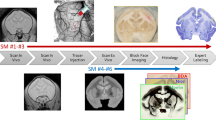
Abstract
To aid in the analysis of rhesus macaque brain images, we aligned digitized anatomical regions from the widely used atlas of Paxinos et al. to a published magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) template based on a large number of subjects. Digitally labelled atlas images were aligned to the template in 2D and then in 3D. The resulting grey matter regions appear qualitatively to be well registered to the template. To quantitatively validate the procedure, MR brain images of 20 rhesus macaques were aligned to the template along with regions drawn by hand in striatal and cortical areas in each subject’s MRI. There was good geometric overlap between the hand drawn regions and the template regions. Positron emission tomography (PET) images of the same subjects showing uptake of a dopamine D2 receptor ligand were aligned to the template space, and good agreement was found between tracer binding measures calculated using the hand drawn and template regions. In conclusion, an anatomically defined set of rhesus macaque brain regions has been aligned to an MRI template and has been validated for analysis of PET imaging in a subset of striatal and cortical areas. The entire set of over 200 regions is publicly available at https://www.nitrc.org/.

ᅟ







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adluru, N., Zhang, H., Fox, A. S., Shelton, S. E., Ennis, C. M., Bartosic, A. M., Oler, J. A., et al. (2012). A diffusion tensor brain template for rhesus macaques. NeuroImage, 59(1), 306–318.
Andreasen, A., Drewes, A. M., Assentoft, J. E., & Larsen, N. E. (1992). Computer-assisted alignment of standard serial sections without use of artificial landmarks. A practical approach to the utilization of incomplete information in 3-D reconstruction of the hippocampal region. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 45(3), 199–207.
Avants, B. B., Epstein, C. L., Grossman, M., & Gee, J. C. (2008). Symmetric diffeomorphic image registration with cross-correlation: evaluating automated labeling of elderly and neurodegenerative brain. Medical Image Analysis, 12(1), 26–41.
Bakker, R., Wachtler, T., & Diesmann, M. (2012). CoCoMac 2.0 and the future of tract-tracing databases. Frontiers in Neuroinformatics, 6, 30. https://doi.org/10.3389/fninf.2012.00030.
Ballanger, B., Tremblay, L., Sgambato-Faure, V., Beaudoin-Gobert, M., Lavenne, F., Le Bars, D., & Costes, N. (2013). A multi-atlas based method for automated anatomical Macaca Fascicularis brain MRI segmentation and PET kinetic extraction. NeuroImage, 77, 26–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.03.029.
Bezgin, G., Reid, A. T., Schubert, D., & Kötter, R. (2009). Matching spatial with ontological brain regions using Java tools for visualization, database access, and integrated data analysis. Neuroinformatics, 7(1), 7–22.
Bogart, S. L., Mangin, J.-F., Schapiro, S. J., Reamer, L., Bennett, A. J., Pierre, P. J., & Hopkins, W. D. (2012). Cortical sulci asymmetries in chimpanzees and macaques: a new look at an old idea. NeuroImage, 61(3), 533–541. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.03.082.
Ceritoglu, C., Wang, L., Selemon, L. D., Csernansky, J. G., Miller, M. I., & Tilak Ratnanather, J. (2010). Large deformation diffeomorphic metric mapping registration of reconstructed 3D histological section images and in vivo MR images. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 4, 43.
Chakravarty, Mallar, M., Bertrand, G., Hodge, C. P., Sadikot, A. F., & Louis Collins, D. (2006). The creation of a brain atlas for image guided neurosurgery using serial histological data. NeuroImage, 30(2), 359–376.
Chakravarty, Mallar, M., Frey, S., Collins, D. L. (2008). Digital atlas of the Rhesus Monkey brain in stereotaxic coordinates. In The rhesus monkey brain in stereotaxic coordinates, 2nd ed. Elsevier.
Christian, B. T., Wooten, D. W., Hillmer, A. T., Tudorascu, D. L., Converse, A. K., Moore, C. F., Ahlers, E. O., et al. (2013). Serotonin transporter genotype affects serotonin 5-HT1A binding in primates. The Journal of Neuroscience, 33(6), 2512–2516. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4182-12.2013.
Cohen, F. S., Yang, Z., Huang, Z., & Nissanov, J. (1998). Automatic matching of homologous histological sections. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 45(5), 642–649.
