Abstract
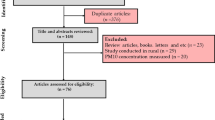
Exposure to potentially toxic elements (PTEs) bound to PM2.5 can cause various health effects, including cardiovascular disease, allergies, and other related diseases. There have been several studies on the concentration of PTEs, including zinc (Zn), iron (Fe), and manganese (Mn) bound PM2.5 in the indoor air of urban schools. In this study, the concentration of Zn, Fe, and Mn in the indoor air of schools bound PM2.5 were meta-analyzed. PubMed and Scopus were used to retrieve papers related to the concentration of PTEs bound PM2.5 in the indoor air of urban schools from January 1, 2000 to March 10, 2020. The concentration of PTEs in PM2.5 was meta-analyzed based on the country subgroup in the random-effects model (REM). Thirty papers with 25 data reports were included in the study. The rank order of PTEs bound PM2.5 was Zn (17.32 ng/m3) > Fe (14.49 ng/m3) > Mn (7.40 ng/m3). The rank order of countries based on the concentration of Fe-bound PM2.5 in the indoor air of urban schools was China > Poland > Italy > Spain > Taiwan > Turkey > Iran) > Chile; Zn, Poland > Iran > Taiwan > Turkey > Spain > Italy > Chile; and for Mn, Poland > China > Iran > Taiwan > Spain > Italy > Chile. The pooled concentration of PTEs (Fe, Mn, and Zn) bound PM2.5 in the indoor air of urban schools in Poland and China was higher than in other countries, hence, therefore, it is recommended to carry out a PM2.5 concentration reduction program in the indoor air of schools in these countries.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data openly available in a public repository.
References
Abdel-Salam MM (2019) Investigation of indoor air quality at urban schools in Qatar. Indoor Built Environ 28:278–288
Amato F, Rivas I, Viana M, Moreno T, Bouso L, Reche C, Àlvarez-Pedrerol M, Alastuey A, Sunyer J, Querol X (2014) Sources of indoor and outdoor PM2.5 concentrations in primary schools. Sci Total Environ 490:757–765
Aranega JP, Oliveira CA (2022) Occurrence of mycotoxins in pastures: a systematic review. Qual Assurance Safety Crops Foods 14:135–144
Arruti A, Fernández-Olmo I, Irabien A (2010) Evaluation of the contribution of local sources to trace metals levels in urban PM2.5 and PM10 in the Cantabria region (Northern Spain). J Environ Monitor 12:1451–1458
Bi D, Qiu Y, Cheng H, Zhou Q, Liu X, Chen J, Cui X, Liu M, Zhu Z (2018) Seasonal characteristics of indoor and outdoor fine particles and their metallic compositions in Nanjing, China. Build Environ 137:118–126
Canha N, Almeida SM, Freitas MdC, Trancoso M, Sousa A, Mouro F, Wolterbeek HT (2014) Particulate matter analysis in indoor environments of urban and rural primary schools using passive sampling methodology. Atmos Environ 83:21–34
Castilla JC, Nealler E (1978) Marine environmental impact due to mining activities of El Salvador copper mine, Chile. Mar Pollut Bull 9:67–70
Cesari D, Contini D, Genga A, Siciliano M, Elefante C, Baglivi F, Daniele L (2012) Analysis of raw soils and their re-suspended PM10 fractions: characterisation of source profiles and enrichment factors. Appl Geochem 27:1238–1246
Chen F, Aqeel M, Maqsood MF, Khalid N, Irshad MK, Ibrahim M, Akhter N, Afzaal M, Ma J, Hashem M (2022a) Mitigation of lead toxicity in Vigna radiata genotypes by silver nanoparticles. Environ Pollut 308:119606
Chen Z, He X, Ge J, Fan G, Zhang L, Parvez AM, Wang G (2022b) Controllable fabrication of nanofibrillated cellulose supported HKUST-1 hierarchically porous membranes for highly efficient removal of formaldehyde in air. Ind Crops Prod 186:115269
Chithra V, Nagendra SS (2014) Seasonal trends of indoor particulate matter concentrations in a naturally ventilated school building. WIT Trans Ecol Environ 183:341–351
Contini D, Cesari D, Donateo A, Chirizzi D, Belosi F (2014): Characterization of PM10 and PM2.5 and their metals content in different typologies of sites in south-eastern Italy. Atmosphere 5
De Souza C, Khaneghah AM, Oliveira CAF (2021) The occurrence of aflatoxin M1 in industrial and traditional fermented milk: a systematic review study. Ital J Food Sci 33:12–23
