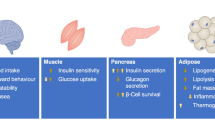
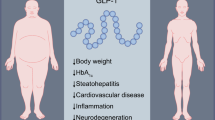
Abstract
Purpose
Proglucagon is expressed in both pancreatic alpha cells and intestinal epithelial L cells and is cleaved into glucagon and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) by different prohormone convertases (PCs). Recent studies have shown that α-cells can also secrete GLP-1, which may improve islet function. However, little is known about the factors influencing GLP-1 secretion by α cells. In this study, we investigated whether insulin promotes GLP-1 secretion by α cells, as well as the mechanisms underlying this phenomenon.
Methods
We cultured the alpha-cell line In-R1-G9 in low- or high-glucose medium in the presence or absence of insulin to determine the influence of glucose concentrations on the actions of insulin. We also treated In-R1-G9 cells with insulin for different times and at different doses. Then GLP-1 and glucagon protein expression levels were estimated. Moreover, ERK and phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase/AKT (PI3K/AKT) pathway activity levels and prohormone convertase expression levels were evaluated to elucidate the mechanism underlying the effects of insulin on GLP-1 secretion by α-cells.
Results
Insulin promoted GLP-1 secretion in a time- and dose-dependent manner under high-glucose conditions. Inhibiting the PI3K/AKT pathway with LY294002 and the Ras/mitogen-activated protein kinase (RAS/MAPK) pathway with PD98059 reduced GLP-1 secretion, respectively, in inhibitor-treated cells compared with insulin-treated cells. Moreover, insulin increased prohormone convertase 1/3 expression levels in the corresponding group of IN-R1-G9 cells compared with the control group of cells.
Conclusion
Insulin facilitates GLP-1 secretion by pancreatic alpha cells by inducing PC1/3 expression under high-glucose conditions, a phenomenon that may be associated mainly with PI3K/AKT pathway activation.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
E. Mannucci, F. Tesi, G. Bardini et al. Effects of metformin on glucagon-like peptide-1 levels in obese patients with and without Type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Nutr. Metab. 17, 336–342 (2004)
C. Over, D.M. Berman, N.S. Kenyon et al.The unique cytoarchitecture of human pancreatic islets has implications for islet cell function. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 103, 2334–2339 (2006)
D.J. Steiner, A. Kim, K. Miller, M. Hara Pancreatic islet plasticity: Interspecies comparison of islet architecture and composition. Islets 2, 135–145 (2010)
R.H. Unger, L. Orci, The essential role of glucagon in the patho-genesis of diabetes mellitus. Lancet 1, 14–16 (1975)
J.S. Moon, K.C. Won, Pancreatic α-cell dysfunction in type 2 diabetes: old kids on the block. Diabetes Metab. J. 39, 1–9 (2015)
F. Thorel, V. Népote, I. Avril et al. Conversion of adult pancreatic alpha-cells to beta-cells after extreme beta-cell loss. Nature 464, 1149–1154 (2010)
C.H. Chung, E. Hao, R. Piran et al. Pancreatic beta cell neogenesis by direct conversion from mature alpha cells. Stem Cells 28, 1630–1638 (2010)
L. Ye, M.A. Robertson, D. Hesselson, D.Y. Stainier, R.M. Anderson, Glucagon is essential for alpha cell transdifferentiation and beta cell neogenesis. Development 142, 1407–1417 (2015)
P. Collombat, X. Xu, P. Ravassard et al. The ectopic expression of Pax4 in the mouse pancreas converts progenitor cells into alpha and subsequently beta cells. Cell 138, 449–462 (2009)
Y.P. Yang, F. Thorel, D.F. Boyer, P.L. Herrera, C.V. Wright, Context-specific alpha-to-beta-cell reprogramming by forced Pdx1 expression. Genes Dev. 25, 1680–1685 (2011)
R.D. Wideman, I.L. Yu, T.D. Webber et al. Improving function and survival of pancreatic islets by endogenous production of glucagon-like peptide 1. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 103, 13468–13473 (2006)
G.E. Fava, E.W. Dong, H. Wu, Intra-islet glucagon-like peptide 1. J. Diabetes Complicat. 30, 1651 (2016)