Converse, A. K., Moore, C. F., Moirano, J. M., Ahlers, E. O., Larson, J. A., Engle, J. W., Barnhart, T. E., et al. (2013). Prenatal stress induces increased striatal dopamine transporter binding in adult nonhuman Primates. Biological Psychiatry, 74(7), 502–510. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2013.04.023.
Converse, A. K., Moore, C. F., Holden, J. E., Ahlers, E. O., Moirano, J. M., Larson, J. A., Resch, L. M., et al. (2014). Moderate-level prenatal alcohol exposure induces sex differences in dopamine D1 receptor binding in adult rhesus monkeys. Alcoholism, Clinical and Experimental Research, 38(12), 2934–2943. https://doi.org/10.1111/acer.12575.
Dauguet, J. (2010). Three-dimensional histological imaging of primate brain and correlation with in vivo medical device images. Revue de Primatologie, February. Société francophone de primatologie. https://doi.org/10.4000/primatologie.546.
Dauguet, J., Delzescaux, T., Condé, F., Mangin, J.-F., Ayache, N., Hantraye, P., & Frouin, V. (2007). Three-dimensional reconstruction of stained histological slices and 3D non-linear registration with in-vivo MRI for whole baboon brain. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 164(1), 191–204.
Dice, L. R. (1945). Measures of the amount of ecologic association between species. Ecology, 26(3), 297–302.
Essen, V., David, C., Glasser, M. F., Dierker, D. L., & Harwell, J. (2012). Cortical Parcellations of the macaque monkey analyzed on surface-based atlases. Cerebral Cortex, 22(10), 2227–2240. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhr290.
Frey, S., Pandya, D. N., Mallar Chakravarty, M., Bailey, L., Petrides, M., & Louis Collins, D. (2011). An MRI based average macaque monkey stereotaxic atlas and space (MNI monkey space). NeuroImage, 55(4). ACADEMIC PRESS INC ELSEVIER SCIENCE), 1435–1442. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.01.040.
Ganser, K. A., Dickhaus, H., Metzner, R., & Wirtz, C. R. (2004). A deformable digital brain atlas system according to Talairach and Tournoux. Medical Image Analysis, 8(1), 3–22.
Goldszal, A. F., Tretiak, O. J., Hand, P. J., Bhasin, S., & McEachron, D. L. (1995). Three-dimensional reconstruction of activated columns from 2-[14C]deoxy-D-glucose data. NeuroImage, 2(1), 9–20.
Heilbroner, P. L., & Holloway, R. L. (1989). Anatomical brain asymmetry in monkeys: frontal, temporoparietal, and limbic cortex in Macaca. American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 80(2), 203–211. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajpa.1330800208.
Hibbard, L. S., & Hawkins, R. A. (1988). Objective image alignment for three-dimensional reconstruction of digital autoradiograms. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 26(1), 55–74.
Hillmer, A. T., Wooten, D. W., Tudorascu, D. L., Barnhart, T. E., Ahlers, E. O., Resch, L. M., Larson, J. A., et al. (2014). The effects of chronic alcohol self-administration on serotonin-1A receptor binding in nonhuman Primates. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 144, 119–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2014.08.015.
Hopkins, W.D., Misiura, M., Pope, S.M., & Latash, E. M. (2015). Behavioral and brain asymmetries in primates: A preliminary evaluation of two evolutionary hypotheses.” In Miller, MB, Kingstone, A (eds.) Year in Cognitive Neuroscience 1359:65–83. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. https://doi.org/10.1111/nyas.12936.
Jenkinson, M., & Smith, S. (2001). A global optimisation method for robust affine registration of brain images. Medical Image Analysis, 5(2), 143–156.
Jenkinson, M., Bannister, P., Brady, M., & Smith, S. (2002). Improved optimization for the robust and accurate linear registration and motion correction of brain images. NeuroImage, 17(2), 825–841.
Kim, B., Boes, J. L., Frey, K. A., & Meyer, C. R. (1997). Mutual information for automated unwarping of rat brain autoradiographs. NeuroImage, 5(1), 31–40.
Klein, A., Andersson, J., Ardekani, B. A., Ashburner, J., Avants, B., Chiang, M.-C., Christensen, G. E., et al. (2009). Evaluation of 14 nonlinear deformation algorithms applied to human brain MRI registration. NeuroImage, 46(3), 786–802.
