Abstract
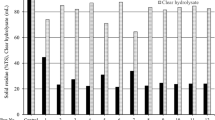
Liquid hot water (LHW) pretreatment is an efficient chemical-free strategy for enhancing enzymatic digestibility of lignocellulosic biomass for conversion to fuels and chemicals in biorefinery. In this study, effects of LHW on removals of hemicelluloses and lignin from corncobs were studied under varying reaction conditions. LHW pretreatment at 160 °C for 10 min promoted the highest levels of hemicellulose solubilization into the liquid phase, resulting into the maximized pentose yield of 58.8% in the liquid and more than 60% removal of lignin from the solid, with 73.1% glucose recovery from enzymatic hydrolysis of the pretreated biomass using 10 FPU/g Celluclast™. This led to the maximal glucose and pentose recoveries of 81.9 and 71.2%, respectively, when combining sugars from the liquid phase from LHW and hydrolysis of the solid. Scanning electron microscopy revealed disruption of the intact biomass structure allowing increasing enzyme’s accessibility to the cellulose microfibers which showed higher crystallinity index compared to the native biomass as shown by x-ray diffraction with a marked increase in surface area as revealed by BET measurement. The work provides an insight into effects of LHW on modification of physicochemical properties of corncobs and an efficient approach for its processing in biorefinery industry.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cara, C., Ruiz, E., Ballesteros, I., Negro, M. J., & Castro, E. (2006). Enhanced enzymatic hydrolysis of olive tree wood by steam explosion and alkaline peroxide delignification. Process Biochemistry, 41(2), 423–429.
Marsran, R., Zanirun, Z., Bahrin, E. K., Ibrahim, M. F., Yee, P. L., & Abd-Aziz, S. (2016). Harnessing the potential of ligninolytic enzymes for lignocellulosic biomass pretreatment. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 100(12), 5231–5246.
Sharma, A., Tewar, R., Rana, S. S., Sono, R., & Soni, S. K. (2016). Cellulases: classification, methods of determination and industrial applications. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 179(8), 1346–1380.
Rabemanolontsoa, H. (2016). Various pretreatments of lignocellulosics. Bioresource Technology, 199, 83–91.
Hendricks, A. T. W. M., & Zeema, G. (2009). Pretreatments to enhance the digestibility of lignocellulosic biomass. Bioresource Technology, 100(1), 10–28.
Yuksel, A. (2013). Hydrothermal degradation of Congo red in hot compressed water and its kinetics. Chemical Engineering and Processing, 4(9), 1–9.
Plaza, M., & Turner, C. (2015). Pressurized hot water extraction of bioactives. Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 71, 39–54.
Imman, S., Arnthong, J., Burapatana, V., Laosiripojana, N., & Champreda, V. (2014). Influence of alkaline catalyst addition on compressed liquid hot water pretreatment of rice straw. Chemical Engineering Journal, 278, 85–91.
Imman, S., Arnthong, J., Burapatana, V., Laosiripojana, N., & Champreda, V. (2015). Effects of acid and alkali promoters on compressed liquid hot water pretreatment of rice straw. Bioresource Technology, 171, 29–36.
Wanitwattanarumlug, B., Luengnaruemitchai, A., & Wongkasemjit, S. (2012). Characterization of corn cobs from microwave and potassium hydroxide pretreatment. International Journal of Innovative Research in Science Engineering, 6(4), 327–331.
Sahare, P., Singh, R., Laxman, R. S., & Rao, M. (2012). Effect of alkali pretreatment on the structural properties and enzymatic hydrolysis of corn cob. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 168(7), 1806–1819.
Bu, L., Xing, Y., Yu, H., Gao, Y., & Jiang, J. (2012). Comparative study of sulfite pretreatment for robust enzymatic saccharification of corn cob residue. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 5(87), 2–8.
Zhang, X., Yuan, Q., & Cheng, G. (2017). Deconstruction of corncob by steam explosion pretreatment: correlations between sugar conversion and recalcitrant structures. Carbohydrate Polymers, 156, 351–356.
Liu, Y., Luo, P., Xu, Q., Wang, E., & Yin, J. (2012). Investigation of the effect of supercritical carbon dioxide pretreatment on reducing sugar yield of lignocellulose hydrolysis. Cellulose Chemistry and Technology, 48(1–2), 89–95.
Sluiter, A., Hames, B., Ruiz, R., Scarlata, C., Sluiter, J., Templeton, D., & Crocker, D. (2004). Laboratory Analytical Procedure (LAP). Denver: The National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL).
Adney, B., & Baker, J. (1996). Measurement of cellulase activities, chemical analysis and testing task. In Laboratory Analytical procedure LAP-006. Denver: The National Renewable Energy Laboraory (NREL).
