Abstract
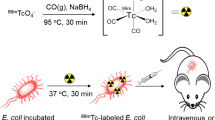
Bacterial infection is one of the vital reasons of morbidity and mortality, especially in developing countries. It appears silently without bothering the geological borders and imposes a grave threat to humanity. Nuclear medicine technique has an important role in helping early diagnosis of deep-seated infections. The aim of this study was to develop a new radiopharmaceutical 99mTc-labeling sulfadiazine as an infection imaging agent. Radiolabeling of sulfadiazine with technetium-99m (99mTc) was carried out using stannous tartrate as a reducing agent in the presence of gentistic acid at pH = 5. The quality control tests revealed ~98% labeling efficiency. Paper chromatographic (PC) and instant thin-layer chromatographic (ITLC) techniques were used to analyze radiochemical yield. Biodistribution and infection specificity of the radiotracer were performed with Escherichia coli (E. coli) infection-induced rats. Scintigraphy and glomerular filtration rate (GFR) study was performed in E. coli-infected rabbits. Scintigraphy indicated E. coli infection targeting potential of 99mTc-SDZ, while biodistribution study showed minimal uptake of 99mTc-SDZ in non-targeted tissues. The uptake in the kidneys was found 2.56 ± 0.06, 2.09 ± 0.10, and 1.68 ± 0.09% at 30 min, 1 h, and 4 h, respectively. The infected muscle (target) to non-infected muscle (non-target) ratio (T/NT) was found 4.49 ± 0.04, 6.78 ± 0.07, and 5.59 ± 0.08 at 30 min, 1 h, and 4 h, respectively.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al Amiry, A. (2015). Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: an occupational health hazard in the prehospital setting. J. Acute. Dis., 4, 274–276.
Morens, D. M., & Fauci, A. S. (2013). Emerging infectious diseases: threats to human health and global stability. PLoS Pathogens, 9, e1003467.
De Winter, F., Van de Wiele, C., Dumont, F., Van Durme, J., Solanki, K., Britton, K., Slegers, G., Dierckx, R. A., & Thierens, H. (2001). Biodistribution and dosimetry of 99mTc-ciprofloxacin, a promising agent for the diagnosis of bacterial infection. European Journal of Nuclear Medicine, 28, 570–574.
Siaens, R. H., Rennen, H. J., Boerman, O. C., Dierckx, R., & Slegers, G. (2004). Synthesis and comparison of 99mTc-enrofloxacin and 99mTc-ciprofloxacin. Journal of Nuclear Medicine, 45, 2088–2094.
Qaiser, S. S., Khan, A. U., & Khan, M. R. (2010). Synthesis, biodistribution and evaluation of 99mTc-sitafloxacin kit: a novel infection imaging agent. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 284, 189–193.
Motaleb, M. A., El-Kolaly, M. T., Ibrahim, A. B., & Abd El-Bary, A. (2011). Study on the preparation and biological evaluation of 99mTc–gatifloxacin and 99mTc–cefepime complexes. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 289, 57–65.
El-Tawoosy, M. (2013). Preparation and biological distribution of 99mTc-cefazolin complex, a novel agent for detecting sites of infection. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 298, 1215–1220.
Mirshojaei, S. F. (2015). Advances in infectious foci imaging using 99mTc radiolabelled antibiotics. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 304, 975–988.
Auletta, S., Galli, F., Lauri, C., Martinelli, D., Santino, I., & Signore, A. (2016). Imaging bacteria with radiolabelled quinolones, cephalosporins and siderophores for imaging infection: a systematic review. Clin. Transl. Imaging., 4, 229–252.
Akbar, M. U., Ahmad, M. R., Shaheen, A., & Mushtaq, S. (2016). A review on evaluation of technetium-99m labeled radiopharmaceuticals. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 310, 477–493.
Sharma, P., Thakur, S., & Awasthi, P. (2015). Synthesis, characterization, biological evaluation and docking study of heterocyclic-based synthetic sulfonamides as potential pesticide against G. mellonella. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 176, 125–139.
Levey, A. S., Greene, T., Schluchter, M. D., Cleary, P. A., Teschan, P. E., Lorenz, R. A., Molitch, M. E., Mitch, W. E., Siebert, C., Hall, P. M., Steffes, M. W., for the Modification of Diet in Renal Disease Study, G, & the Diabetes, C and Complications Trial Research, G. (1993). Glomerular filtration rate measurements in clinical trials. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology, 4, 1159–1171.