Di Gilio A, Farella G, Marzocca A, Giua R, Assennato G, Tutino M, de Gennaro G (2017a) Indoor/outdoor air quality assessment at school near the steel plant in Taranto (Italy). Adv Meteorol 2017:1526209
Di Gilio A, Farella G, Marzocca A, Giua R, Assennato G, Tutino M, De Gennaro G (2017b): Indoor/outdoor air quality assessment at school near the steel plant in Taranto (Italy). Adv Meteorol 2017b
Ekmekcioglu D, Keskin SS (2007) Characterization of indoor air particulate matter in selected elementary schools in Istanbul, Turkey. Indoor Built Environ 16:169–176
Ergenekon P, Ulutaş K (2014) Heavy metal content of total suspended air particles in the heavily industrialized town of Gebze, Turkey. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 92:90–95
Fang G-C, Chang C-N, Chu C-C, Wu Y-S, Fu PP-C, Yang IL, Chen M-H (2003) Characterization of particulate, metallic elements of TSP, PM2.5 and PM2.5-10 aerosols at a farm sampling site in Taiwan Taichung. Sci Total Environ 308:157–166
Fang G-C, Chiang H-C, Chen Y-C, Xiao Y-F, Zhuang Y-J (2014) Particulates and metallic elements monitoring at two sampling sites (Harbor, Airport) in Taiwan. Environ Forensics 15:296–305
Fang G-C, Chen Y-C, Lo C-T, Cho M-H, Zhuang Y-J, Tsai K-H, Huang C-Y, Xiao Y-F (2018) Concentrations and analysis of health risks of ambient air metallic elements at Longjing site in central Taiwan. Environ Geochem Health 40:461–472
Fang GC, Huang YL, Huang JH, Liu CK (2012) Dry deposition of Mn, Zn, Cr, Cu and Pb in particles of sizes of 3 μm, 5.6 μm and 10 μm in central Taiwan. J Hazard Mater 203–204:158–168
Gali NK, Yang F, Jiang SY, Chan KL, Sun L, Ho K-f, Ning Z (2015) Spatial and seasonal heterogeneity of atmospheric particles induced reactive oxygen species in urban areas and the role of water-soluble metals. Environ Pollut 198:86–96
Gao L, Huang X, Wang P, Chen Z, Hao Q, Bai S, Tang S, Li C, Qin D (2022) Concentrations and health risk assessment of 24 residual heavy metals in Chinese mitten crab (Eriocheir sinensis). Qual Assurance Safety Crops Foods 14:82–91
Ghozikali MG, Ansarin K, Naddafi K, Nodehi RN, Yaghmaeian K, Hassanvand MS, Kashani H, Jaafari J, Atafar Z, Faraji M (2018) Short-term effects of particle size fractions on lung function of late adolescents. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:21822–21832
Gidhagen L, Kahelin H, Schmidt-Thomé P, Johansson C (2002) Anthropogenic and natural levels of arsenic in PM10 in Central and Northern Chile. Atmos Environ 36:3803–3817
Halek F, Kavousi A, Hassani F (2009) Evaluation of indoor-outdoor particle size distribution in Tehran’s elementary schools. World Acad of Sci Eng and Tech 57:463–466
Hassanvand MS, Naddafi K, Faridi S, Nabizadeh R, Sowlat MH, Momeniha F, Gholampour A, Arhami M, Kashani H, Zare A (2015a) Characterization of PAHs and metals in indoor/outdoor PM10/PM2.5/PM1 in a retirement home and a school dormitory. Sci Total Environ 527:100–110
Hassanvand MS, Naddafi K, Faridi S, Nabizadeh R, Sowlat MH, Momeniha F, Gholampour A, Arhami M, Kashani H, Zare A, Niazi S, Rastkari N, Nazmara S, Ghani M, Yunesian M (2015b) Characterization of PAHs and metals in indoor/outdoor PM10/PM2.5/PM1 in a retirement home and a school dormitory. Sci Total Environ 527–528:100–110
Higgins J, White IR, Anzures-Cabrera J (2008) Meta-analysis of skewed data: combining results reported on log-transformed or raw scales. Stat Med 27:6072–6092
Higgins JPT, Green S (2011) Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. Wiley
Huang B-F, Chang Y-C, Han A-L, Hsu H-T (2018) Metal composition of ambient PM2.5 influences the pulmonary function of schoolchildren: a case study of school located nearby of an electric arc furnace factory. Toxicol Ind Health 34:253–261
Jorquera H, Barraza F (2013) Source apportionment of PM10 and PM2.5 in a desert region in northern Chile. Sci Total Environ 444:327–335
Liu G, Nie R, Liu Y, Mehmood A (2022a) Combined antimicrobial effect of bacteriocins with other hurdles of physicochemic and microbiome to prolong shelf life of food: a review. Sci Total Environ 154058