Ruiz, H. A., Silva, D. P., Ruzene, D. S., Lima, L. F., Vicente, A. A., & Teixeira, J. A. (2012). Bioethanol production from thermal pretreated wheat straw by a flocculating Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain—effect of process conditions. Fuel, 95, 528–536.
Wan, C., & Li, Y. (2011). Effectiveness of microbial pretreatment by Ceriporiopsis subvermispora on different biomass feedstocks. Bioresource Technology, 102(16), 7507–75123.
Sindhu, R., Kuttiraja, M., Binod, P., Janu, K. U., Sukumara, R. J., & Pandey, A. (2011). Dilute acid pretreatment and enzymatic saccharification of sugarcane tops for bioethanol production. Bioresource Technology, 102(23), 10915–10921.
Kim, Y., Ximenes, N. S., & Ladisch, M. R. (2011). Soluble inhibitors/deactivators of cellulose enzymes from lignocellulosic biomass. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 48(4–5), 408–415.
Yu, Q., Zhuang, X., Yuan, Z., Wang, Q., Qi, W., Wang, Q., & Tan, X. (2011). Step-change flow rate liquid hot water pretreatment of sweet sorghum bagasse for enhancement of total sugars recovery. Applied Energy, 88(7), 2472–2479.
Zhuang, X., Yu, Q., Wang, W., Qi, W., Wang, Q., Tan, X., & Yuan, Z. (2012). Decomposition behavior of hemicellulose and lignin in the step-change flow rate liquid hot water. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 168(1), 206–218.
Sanchez, B., & Bautista, J. (1988). Effect of furfural and 5-hydroxymethylfurfural on the fermentation on saccharomyces cervisiae and biomass products Candida guilliermondii. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 10, 315–318.
Zeng, M., Mosier, N. S., Huang, C. P., Sherman, D. M., & Ladisch, M. R. (2007). Microsopic examination of changes of plant cell in corn stover due to hot water pretreatment and enzymatic hydrolysis. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 97(2), 265–278.
Yu, G., Yano, S., Inoue, H., Inoue, S., Endo, T., & Sawayama, S. (2010). Pretreatment of rice straw by a hot-compressed water process for enzymatic hydrolysis. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 160, 539–551.
Imman, S., Arnthong, J., Burapatana, V., Laosiripojana, N., & Champreda, V. (2013). Autohydrolysis of tropical agricultural residues by compressed liquid hot water pretreatment. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 170(8), 1982–1995.
Kim, T. H., Kim, J. S., Sunwoo, C., & Lee, Y. Y. (2003). Pretreatment of corn stover by aqueous ammonia. Bioresource Technology, 90(1), 39–47.
Cheng, K. K., Wang, W., Zhang, J. A., Zhao, Q., Li, J. P., & Xue, J. W. (2011). Statistical optimization of sulfite pretreatment of corncob residues for high concentration ethanol production. Bioresource Technology, 102, 3014–3019.
Cai, B. Y., Ge, J. P., Ling, H. Z., Cheng, K. K., & Pin, W. X. (2012). Statistical optimization of dilute sulfuric acid pretreatment of corncob for xylose recovery and ethanol production. Biomass & Bioenergy, 36, 250–257.
Satimanont, S., Luengnaruemitchai, A., & Wongkasemjit, S. (2012). Effect of temperature and time on dilute acid pretreatment of corn cobs. International journal of chemical, molecular, Nuclear. Materials and Metallurgical Engineering, 6(4), 316–320.
Guo, X., Zhang, T., Shu, S., Zheng, W., & Gao, M. (2017). Compositional and structural changes of corn cob pretreated by electron beam irradiation. Sustainable Chemistry and Engineering., 5, 420–425.
Procentese, A., Johnson, E., Or, V., Campanile, A. G., Wood, A. J., Marzocchella, A., & Rehmann, L. (2016). Deep eutectic solvent pretreatment and subsequent saccharification of corncob. Bioresource Technology, 192, 31–36.
Alvira, P., Tomas-Pejo, E., Ballesteros, M., & Negro, M. J. (2010). Pretreatment technologies for an efficient bioethanol production process based on enzymatic hydrolysis: a review. Bioresource Technology, 101(13), 4851–4861.
Li, H., Chen, X., Ren, J., Deng, H., Peng, F., & Sun, R. (2015). Functional relationship of furfural yields and the hemicellulose-derived sugars in the hydrolysates from corncob by microwave-assisted hydrothermal pretreatment. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 8, 127. doi:10.1186/s13068-015-0314-z.
Acknowledgments
This project was financially supported by research grants from the Thailand Research Fund and the Office of the Higher Education Commission (MRG6080162). N.L. was supported by a research grant (RTA 598006) from the Thailand Research Fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Imman, S., Laosiripojana, N. & Champreda, V. Effects of Liquid Hot Water Pretreatment on Enzymatic Hydrolysis and Physicochemical Changes of Corncobs. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 184, 432–443 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-017-2541-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-017-2541-1