Abstract
Purpose of Review
We aimed to review the sleep disorders described in Wilson’s disease (WD), focusing on their mechanisms and treatments.
Recent Findings
REM sleep behavior disorder or sleepiness can be warning signs of future WD. These early symptoms may significantly reduce the time to WD diagnosis. Early anti-copper therapies (chelators or zinc salts), reducing copper accumulation in the brain and though saving brain tissue, can allow the complete disappearance of these sleep disorders and of course improve the other symptoms of WD.
Summary
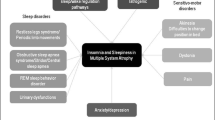
Insomnia, restless legs syndrome (RLS), daytime sleepiness, cataplexy, and REM sleep behavior disorder (RBD) are present in WD and should be explored with video polysomnography and multiple sleep latency test. Suggested immobilization test could be useful in the diagnosis of RLS in WD. Motor and non-motor symptoms, dysautonomic dysfunctions, drugs, and lesions of the circuits regulating wake and sleep may be involved in the mechanisms of these sleep abnormalities. Adapted treatments should be proposed.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
Dusek P, Litwin T, Członkowska A. Neurologic impairment in Wilson disease. Ann Transl Med. 2019;7(Suppl 2):S64.
• Członkowska A, Litwin T, Chabik G. Wilson disease. neurologic features. Handb Clin Neurol. 2017;142:101–19 A comprehensive review of the neurological presentations in WD.
Zimbrean P, Seniów J. Cognitive and psychiatric symptoms in Wilson disease. Handbook of Clinical Neurology. 2017;142:121–40.
Poujois A, Woimant F. Wilson’s disease: A 2017 update. Clinics and research in hepatology and gastroenterology. 2018.Elsevier Masson SAS; 2018;42:512–520.
Lo C, Bandmann O. Epidemiology and introduction to the clinical presentation of Wilson disease. In: Handbook of Clinical Neurology. Elsevier; 2017;142:7–17.
Oder W, Prayer L, Grimm G, Spatt J, Ferenci P, Kollegger H, et al. Wilson’s disease: evidence of subgroups derived from clinical findings and brain lesions. Neurology. 1993;43:120–0.
• Poujois A, Mikol J, Woimant F. Wilson disease: brain pathology. Handb Clin Neurol. 2017;142:77–89 A detailed review of normal and pathological copper deposition in the brain and the specificity of WD.
Giagheddu M, Tamburini G, Piga M, Tacconi P, Giagheddu A, Serra A, et al. Comparison of MRI, EEG, EPs and ECD-SPECT in Wilson’s disease. Acta Neurol Scand. 2001;103:71–81.
Biswas S, Paul N, Das SK. Nonmotor manifestations of Wilson’s disease. International Review of Neurobiology. 2017:1443–59.
Portala K, Westermark K, Ekselius L, Broman J-E. Sleep in patients with treated Wilson’s disease. A questionnaire study. Nord J Psychiatry. 2002;56:291–7.
•• Nevsimalova S, Buskova J, Bruha R, Kemlink D, Sonka K, Vitek L, et al. Sleep disorders in Wilson’s disease. Eur J Neurol. 2011;18:184–90 The only study on sleep disorders in WD with objective measures on sleepiness.
Netto A, Sinha S, Taly A, Panda S. Sleep in Wilson’s disease: questionnaire based study. Ann Indian Acad Neurol. 2011;14:31–4.
•• Trindade MC, Bittencourt T, Lorenzi-Filho G, Alves RC, de Andrade DC, Fonoff ET, et al. Restless legs syndrome in Wilson’s disease: frequency, characteristics, and mimics. Acta Neurol Scand. 2017;135:211–8 Interesting study focusing on RLS in WD.
Tribl GG, Bor-Seng-Shu E, Trindade MC, Lucato LT, Teixeira MJ, Barbosa ER. Wilson’s disease presenting as rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder: a possible window to early treatment. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2014;72:653–8.
Netto A, Sinha S, Taly A, Panda S, Rao S. Sleep in Wilson’s disease: a polysomnography-based study. Neurol India. 2010;58:933.
American Academy of Sleep Medicine. American Academy of Sleep Medicine. 3rd ed. Westchester, IL: International Classification of Sleep Disorders; 2014.
Tribl GG, Trindade MC, Bittencourt T, Lorenzi-Filho G, Cardoso Alves R, Ciampi de Andrade D, et al. Wilson’s disease with and without rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder compared to healthy matched controls. Sleep Med. 2016;17:179–85.
Litwin T, Dusek P, Szafrański T, Dzieżyc K, Członkowska A, Rybakowski J. Psychiatric manifestations in Wilson’s disease: possibilities and difficulties for treatment. Ther Adv. 2018;8:199–211.
Dening TR, Berrios GE. Wilson’s disease: psychiatric symptoms in 195 cases. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1989;46:1126–34.
Shanmugiah A, Sinha S, Taly AB, Prashanth LK, Tomar M, Arunodaya GR, et al. Psychiatric manifestations in Wilson’s disease: a cross-sectional analysis. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2008;20:81–5.
Guillaud O, Dumortier J, Sobesky R, Debray D, Wolf P, Vanlemmens C. Long term results of liver transplantation for Wilson’s disease: experience in France. J Hepatol. 2014;60:579–89.
Laurencin C, Brunet A-S, Dumortier J, Lion-François L, Thobois S, Mabrut J. Liver Transplantation in Wilson’s disease with neurological impairment: evaluation in 4 patients. Eur Neurol. 2017;77:5–15.
