Abstract
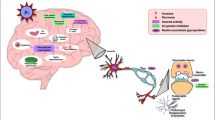
Fluorine, a toxic and reactive element, is widely prevalent throughout the environment and can induce toxicity when absorbed into the body. This study was to explore the possible mechanisms of developmental neurotoxicity in rats treated with different levels of sodium fluoride (NaF). The rats’ intelligence, as well as changes in neuronal morphology, glucose absorption, and functional gene expression within the brain were determined using the Morris water maze test, transmission electron microscopy, small-animal magnetic resonance imaging and Positron emission tomography and computed tomography, and Western blotting techniques. We found that NaF treatment-impaired learning and memory in these rats. Furthermore, NaF caused neuronal degeneration, decreased brain glucose utilization, decreased the protein expression of glucose transporter 1 and glial fibrillary acidic protein, and increased levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in the rat brains. The developmental neurotoxicity of fluoride may be closely associated with low glucose utilization and neurodegenerative changes.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akman, C. I., Ichise, M., Olsavsky, A., Tikofsky, R. S., Van Heertum, R. L., & Gilliam, F. (2010). Epilepsy duration impacts on brain glucose metabolism in temporal lobe epilepsy: Results of voxel-based mapping. Epilepsy & Behavior, 17, 373–380.
Augustin, R. (2010). The protein family of glucose transport facilitators: It’s not only about glucose after all. IUBMB Life, 62, 315–333.
Banks, C. N., & Lein, P. J. (2012). A review of experimental evidence linking neurotoxic organophosphorus compounds and inflammation. Neurotoxicology, 33, 575–584.
Barbier, O., Arreola-Mendoza, L., & Del Razo, L. M. (2010). Molecular mechanisms of fluoride toxicity. Chemico-Biological Interactions, 188, 319–333.
Bartlett, R. M., Murali, D., Nickles, R. J., Barnhart, T. E., Holden, J. E., & DeJesus, O. T. (2011). Assessment of fetal brain uptake of paraquat in utero using in vivo PET/CT imaging. Toxicological Sciences, 122, 551–556.
Basha, P. M., Rai, P., & Begum, S. (2011). Fluoride toxicity and status of serum thyroid hormones, brain histopathology, and learning memory in rats: A multigenerational assessment. Biological Trace Element Research, 144, 1083–1094.
Blaylock, R. L. (2004). Excitotoxicity: A possible central mechanism in fluoride neurotoxicity. Fluoride, 37, 301–314.
Cammarota, M., Bevilaqua, L. R., Rossato, J. I., Lima, R. H., Medina, J. H., & Izquierdo, I. (2008). Parallel memory processing by the CA1 region of the dorsal hippocampus and the basolateral amygdala. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 105, 10279–10284.
Carruthers, A., DeZutter, J., Ganguly, A., & Devaskar, S. U. (2009). Will the original glucose transporter isoform please stand up! American Journal of Physiology-Endocrinology and Metabolism, 297, E836–E848.
Ceccanti, M., Mancinelli, R., Tirassa, P., Laviola, G., Rossi, S., Romeo, M., et al. (2010). Early exposure to ethanol or red wine and long-lasting effects in aged mice. A study on nerve growth factor, brain-derived neurotrophic factor, hepatocyte growth factor, and vascular endothelial growth factor. Neurobiology of Aging, 33, 359–367.
Choi, A. L., Sun, G., Zhang, Y., & Grandjean, P. (2012). Developmental fluoride neurotoxicity: A systematic review and Meta-analysis. Environmental Health Perspectives, 120, 1362–1368.
Cicek, E., Aydin, G., Akdogan, M., & Okutan, H. (2005). Effects of chronic ingestion of sodium fluoride on myocardium in a second generation of rats. Human and Experimental Toxicology, 24, 79–87.
Collins, T. F., Sprando, R. L., Black, T. N., Shackelford, M. E., Olejnik, N., Ames, M. J., et al. (2001). Developmental toxicity of sodium fluoride measured during multiple generations. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 39, 867–876.
Cotman, C. W., Berchtold, N. C., & Christie, L. A. (2007). Exercise builds brain health: Key roles of growth factor cascades and inflammation. Trends in Neurosciences, 30, 464–472.
Cunnane, S., Nugent, S., Roy, M., Courchesne-Loyer, A., Croteau, E., Tremblay, S., et al. (2011). Brain fuel metabolism, aging, and Alzheimer’s disease. Nutrition, 27, 3–20.