Logan, J., Fowler, J. S., Volkow, N. D., Wang, G. J., Ding, Y. S., & Alexoff, D. L. (1996). Distribution volume ratios without blood sampling from graphical analysis of PET data. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism, 16(5), 834–840.
Logothetis, N. K., Pauls, J., Augath, M., Trinath, T., & Oeltermann, A. (2001). Neurophysiological investigation of the basis of the FMRI signal. Nature, 412(6843), 150–157.
MacKenzie-Graham, A., Lee, E.-F., Dinov, I. D., Bota, M., Shattuck, D. W., Ruffins, S., Yuan, H., et al. (2004). A multimodal, multidimensional atlas of the C57BL/6J mouse brain. Journal of Anatomy, 204(2), 93–102.
Malandain, G., Bardinet, E., Nelissen, K., & Vanduffel, W. (2004). Fusion of autoradiographs with an MR volume using 2-D and 3-D linear transformations. NeuroImage, 23(1), 111–127.
McLaren, D. G., Kosmatka, K. J., Oakes, T. R., Kroenke, C. D., Kohama, S. G., Matochik, J. a., Ingram, D. K., & Johnson, S. C. (2009). A population-average MRI-based atlas collection of the rhesus macaque. NeuroImage, 45(1), 52–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2008.10.058.
Mega, M. S., Chen, S. S., Thompson, P. M., Woods, R. P., Karaca, T. J., Tiwari, A., Vinters, H. V., Small, G. W., & Toga, A. W. (1997). Mapping histology to metabolism: Coregistration of stained whole-brain sections to Premortem PET in alzheimer’s disease. NeuroImage, 5(2), 147–153.
Oakes, T R. (n.d.) Spamalize: http://Brainimaging.Waisman.Wisc.Edu/~oakes/Spam/Spam_frames.Htm.
Ourselin, S, A Roche, G Subsol, X Pennec, and N Ayache. 2001. “Reconstructing a 3D structure from serial histological sections.” Image and Vision Computing 19 (1–2, SI): 25–31. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/S0262-8856(00)00052-4.
Passingham, R. (2009). How good is the macaque monkey model of the human brain? Current Opinion in Neurobiology, 19(1), 6–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conb.2009.01.002.
Paxinos, G., Huang, X.-F., & Toga, A. W. (2000). The rhesus monkey brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Cambridge: Academic Press.
Paxinos, G., Huang, X.-F., Petrides, M., & Toga, A. W. (2009). The rhesus monkey brain in stereotaxic coordinates (2nd ed.). Cambridge: Academic Press.
Reveley, C., Gruslys, A., Ye, F. Q., Glen, D., Samaha, J., Russ, B. E., Saad, Z., Seth, A. K., Leopold, D. A., & Saleem, K. S. (2017). Three-dimensional digital template atlas of the macaque brain. Cerebral Cortex, 27(9), 4463–4477. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhw248.
Rohlfing, T., Kroenke, C. D., Sullivan, E.V., Dubach, M. F., Bowden, D. M, Grant, K. A., & Pfefferbaum, A.. (2012). The INIA19 template and NeuroMaps atlas for primate brain image parcellation and spatial normalization. Front Neuroinform 6. https://doi.org/10.3389/fninf.2012.00027.
Rubins, D. J., Melega, W. P., Lacan, G., Way, B., Plenevaux, A., Luxen, A., & Cherry, S. R. (2003). Development and evaluation of an automated atlas-based image analysis method for MicroPET studies of the rat brain. NeuroImage, 20(4), 2100–2118.
Saleem, K. S., & Logothetis, N. K. (2006). A combined MRI and histology atlas of the rhesus monkey brain. Amsterdam: Academic Press.
Shi, Y., Budin, F., Yapuncich, E., Rumple, A., Young, J. T, Payne, C., Zhang, X, et al. (2017). UNC-emory infant atlases for macaque brain image analysis: postnatal brain development through 12 months. Front Neurosci 10. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2016.00617.
Stephan, K. E., Kamper, L., Bozkurt, A., Burns, G. A., Young, M. P., & Kötter, R. (2001). Advanced database methodology for the collation of connectivity data on the macaque brain (CoCoMac). Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B, Biological Sciences, 356(1412), 1159–1186.
Stephan, K. E., McIntosh, A. R., Hilgetag, C. C. (2010). In Memoriam: Rolf Kötter (1961–2010). PLoS Computational Biology, 6(10), e1000965. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000965.
