case report. Surg Neurol. 1993;39:451–7.
Rigamonti D, Johnson PC, Spetzler RF, et al. Cavernous malformations and capillary telangiectasia: a spectrum within a single pathological entity. Neurosurgery. 1991;28:60–4.
Gross BA, Puri AS, Popp AJ, et al. Cerebral capillary telangiectasias: a meta-analysis and review of the literature. Neurosurg Rev. 2013;36:187–93 discussion 94.
Huberfeld G, Blauwblomme T, Miles R. Hippocampus and epilepsy: findings from human tissues. Rev Neurol (Paris). 2015;171:236–51.
Tatum WO. Mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2012;29:356–65.
Gilad R, Boaz M, Sadeh M, et al. Seizures after very mild head or spine trauma. J Neurotrauma. 2013;30:469–72.
Wang HC, Chang WN, Chang HW, et al. Factors predictive of outcome in posttraumatic seizures. J Trauma. 2008;64:883–8.
Thom M. Review: hippocampal sclerosis in epilepsy: a neuropathology review. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2014;40:520–43.
Sayama CM, Osborn AG, Chin SS, et al. Capillary telangiectasias: clinical, radiographic, and histopathological features. J Neurosurg. 2010;113:709–14.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2016YFC0800701), the Foundamental Developmental Reasearch Funds for the Central Universities, HUST(No. 2016JCTD117).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None.
Ethical approval
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, Hubei, China.
Informed consent
Written informed consent was obtained from the family members of the patient.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Liang, Y., Tong, F. et al. Sudden death from an epileptic seizure due to capillary telangiectasias in the hippocampus. Forensic Sci Med Pathol 15, 243–248 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12024-018-0075-7
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12024-018-0075-7