Tarter R, Van Thiel D, Hegedus A, Schade R, Gavaler J, Starzl T. Neuropsychiatric status after liver transplantation. J Lab Clin Med. 1984;103:776–82.
Bergonzi P, Chiurulla C. Cianchetti et al. Clinical pharmacology as an approach to the study of biochemical sleep mechanisms: the action of l-dopa. Conflin Neurol. 1974;36:5–22.
Scheiber I, Mercer J, Dringen R. Metabolism and functions of copper in brain. Prog Neurobiol. 2014;116:33–57.
Huang Z, Deng J, Borjigin J. A novel H28Y mutation in LEC rats leads to decreased NAT protein stability in vivo and in vitro. J Pineal Res. 2005;39:84–90.
Borjigin J, Payne A, Deng J, Li X, Wang M, Ovodenko B. A novel pineal night-specific ATPase encoded by the Wilson disease gene. J Neurosci. 1999;19:1018–26.
De Cruz S, Espiritu J, Zeidler M, Wang T. Sleep disorders in chronic liver disease. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2012;33:26–35.
Johns MW. A new method for measuring daytime sleepiness: the Epworth sleepiness scale. Sleep. 1991;14:540–5.
Roth T, Roehrs TA. Measurement of sleepiness and alertness: multiple sleep latency test. In: Sleep Disorders Medicine. 2009: 218–23.
Firneisz G, Szlay F, Halasz P, Komoly S. Hypersomnia in Wilson’s disease: an unusual symtom in an unusual case. Acta Neurol Scand. 2000;101:286–8.
Amann VC, Maru NK, Jain V. Hypersomnolence in Wilson disease. J Clin Sleep Med. 2015;11:1341–3.
Allen RP, Picchietti DL, Garcia-Borreguero D, Ondo WG, Walters AS, Winkelman JW, et al. Restless legs syndrome/Willis-Ekbom disease diagnostic criteria: updated International Restless Legs Syndrome Study Group (IRLSSG) consensus criteria - history, rationale, description, and significance. Sleep Med. 2014;15:860–73.
Walters AS, LeBrocq C, Dhar A, Hening W, Rosen R, Allen RP, et al. Validation of the International Restless Legs Syndrome Study Group rating scale for restless legs syndrome. Sleep Med. 2003;4:121–32.
Bandmann O, Weiss KH, Kaler SG. Wilson’s disease and other neurological copper disorders. The Lancet Neurology. 2015;14:103–13 * A complete and thorough review of WD.
Papapetripoulos S, Singer C. Painless legs moving toes in a patient with Wilson’s disease. Mov Disord. 2006;21:579–80.
De Cock VC, Bayard S, Yu H, Grini M, Carlander B, Postuma R, et al. Suggested immobilization test for diagnosis of restless legs syndrome in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord. 2012;27:743–9.
Earley CJ, Connor J, Garcia-Borreguero D, Jenner P, Winkelman J, Zee PC, et al. Altered brain iron homeostasis and dopaminergic function in restless legs syndrome (Willis-Ekbom Disease). Sleep Medicine. 2014;15:1288–301.
Connor JR, Wang XS, Allen RP, Beard JL, Wiesinger JA, Felt BT, et al. Altered dopaminergic profile in the putamen and substantia nigra in restless leg syndrome. Brain. 2009;132:2403–12.
Pittock SJ, Parrett T, Adler CH, Parisi JE, Dickson DW, Ahlskog JE. Neuropathology of primary restless leg syndrome: absence of specific??- and??-synuclein pathology. Mov Disord. 2004;19:695–699.
Barthel H, Hermann W, Kluge R, Hesse S, Collingridge DR, Wagner A, et al. Concordant pre- and postsynaptic deficits of dopaminergic neurotransmission in neurologic Wilson disease. Am J Neuroradiol. 2003;24:234–8.
Dusek P, Bahn E, Litwin T, Jabłonka-Salach K, Łuciuk A, Huelnhagen T, et al. Brain iron accumulation in Wilson disease: a post mortem 7 Tesla MRI - histopathological study. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2017;43:514–32.
Schenck CH, Mahowald MW. REM sleep behavior disorder: clinical, developmental, and neuroscience perspectives 16 years after its formal identification in SLEEP. Sleep [Internet. 2002;25:120–38.
Comella CL, Nardine TM, Diederich NJ, Stebbins GT. Sleep-related violence, injury, and REM sleep behavior disorder in Parkinson’s disease. 1998;51:526–529.
Litwin T, Dusek P, Członkowska A. Symptomatic treatment of neurologic symptoms in Wilson disease. Handb Clin Neurol. 2017;142:211–23.
Zimbrean P, Schilsky M. The spectrum of psychiatric symptoms in Wilson’s disease: treatment and prognostic considerations. AmJ Psychiatry. 2015;172:1068–72.
Kunz D, Bes F. Melatonin effects in a patient with severe REM sleep behavior disorder: case report and theoretical considerations. Neuropsychobiology. 1997;36:211–4.
Nishino S, Ripley B, Overeem S, Lammers GJ, Mignot E. Hypocretin (orexin) deficiency in human narcolepsy. Lancet. 2000;355:39–40.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Valérie Cochen De Cock, France Woimant, and Aurélia Poujois each declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
All the studies have already been published and follow ethical standards.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of Topical Collection on Sleep
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cochen De Cock, V., Woimant, F. & Poujois, A. Sleep Disorders in Wilson’s Disease. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep 19, 84 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11910-019-1001-4
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11910-019-1001-4