Streicher, J., Weninger, W. J., & Müller, G. B. (1997). External marker-based automatic Congruencing: a new method of 3D reconstruction from serial sections. The Anatomical Record, 248(4), 583–602.
Strome, E. M., & Doudet, D. J. (2007). Animal models of neurodegenerative disease: Insights from in vivo imaging studies. Molecular Imaging and Biology, 9(4), 186–195. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-007-0093-4.
Studholme, C., Drapaca, C., Iordanova, B., & Cardenas, V. (2006). Deformation-based mapping of volume change from serial brain MRI in the presence of local tissue contrast change. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 25(5), 626–639.
Tai, Y. C., Chatziioannou, A., Siegel, S., Young, J., Newport, D., Goble, R. N., Nutt, R. E., & Cherry, S. R. (2001). Performance evaluation of the MicroPET P4: A PET system dedicated to animal imaging. Physics in Medicine and Biology, 46(7), 1845–1862.
Thompson, P. M., Woods, R. P., Mega, M. S., & Toga, A. W. (2000). Mathematical/computational challenges in creating deformable and probabilistic atlases of the human brain. Human Brain Mapping, 9(2), 81–92.
Tzourio-Mazoyer, N., Landeau, B., Papathanassiou, D., Crivello, F., Etard, O., Delcroix, N., Mazoyer, B., & Joliot, M. (2002). Automated anatomical labeling of activations in SPM using a macroscopic anatomical Parcellation of the MNI MRI single-subject brain. NeuroImage, 15(1), 273–289. https://doi.org/10.1006/nimg.2001.0978.
Virdee, K., Cumming, P., Caprioli, D., Jupp, B., Rominger, A., Aigbirhio, F. I., Fryer, T. D., Riss, P. J., & Dalley, J. W. (2012). Applications of positron emission tomography in animal models of neurological and neuropsychiatric disorders. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 36(4), 1188–1216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2012.01.009.
Wooten, D. W., Hillmer, A. T., Moirano, J. M., Tudorascu, D. L., Ahlers, E. O., Slesarev, M. S., Barnhart, T. E., Mukherjee, J., Schneider, M. L., & Christian, B. T. (2013). 5-HT1A sex based differences in Bmax, in vivo KD, and BPND in the nonhuman primate. NeuroImage, 77, 125–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.03.027.
Yushkevich, P. A., Avants, B. B., Ng, L., Hawrylycz, M., Burstein, P. D., Zhang, H., & Gee, J. C. (2006). 3D Mouse brain reconstruction from histology using a coarse-to-fine approach. In Pluim, J. P. W., Likar, B., & Gerritsen, F. A. (eds) Biomedical Image Registration, Proceedings, 4057:230–37. Lecture Notes in Computer Science.
Zakszewski, E., Adluru, N., Tromp, D. P. M., Kalin, N., & Alexander, A. L. (2014). A diffusion-tensor-based white matter atlas for rhesus macaques. PLoS One, 9(9). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0107398.
Zijdenbos, A. P., Dawant, B. M., Margolin, R. A., & Palmer, A. C. (1994). Morphometric analysis of white matter lesions in MR images: Method and validation. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 13(4), 716–724.
Acknowledgements
This work was primarily funded by NIH grant R21EB004482 to A.K.C. with additional support from R01AA012277, P50MH100031, and U54HD090256. G.Y.B. acknowledges JS McDonnell Collaborative Research Grant 220020255. The authors are grateful to Mary L. Schneider for the use of PET and MR images. The authors are grateful to Max Albiero, Erin Crain, Shilpa Cyriac, Sabrina Koehler, Parker Johnson, and Alysha Rameshk for assistance drawing and analyzing ROIs for validation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Author notes
Rolf Kotter is deceased (Stephan et al. 2010). His coauthors are grateful for his contributions to this work.
- Rolf Kötter
• Anatomical regions from the Paxinos atlas were aligned to a published MRI template
• ROIs were validated against hand drawn ROIs for PET image analysis
• The full set of aligned ROIs is available online.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Research Highlights
• Anatomical regions from the Paxinos atlas were aligned to a published MRI template
• ROIs were validated against hand drawn ROIs for PET image analysis
• The full set of aligned ROIs is available online.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 718 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moirano, J.M., Bezgin, G.Y., Ahlers, E.O. et al. Rhesus Macaque Brain Atlas Regions Aligned to an MRI Template. Neuroinform 17, 295–306 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12021-018-9400-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12021-018-9400-2