Liu J, Chen Y, Wang X (2022b) Factors driving waste sorting in construction projects in China. J Clean Prod 336:130397
Liu Y, Tian J, Zheng W, Yin L (2022c) Spatial and temporal distribution characteristics of haze and pollution particles in China based on spatial statistics. Urban Climate 41:101031
Medina M, Andrade S, Faugeron S, Lagos N, Mella D, Correa JA (2005) Biodiversity of rocky intertidal benthic communities associated with copper mine tailing discharges in northern Chile. Mar Pollut Bull 50:396–409
Mesías Monsalve S, Martínez L, Yohannessen Vásquez K, Alvarado Orellana S, Klarián Vergara J, Martín Mateo M, Costilla Salazar R, Fuentes Alburquenque M, Cáceres Lillo DD (2018a) Trace element contents in fine particulate matter (PM2.5) in urban school microenvironments near a contaminated beach with mine tailings, Chañaral. Chile Environ Geochem Health 40:1077–1091
Mesías Monsalve S, Martínez L, Yohannessen Vásquez K, Alvarado Orellana S, Klarián Vergara J, Martín Mateo M, Costilla Salazar R, Fuentes Alburquenque M, Cáceres Lillo DD (2018b) Trace element contents in fine particulate matter (PM(2.5)) in urban school microenvironments near a contaminated beach with mine tailings, Chañaral. Chile Environ Geochem Health 40:1077–1091
Mohammadyan M, Alizadeh Larimi A, Etemadinejad S, Yosefinejad R (2013) Respirable particle concentrations in primary schools’ classrooms in Sari. J Mazandaran Univ Med Sci 23:67–75
Mohammadyan M, Alizadeh-Larimi A, Etemadinejad S, Latif MT, Heibati B, Yetilmezsoy K, Abdul-Wahab SA, Dadvand P (2017) Particulate air pollution at schools: indoor-outdoor relationship and determinants of indoor concentrations. Aerosol Air Qual Res 17:857–864
Naderizadeh Z, Khademi H, Ayoubi S (2016) Biomonitoring of atmospheric heavy metals pollution using dust deposited on date palm leaves in southwestern Iran. Atmósfera 29:141–155
Neary DG, Garcia-Chevesich P (2008) Hydrology and erosion impacts of mining derived coastal sand dunes, Chañaral Bay. Arizona-Nevada Academy of Science, Chile
Norouzi S, Khademi H, Ayoubi S, Cano AF, Acosta JA (2017) Seasonal and spatial variations in dust deposition rate and concentrations of dust-borne heavy metals, a case study from Isfahan, central Iran. Atmos Pollut Res 8:686–699
Pastuszka JS, Rogula-Kozłowska W, Zajusz-Zubek E (2010) Characterization of PM10 and PM2.5 and associated heavy metals at the crossroads and urban background site in Zabrze, Upper Silesia, Poland, during the smog episodes. Environ Monit Assess 168:613–627
Quan Q, Liang W, Yan D, Lei J (2022) Influences of joint action of natural and social factors on atmospheric process of hydrological cycle in Inner Mongolia. China Urban Climate 41:101043
Querol X, Alastuey A, Rodríguez S, Viana MM, Artíñano B, Salvador P, Mantilla E, García do Santos S, Fernandez Patier R, de Rosa J, Sanchez de la Campa A, Menéndez M, Gil JJ (2004) Levels of particulate matter in rural, urban and industrial sites in Spain. Sci Total Environ 334–335:359–76
Ramirez M, Massolo S, Frache R, Correa JA (2005) Metal speciation and environmental impact on sandy beaches due to El Salvador copper mine. Chile Mar Pollut Bull 50:62–72
Raysoni AU, Armijos RX, Weigel MM, Echanique P, Racines M, Pingitore NE, Li W-W (2017) Evaluation of sources and patterns of elemental composition of PM2.5 at three low-income neighborhood schools and residences in Quito, Ecuador. Int J Environ Res Public Health 14:674
Raysoni AU, Armijos RX, Weigel MM, Echanique P, Racines M, Pingitore NE, Li WW (2017b) Evaluation of sources and patterns of elemental composition of PM(2.5) at Three low-income neighborhood schools and residences in Quito, Ecuador. Int J Environ Res Public Health 14
Rogula-Kozłowska W, Pastuszka JS, Talik E (2008) Influence of Vehicular traffic on concentration and particle surface composition of PM10 and PM2.5 in Zabrze. Poland Pol J Environ Stud 17:539–548