Ge, Y., Ning, H., Feng, C., Wang, H., Yan, X., Wang, S., et al. (2006). Apoptosis in brain cells of offspring rats exposed to high fluoride and low iodine. Fluoride, 39, 173–178.
Ge, Y., Niu, R., Zhang, J., & Wang, J. (2011). Proteomic analysis of brain proteins of rats exposed to high fluoride and low iodine. Archives of Toxicology, 85, 27–33.
Greenberg, M. E., Xu, B., Lu, B., & Hempstead, B. L. (2009). New insights in the biology of BDNF synthesis and release: Implications in CNS function. The Journal of Neuroscience, 29, 12764–12767.
Gui, C. Z., Ran, L. Y., Li, J. P., & Guan, Z. Z. (2010). Changes of learning and memory ability and brain nicotinic receptors of rat offspring with coal burning fluorosis. Neurotoxicology and Teratology, 32, 536–541.
Guney, M., Oral, B., Karahan, N., & Mungan, T. (2007). Protective effect of caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE) on fluoride-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in rat endometrium. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology, 24, 86–91.
Harry, G. J., Schmitt, T. J., Gong, Z., Brown, H., Zawia, N., & Evans, H. L. (1996). Lead-induced alterations of glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) in the developing rat brain. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 139, 84–93.
Hassan, H. A., & Yousef, M. I. (2009). Mitigating effects of antioxidant properties of black berry juice on sodium fluoride induced hepatotoxicity and oxidative stress in rats. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 47, 2332–2337.
Heindel, J. J., Bates, H. K., Price, C. J., Marr, M. C., Myers, C. B., & Schwetz, B. A. (1996). Developmental toxicity evaluation of sodium fluoride administered to rats and rabbits in drinking water. Toxicological Sciences, 30, 162–177.
Kurauchi, Y., Hisatsune, A., Isohama, Y., Mishima, S., & Katsuki, H. (2012). Caffeic acid phenethyl ester protects nigral dopaminergic neurons via dual mechanisms involving haem oxygenase-1 and brain-derived neurotrophic factor. British Journal of Pharmacology, 166, 1151–1168.
Marklund, N., Sihver, S., Hovda, D. A., Langstrom, B., Watanabe, Y., Ronquist, G., et al. (2009). Increased cerebral uptake of [18F]fluoro-deoxyglucose but not [1-14C]glucose early following traumatic brain injury in rats. Journal of Neurotrauma, 26, 1281–1293.
Middeldorp, J., & Hol, E. M. (2011). GFAP in health and disease. Progress in Neurobiology, 93, 421–443.
Morris, R. (1984). Developments of a water-maze procedure for studying spatial learning in the rat. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 11, 47–60.
Mullenix, P. J., Denbesten, P. K., Schunior, A., & Kernan, W. J. (1995). Neurotoxicity of sodium fluoride in rats. Neurotoxicology and Teratology, 17, 169–177.
Müller, Y. M. R., Kobus, K., Schatz, J. C., Ammar, D., & Nazari, E. M. (2012). Prenatal lead acetate exposure induces apoptosis and changes GFAP expression during spinal cord development. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 75, 223–229.
Muneer, P. A., Alikunju, S., Szlachetka, A. M., Mercer, A. J., & Haorah, J. (2011a). Ethanol impairs glucose uptake by human astrocytes and neurons: protective effects of acetyl-l-carnitine. International Journal of Physiology, Pathophysiology and Pharmacology, 3, 48–56.
Muneer, P. A., Alikunju, S., Szlachetka, A. M., Murrin, C. L., & Haorah, J. (2011b). Impairment of brain endothelial glucose transporter by methamphetamine causes blood–brain barrier dysfunction. Molecular Neurodegeneration, 6, 1–13.
Niu, R., Sun, Z., Cheng, Z., Li, Z., & Wang, J. (2009). Decreased learning ability and low hippocampus glutamate in offspring rats exposed to fluoride and lead. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology, 28, 254–258.
Pizarro, J. M., Chang, W. E., Bah, M. J., Wright, L. K., Saviolakis, G. A., Alagappan, A., et al. (2012). Repeated exposure to sublethal doses of the organophosphorus compound VX activates BDNF expression in mouse brain. Toxicological Sciences, 126, 497–505.
Rai, A., Maurya, S. K., Khare, P., Srivastava, A., & Bandyopadhyay, S. (2010). Characterization of developmental neurotoxicity of As, Cd, and Pb mixture: Synergistic action of metal mixture in glial and neuronal functions. Toxicological Sciences, 118, 586–601.