Shah, S. Q., & Khan, M. R. (2011). Radiolabeling of gemifloxacin with technetium-99m and biological evaluation in artificially Streptococcus pneumoniae infected rats. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 288, 307–312.
Iglesias, F., Roca, M., Martín-Comín, J., Tubau, F., & Barreto, V. G. (2000). Marcaje de ceftizoxima con 99mTc. Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear., 19, 479–483.
Roohi, S., Mushtaq, A., Jehangir, M., & Malik, S. A. (2006). Synthesis, quality control and biodistribution of 99mTc-kanamycin. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 267, 561–566.
Mirshojaei, S. F., Gandomkar, M., Najafi, R., Sadat Ebrahimi, S. E., Babaei, M. H., Shafiei, A., & Talebi, M. H. (2011). Radio labeling, quality control and biodistribution of 99mTc-cefotaxime as an infection imaging agent. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 287, 21–25.
Essouissi, I., Darghoutha, F., Saied, N. M., Saidi, M., Kanoun, A., & Saidi, M. (2015). Radiolabeling, quality control, and biodistribution of 99mTc-sulfadiazine as an infection imaging agent. Radiochemistry, 57, 307–311.
Erfani, M., Rekabgardan, M., Mortazavi, P., & Shafiei, M. (2016). Radiocomplexation and evaluation of the 99mTc-gemifloxacin in artificially Escherichia coli infected mice. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 308, 825–833.
Amin, A. M., Ibrahim, I. T., Attallah, K. M., & Ali, S. M. (2014). 99mTc-sulfadimidine as a potential radioligand for differentiation between septic and aseptic inflammations. Radiochemistry, 56, 72–75.
Chattopadhyay, S., Ghosh, M., Sett, S., Das, M. K., Chandra, S., De, K., Mishra, M., Sinha, S., Ranjan Sarkar, B., & Ganguly, S. (2012). Preparation and evaluation of 99mTc-cefuroxime, a potential infection specific imaging agent: a reliable thin layer chromatographic system to delineate impurities from the 99mTc-antibiotic. App. Rad. Isotop., 70, 2384–2387.
Fazli, A., Salouti, M., Ahmadi, G., Mirshojaei, F., Mazidi, M., & Heydari, Z. (2012). Radiolabeling of ceftriaxone with 99mTc as a targeting radiopharmaceutical for Staphylococcus aureus detection in mouse model. Iran. J. Med. Phy., 9, 103–110.
Sanad, M. H., & Borai, E. (2014). Performance characteristics of biodistribution of 99mTc-cefprozil for in vivo infection imaging. J. Anal. Sci. Tech., 5, 32.
Hina, S., Rajoka, M. I., Roohi, S., Haque, A., & Qasim, M. (2014). Preparation, biodistribution, and scintigraphic evaluation of 99mTc-clindamycin: an infection imaging agent. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 174, 1420–1433.
Sanad, M. H. (2013). Labeling and biological evaluation of 99mTc-azithromycin for infective inflammation diagnosis. Radiochemistry, 55, 539–544.
Rasheed, R., Tariq, S., Naqvi, S. A. R., Gillani, S. J. H., Rizvi, F. A., Sajid, M., & Rasheed, S. (2016). 177Lu-5-fluorouracil a potential theranostic radiopharmaceutical: radiosynthesis, quality control, biodistribution, and scintigraphy. J. Label. Comp. Radiopharm., 59, 398–403.
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the Higher Education Commission (HEC), Islamabad, Pakistan, for providing funds (No. 20-3413/NRPU/R&D/HEC/2014/702) for the development of radiopharmaceuticals and promoting the research culture in Pakistan. The authors are also thankful to Director INOR, Abbottabad for providing the lab and SPECT camera facility.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmed, M.T., Naqvi, S.A.R., Rasheed, R. et al. Technetium-99m-Labeled Sulfadiazine: a Targeting Radiopharmaceutical for Scintigraphic Imaging of Infectious Foci Due To Escherichia coli in Mouse and Rabbit Models. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 183, 374–384 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-017-2451-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-017-2451-2