Abstract
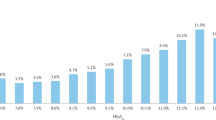
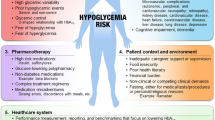
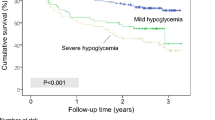
Hypoglycemia is one of the major barriers in optimizing glycemic control. In type 2 diabetes, hypoglycemia is associated with multiple morbidities (eg, myocardial ischemia, cardiac arrhythmia, stroke, dementia, psychosocial dysfunction, obesity, microvascular complications, cancer, and diseases of respiratory, digestive, and dermatological systems). Risk factors associated with hypoglycemia in patients with type 2 diabetes include old age, long disease duration, low body mass index, high baseline glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c), treatment with insulin and sulphonylurea, renal dysfunction, albuminuria, reduced level of low density lipoprotein cholesterol, low triglyceride and depression. There are considerable overlaps between phenotypes associated with severe hypoglycemia and all-site cancer suggesting that hypoglycemia may be a marker of vulnerability. In patients with severe hypoglycemia, comprehensive assessment is recommended to detect silent conditions, such as renal dysfunction, cancer, depression as well as review of treatment strategies including drug use to prevent morbidities and mortality.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
UKPDS. Intensive blood glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 33). Lancet. 1998;352:837–53.
Ohkubo Y, Kishikawa H, Araki E, et al. Intensive insulin therapy prevents the progression of diabetic microvascular complications in Japanese patients with NIDDM: a randomised prospective 6-year study. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 1995;28:103–17.
Holman RR, Paul SK, Bethel MA, Matthews DR, Neil HA. Ten-year follow-up of intensive glucose control in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2008;359(15):1577–89.
Patel A, MacMahon S, Chalmers J, et al. Intensive blood glucose control and vascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2008;358(24):2560–72.
Gerstein HC, Miller ME, Byington RP, et al. Effects of intensive glucose lowering in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2008;358(24):2545–59.
Patel A, MacMahon S, Chalmers J, et al. Effects of a fixed combination of perindopril and indapamide on macrovascular and microvascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (the ADVANCE trial): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2007;370(9590):829–40.
Duckworth W, Abraira C, Moritz T, et al. Glucose control and vascular complications in veterans with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2009;360(2):129–39.
Bonds DE, Miller ME, Bergenstal RM, et al. The association between symptomatic, severe hypoglycaemia and mortality in type 2 diabetes: retrospective epidemiological analysis of the ACCORD study. BMJ. 2010;340:b4909.
Skyler JS, Bergenstal R, Bonow RO, et al. Intensive glycemic control and the prevention of cardiovascular events: implications of the ACCORD, ADVANCE, and VA diabetes trials: a position statement of the American Diabetes Association and a scientific statement of the American College of Cardiology Foundation and the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2009;119(2):351–7.
Zoungas S, Patel A, Chalmers J, et al. Severe hypoglycemia and risks of vascular events and death. N Engl J Med. 2010;363(15):1410–8.
Wright RJ, Frier BM. Vascular disease and diabetes: is hypoglycaemia an aggravating factor? Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2008;24(5):353–63.
Desouza C, Salazar H, Cheong B, Murgo J, Fonseca V. Association of hypoglycemia and cardiac ischemia: a study based on continuous monitoring. Diabetes Care. 2003;26(5):1485–9.
Desouza CV, Bolli GB, Fonseca V. Hypoglycemia, diabetes, and cardiovascular events. Diabetes Care. 2010;33(6):1389–94.
Chow E, Bernjak A, Williams S, et al. Risk of cardiac arrhythmias during hypoglycemia in patients with type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular risk. Diabetes. 2014;63(5):1738–47.
Hoffman RP. Sympathetic mechanisms of hypoglycemic counterregulation. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2007;3(3):185–93.