Ranpariya, V. L., Parmar, S. K., Sheth, N. R., & Chandrashekhar, V. M. (2012). Neuroprotective activity of Matricaria recutita against fluoride-induced stress in rats. Pharmaceutical Biology, 49, 696–701.
Reddy, P. Y., Reddy, K. P., & Kumar, K. P. (2011). Neurodegenerative changes in different regions of brain, spinal cord and sciatic nerve of rats treated with sodium fluoride. Journal of Medical and Allied Sciences, 1, 30–35.
Rocha-Amador, D., Navarro, M. E., Carrizales, L., Morales, R., & Calderón, J. (2007). Decreased intelligence in children and exposure to fluoride and arsenic in drinking water. Cadernos de Saúde Pública, 23, S579–S587.
Sharma, R., Tsuchiya, M., & Bartlett, J. D. (2008). Fluoride induces endoplasmic reticulum stress and inhibits protein synthesis and secretion. Environmental Health Perspectives, 116, 1142–1146.
Smith, M. A., Riby, L. M., Eekelen, J. A., & Foster, J. K. (2011). Glucose enhancement of human memory: a comprehensive research review of the glucose memory facilitation effect. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 35, 770–783.
Strużyñska, L., Bubko, I., Walski, M., & Rafałowska, U. (2001). Astroglial reaction during the early phase of acute lead toxicity in the adult rat brain. Toxicology, 165, 121–131.
Turnbull, D. H., & Mori, S. (2007). MRI in mouse developmental biology. NMR in Biomedicine, 20, 265–274.
Valdez-Jimenez, L., Soria Fregozo, C., Miranda Beltran, M. L., Gutierrez Coronado, O., & Perez Vega, M. I. (2010). Effects of the fluoride on the central nervous system. Neurologia, 26, 297–300.
Van der Jeugd, A., Ahmed, T., Burnouf, S., Belarbi, K., Hamdame, M., Grosjean, M. E., et al. (2011). Hippocampal tauopathy in tau transgenic mice coincides with impaired hippocampus-dependent learning and memory, and attenuated late-phase long-term depression of synaptic transmission. Neurobiology of Learning and Memory, 95, 296–304.
Vann, S. D., & Albasser, M. M. (2011). Hippocampus and neocortex: Recognition and spatial memory. Current Opinion in Neurobiology, 21, 440–445.
Wang, X., Song, X., Takata, T., Miichi, Y., Yokono, K., & Sakurai, T. (2010). Amyloid-beta neurotoxicity restricts glucose window for neuronal survival in rat hippocampal slice cultures. Experimental Gerontology, 45, 904–908.
Wu, X., Chen, P. S., Dallas, S., Wilson, B., Block, M. L., Wang, C. C., et al. (2008). Histone deacetylase inhibitors up-regulate astrocyte GDNF and BDNF gene transcription and protect dopaminergic neurons. The International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology, 11, 1123–1134.
Xia, Y., Eberl, S., Wen, L., Fulham, M., & Feng, D. D. (2011). Dual-modality brain PET-CT image segmentation based on adaptive use of functional and anatomical information. Computerized Medical Imaging and Graphics, 36, 47–53.
Zhang, J., Mitsis, E. M., Chu, K., Newmark, R. E., Hazlett, E. A., & Buchsbaum, M. S. (2010). Statistical parametric mapping and cluster counting analysis of [18F] FDG-PET imaging in traumatic brain injury. Journal of Neurotrauma, 27, 35–49.
Zhang, M., Wang, A., He, W., He, P., Xu, B., Xia, T., et al. (2007). Effects of fluoride on the expression of NCAM, oxidative stress, and apoptosis in primary cultured hippocampal neurons. Toxicology, 236, 208–216.
Zhang, J., Zhu, W. J., Xu, X. H., & Zhang, Z. G. (2011). Effect of fluoride on calcium ion concentration and expression of nuclear transcription factor kappa-B ρ65 in rat hippocampus. Experimental and Toxicologic Pathology, 63, 407–411.
Zlokovic, B. V. (2008). The blood–brain barrier in health and chronic neurodegenerative disorders. Neuron, 57, 178–201.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Grants from the National Nature Science Foundation of China (Nos. 81273021, 81072266, and 30972555) and the Foundation in the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (2010DFB30530).
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Chunyang Jiang and Shun Zhang have contributed equally to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, C., Zhang, S., Liu, H. et al. Low Glucose Utilization and Neurodegenerative Changes Caused by Sodium Fluoride Exposure in Rat’s Developmental Brain. Neuromol Med 16, 94–105 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-013-8260-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-013-8260-z