G.E. Lim, P.L. Brubaker, Glucagon-like peptide 1 secretion by the L-cell: the view from within. Diabetes 55, S70 (2006)
P. Marchetti, R. Lupi, M. Bugliani et al. A local glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) system in human pancreatic islets. Diabetologia 55, 3262–3272 (2012)
Z. Liu, V. Stanojevic, S. Avadhani, T. Yano, J.F. Habener, Stromal cell-derived factor-1 (SDF-1)/chemokine (C-X-C motif) receptor 4 (CXCR4) axis activation induces intra-islet glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) production and enhances beta cell survival. Diabetologia 54, 2067–2076 (2011)
H. Ellingsgaard, I. Hauselmann, B. Schuler et al. Interleukin-6 enhances insulin secretion by increasing glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion from L cells and alpha cells. Nat. Med. 17, 1481–1489 (2011)
K. Timper, E. Dalmas, E. Dror et al. Glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide stimulates glucagon-like peptide 1 production by pancreatic islets via interleukin-6, produced by α cells. Gastroenterology 151, 165 (2016)
R.D. Wideman, I.L. Yu, T.D. Webber et al. Improving function and survival of pancreatic islets by endogenous production of glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1). Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 103, 13468–13473 (2006)
S. Piro, L.G. Mascali, F. Urbano et al. Chronic exposure to GLP-1 increases GLP-1 synthesis and release in a pancreatic alpha cell line (α-TC1): evidence of a direct effect of GLP-1 on pancreatic alpha cells. PLoS ONE 9, e90093 (2014)
G.E. Lim, G.J. Huang, N. Flora et al. Insulin regulates glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion from the enteroendocrine L cell. Endocrinology 150, 580–591 (2008)
B. Domenico, A. Mathieu, M. Philippe et al. Unique arrangement of alpha- and beta-cells in human islets of Langerhans. Diabetes 59, 1202–1210 (2010)
P.J. Lefèbvre, Early milestones in glucagon research. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 13(Suppl. 1), 1–4 (2011)
S. Dhanvantari, N.G. Seidah, P.L. Brubaker, Role of prohormone convertases in the tissue-specific processing of proglucagon. Mol. Endocrinol. 10, 342–355 (1996)
S. Vasu, R.C. Moffett, N.H. McClenaghan, P.R. Flatt, Differential molecular and cellular responses of GLP-1 secreting L-cells and pancreatic alpha cells to glucotoxicity and lipotoxicity. Exp. Cell Res. 336, 100–108 (2015)
R. Takaki, J. Ono, M. Nakamura et al. Isolation of glucagon-secreting cell lines by cloning insulinoma cells. In Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol. 22, 120–126 (1986)
N.M. Whalley, L.E. Pritchard, D.M. Smith et al. Processing of proglucagon to GLP-1 in pancreatic α-cells: is this a paracrine mechanism enabling GLP-1 to act on β-cells? J. Endocrinol. 211, 99–106 (2011)
S. Muntoni, S. Muntoni, Insulin resistance: pathophysiology and rationale for treatment. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 58, 25–36 (2011)
K. Kisanuki, H. Kishikawa, E. Araki et al. Expression of insulin receptor on clonal pancreatic alpha cells and its possible role for insulin-stimulated negative regulation of glucagon secretion. Diabetologia 38, 422–429 (1995)
C.M. Taniguchi, B. Emanuelli, C.R. Kahn, Critical nodes in signalling pathways: insights into insulin action. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 7, 85–96 (2006)
Y. Anini, P.L. Brubaker, Muscarinic receptors control glucagon-like peptide 1 secretion by human endocrine L cells. Endocrinology 144, 3244–3250 (2003)
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81670706 and 81770818), National Special Scientific Research Fund of Public Welfare Profession (No. 201502007), National Key Research and Development Plan (No. 2016YFC0901204).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, P., Song, J., Liu, H. et al. Insulin regulates glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion by pancreatic alpha cells. Endocrine 62, 394–403 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-018-1684-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-018-1684-3