Nordin C. The proarrhythmic effect of hypoglycemia: evidence for increased risk from ischemia and bradycardia. Acta Diabetol. 2014;51(1):5–14.
Shih CJ, Wu YL, Lo YH, et al. Association of hypoglycemia with incident chronic kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetes: a nationwide population-based study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015;94(16), e771.
Hsu PF, Sung SH, Cheng HM, et al. Association of clinical symptomatic hypoglycemia with cardiovascular events and total mortality in type 2 diabetes: a nationwide population-based study. Diabetes Care. 2013;36(4):894–900.
Kong AP, Yang X, Luk A, et al. Severe hypoglycemia identifies vulnerable patients with type 2 diabetes at risk for premature death and all-site cancer: the Hong Kong Diabetes Registry. Diabetes Care. 2014;37:1–8. This study highlights the overlaps between phenotypes associated with cancer and hypoglycemia in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Kong AP, Chan JC. Cancer risk in type 2 diabetes. Curr Diabetes Rep. 2012;12(4):325–8.
Harding JL, Shaw JE, Peeters A, Cartensen B, Magliano DJ. Cancer risk among people with type 1 and type 2 diabetes: disentangling true associations, detection bias, and reverse causation. Diabetes Care. 2015;38(2):264–70.
Yang X, Lee HM, Chan JC. Drug-subphenotype interactions for cancer in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2015;11(6):372–9.
Schrijvers BF, De Vriese AS, Flyvbjerg A. From hyperglycemia to diabetic kidney disease: the role of metabolic, hemodynamic, intracellular factors and growth factors/cytokines. Endocr Rev. 2004;25(6):971–1010.
Yang XL, Ma RC, So WY, Kong AP, Xu G, Chan JC. Addressing different biases in analysing drug use on cancer risk in diabetes in nonclinical trial settings--what, why and how? Diabetes Obes Metab. 2012;14(7):579–85.
Reuter S, Gupta SC, Chaturvedi MM, Aggarwal BB. Oxidative stress, inflammation, and cancer: how are they linked? Free Radic Biol Med. 2010;49(11):1603–16.
Kong AP, Yang X, So WY, et al. Additive effects of blood glucose lowering drugs, statins and renin-angiotensin system blockers on all-site cancer risk in patients with type 2 diabetes. BMC Med. 2014;12(76):1–11.
Seshasai SR, Kaptoge S, Thompson A, et al. Diabetes mellitus, fasting glucose, and risk of cause-specific death. N Engl J Med. 2011;364(9):829–41.
Carton JA, Maradona JA, Nuno FJ, Fernandez-Alvarez R, Perez-Gonzalez F, Asensi V. Diabetes mellitus and bacteraemia: a comparative study between diabetic and nondiabetic patients. Eur J Med. 1992;1(5):281–7.
Aragon D, Ring CA, Covelli M. The influence of diabetes mellitus on postoperative infections. Crit Care Nurs Clin N Am. 2003;15(1):125–35.
Frier BM. Hypoglycaemia in diabetes mellitus: epidemiology and clinical implications. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2014;10(12):711–22. This review has comprehensive review of the topic of hypoglycemia in patients with diabetes.
Lorber D, Anderson J, Arent S, et al. Diabetes and driving. Diabetes Care. 2014;37 Suppl 1:S97–103.
Del Prato S, LaSalle J, Matthaei S, Bailey CJ. Tailoring treatment to the individual in type 2 diabetes practical guidance from the global partnership for effective diabetes management. Int J Clin Pract. 2010;64(3):295–304.
Lawton J, Rankin D, Elliott J, et al. Experiences, views, and support needs of family members of people with hypoglycemia unawareness: interview study. Diabetes Care. 2014;37(1):109–15.
Warren RE, Frier BM. Hypoglycaemia and cognitive function. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2005;7(5):493–503.
Whitmer RA, Karter AJ, Yaffe K, Quesenberry Jr CP, Selby JV. Hypoglycemic episodes and risk of dementia in older patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. JAMA. 2009;301(15):1565–72.