Shang K, Chen Z, Liu Z, Song L, Zheng W, Yang B, Liu S, Yin L (2021) Haze prediction model using deep recurrent neural network. Atmosphere 12:1625
Slezakova K, Pires JCM, Martins FG, Pereira MC, Alvim-Ferraz MC (2011) Identification of tobacco smoke components in indoor breathable particles by SEM–EDS. Atmos Environ 45:863–872
Soleimani M, Amini N, Sadeghian B, Wang D, Fang L (2018) Heavy metals and their source identification in particulate matter (PM2.5) in Isfahan City Iran. J Environ Sci 72:166–175
Sun Y, Li J, Zhu L, Jiang L (2022) Cooperation and competition between CRISPR-and omics-based technologies in foodborne pathogens detection: a state of the art review. Curr Opin Food Sci 44:100813
Tian J, Liu Y, Zheng W, Yin L (2022) Smog prediction based on the deep belief-BP neural network model (DBN-BP). Urban Climate 41:101078
Viana M, Rivas I, Querol X, Alastuey A, Sunyer J, Álvarez-Pedrerol M, Bouso L, Sioutas C (2014) Indoor/outdoor relationships and mass closure of quasi-ultrafine, accumulation and coarse particles in Barcelona schools. Atmos Chem Phys 14:4459–4472
Wang K, Wang W, Li L, Li J, Wei L, Chi W, Hong L, Zhao Q, Jiang J (2020) Seasonal concentration distribution of PM1.0 and PM2.5 and a risk assessment of bound trace metals in Harbin, China: effect of the species distribution of heavy metals and heat supply. Sci. Rep. 10:8160
Wang Y, Wu X, Liu J, Zhai Z, Yang Z, Xia J, Deng S, Qu X, Zhang H, Wu D (2022) Mo-modified band structure and enhanced photocatalytic properties of tin oxide quantum dots for visible-light driven degradation of antibiotic contaminants. J Environ Chem Eng 10:107091
Wu X, Liu Z, Yin L, Zheng W, Song L, Tian J, Yang B, Liu S (2021) A haze prediction model in chengdu based on LSTM. Atmosphere 12:1479
Yang Y, Zhu H, Xu X, Bao L, Wang Y, Lin H, Zheng C (2021) Construction of a novel lanthanum carbonate-grafted ZSM-5 zeolite for effective highly selective phosphate removal from wastewater. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 324:111289
Yin L, Wang L, Huang W, Liu S, Yang B, Zheng W (2021) Spatiotemporal analysis of haze in Beijing based on the multi-convolution model. Atmosphere 12:1408
Yu C, Chen X, Li N, Zhang Y, Li S, Chen J, Yao L, Lin K, Lai Y, Deng X (2022) Ag3PO4-based photocatalysts and their application in organic-polluted wastewater treatment. Environ Sci Pollut Res 1–17
Zhang Z, Tian J, Huang W, Yin L, Zheng W, Liu S (2021) A haze prediction method based on one-dimensional convolutional neural network. Atmosphere 12:1327
Zoghi A, Salimi M, Mirmahdi RS, Massoud R, Khosravi-Darani K, Mohammadi R, Rouhi M, Tripathy AD (2022) Effect of pretreatments on bioremoval of metals and subsequent exposure to simulated gastrointestinal conditions. Qual Assurance Safety Crops Foods 14:145–155
Zwoździak A, Sówka I, Krupińska B, Zwoździak J, Nych A (2013) Infiltration or indoor sources as determinants of the elemental composition of particulate matter inside a school in Wrocław, Poland? Build Environ 66:173–180
Funding
Tobacco and Health Research Center, Hormozgan University of Medical Sciences, Bandar Abbas, Iran, is the financer of this project (IR.HUMS.REC.1399.415).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Searching in databases was performed by Amenh Bahreini; data extraction by Amenh Bahreini; meta-analysis of data by Yadolah Fakhri and prepared manuscript by Trias Mahmudiono; Yadolah Fakhri, Zoha Hedari Nejad, Hasti Daraei, Amin Mousavi Khaneghah.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Ethical approval was approved from Tobacco and Health Research Center, Hormozgan University of Medical Sciences, Bandar Abbas, Iran (IR.HUMS.REC.1399.415).
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Fakhri, Y., Akhlaghi, M., Daraei, H. et al. The concentration of potentially toxic elements (zinc, iron, manganese) bound PM2.5 in the indoor air of urban schools: a global systematic review and meta-analysis. Air Qual Atmos Health 16, 77–84 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11869-022-01257-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11869-022-01257-1