Yaffe K, Falvey CM, Hamilton N, et al. Association between hypoglycemia and dementia in a biracial cohort of older adults with diabetes mellitus. JAMA Int Med. 2013;173(14):1300–6.
Zhang Y, Ting RZ, Yang W, et al. Depression in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes: associations with hyperglycemia, hypoglycemia, and poor treatment adherence. J Diabetes. 2014. doi:10.1111/1753-0407.12238.
Inkster B, Zammitt NN, Frier BM. Drug-induced hypoglycaemia in type 2 diabetes. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2012;11(4):597–614.
So WY, Chan JC, Yeung VT, et al. Sulphonylurea-induced hypoglycaemia in institutionalized elderly in Hong Kong. Diabetes Med. 2002;19(11):966–8.
Xie L, Zhou S, Pinsky BW, Buysman EK, Baser O. Impact of initiating insulin glargine disposable pen versus vial/syringe on real-world glycemic outcomes and persistence among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in a large managed care plan: a claims database analysis. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2014;16(9):567–75.
Asche CV, Luo W, Aagren M. Differences in rates of hypoglycemia and health care costs in patients treated with insulin aspart in pens versus vials. Curr Med Res Opin. 2013;29(10):1287–96.
Moen MF, Zhan M, Hsu VD, et al. Frequency of hypoglycemia and its significance in chronic kidney disease. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009;4(6):1121–7.
Ma RC, Kong AP, Chan N, Tong PC, Chan JC. Drug-induced endocrine and metabolic disorders. Drug Saf. 2007;30(3):215–45.
Kong AP, Yang X, Luk A, et al. Hypoglycaemia, chronic kidney disease and death in type 2 diabetes: the Hong Kong diabetes registry. BMC Endocr Disord. 2014;14(1):48.
Pozzilli P, Leslie RD, Chan J, et al. The A1C and ABCD of glycaemia management in type 2 diabetes: a physician's personalized approach. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2010;26(4):239–44.
Inzucchi SE, Bergenstal RM, Buse JB, et al. Management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes, 2015: a patient-centered approach: update to a position statement of the American Diabetes Association and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2015;38(1):140–9.
Soe K, Sacerdote A, Karam J, Bahtiyar G. Management of type 2 diabetes mellitus in the elderly. Maturitas. 2011;70(2):151–9. This article provides evidence-based recommendations for management of elderly with diabetes which is an excellent example to illustrate the importance of personalized approach in diabetes care.
Yang X, Wang Y, Luk AO, et al. Enhancers and attenuators of risk associations of chronic hepatitis B virus infection with hepatocellular carcinoma in type 2 diabetes. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2013;20(2):161–71.
Yang X, So W, Ko GT, et al. Independent associations between low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and cancer among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. CMAJ. 2008;179(5):427–37.
Yang X, So WY, Ma RC, et al. Low LDL cholesterol, albuminuria, and statins for the risk of cancer in type 2 diabetes: the Hong Kong diabetes registry. Diabetes Care. 2009;32(10):1826–32.
Compliance with Ethics Guidelines
Conflict of Interest
Alice P.S. Kong has received honorarium for consultancy or giving lectures from Abbott, Astra Zeneca, Sanofi, Novo-Nordisk, Eli-Lilly, Merck Serono, Pfizer, and Nestle. Juliana C.N. Chan has received research grant and/or honorarium for consultancy or giving lectures, from Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Daiichi-Sankyo, Eli-Lilly, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck Sharp and Dohme, Merck Serono, Pfizer, Astra Zeneca, Sanofi, Novo-Nordisk, and/or Bristol-Myers Squibb. The proceeds have been partially donated to the Chinese University of Hong Kong, American Diabetes Association, and other charity organizations to support diabetes research and education.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Pharmacologic Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kong, A.P.S., Chan, J.C.N. Hypoglycemia and Comorbidities in Type 2 Diabetes. Curr Diab Rep 15, 80 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11892-015-0646-x
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11892-015-0646-x