Abstract
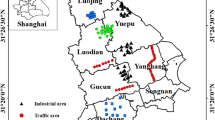
Industrial and vehicular emissions of particles cause multiple damages to human health due to concentration, size, and composition. These emissions contain magnetic particles; therefore, low-cost properties allow tracking and monitoring them. This study is aimed at identifying the primary sources of magnetic material in 100 samples of urban road dust from San Luis Potosí, Mexico, analyzing the influence of land use and the type of road on these particles. Magnetic susceptibility (χlf) and isothermal remanent magnetization at 0.7 T (IRM0.7T) were determined, as well as the iron and manganese content using X-ray fluorescence. The distribution of particles was examined by land use and type of road through geostatistical maps and variance analysis. The results showed that the iron and manganese content, χlf, and IRM0.7T were positively correlated, indicating a possible common origin. The primary sources identified were the iron smelter and laminator in the industrial park. Urban land use influenced the content of iron, manganese, and magnetic material in urban road dust. The land uses with the more significant transformation (industrial and mixed) presented the highest values of iron, manganese, χlf, and IRM0.7T. On the other hand, vehicular traffic was indirectly assessed through the type of road, influencing the magnetic signal of urban road dust and finding the highest signals in primary and secondary roads. Then, the magnetic properties allowed the tracking and monitoring of magnetic particles from industrial and vehicle emissions.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguilera A, Armendariz C, Quintana P, García-Oliva F, Bautista F (2019) Influence of land use and road type on the elemental composition of urban dust in a Mexican metropolitan area. Pol J Environ Stud 28(3):1535–1547. https://doi.org/10.15244/pjoes/90358
Aragón-Piña A, Torres-Villaseñor G, Santiago-Jacinto P, Monroy-Fernández M (2002) Scanning and transmission electron microscope of suspended lead-rich particles in the air of San Luis Potosi, Mexico. Atmos Environ 36(33):5235–5243. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1352-2310(02)00588-5
Aragón-Piña A, Campos-Ramos AA, Leyva-Ramos R, Hernández-Orta M, Miranda-Ortiz N, Luszczewski-Kudra A (2006) Influencia de Emisiones Industriales En El Polvo Atmosférico de La Ciudad de San Luis Potosí, México. Rev Intl Contam Ambiental 22(1):5–19 http://www.redalyc.org/pdf/370/37022101.pdf
Bautista F, Cejudo R, Zapata-Carbonell G, Cortés JL, Quintana P, Aguilar D, Aguilar B, Morales J, Gogichaishvili A (2013) Magnetic parameters and their relationship with heavy metals in urban dusts of Mexico City. Latinmag Lett 3(Special Issue):1–4
Budai P, Clement A (2018) Spatial distribution patterns of four traffic-emitted heavy metals in urban road dust and the resuspension of brake-emitted particles: findings of a field study. Transp Res Part D: Transp Environ 62(March):179–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trd.2018.02.014
Cejudo-Ruíz R, Bautista F, Quintana P, Delgado-Carranza MC, Aguilar D, Goguitchaichvili A, Morales-Contreras JJ (2015) Correlación Entre Elementos Potencialmente Tóxicos y Propiedades Magnéticas En Suelos de La Ciudad de México Para La Identificación de Sitios Contaminados : Definición de Umbrales Magnéticos. Rev Mex Cien Geol 32(1):50–61
Dearing John A (1999) Using the Bartington MS2 system. Environmental magnetic susceptibility
Dearing JA, Dann RJL, Hay K, Lees JA, Loveland PJ, Maher BA, O’Grady K (1996) Frequency-dependent susceptibility measurements of environmental materials. Geophys J Int 124(1):228–240. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-246X.1996.tb06366.x
Declercq Y, Samson R, Castanheiro A, Spassov S, Tack FMG, Van De Vijver E, De Smedt P (2019) Evaluating the potential of topsoil magnetic pollution mapping across different land use classes. Sci Total Environ 685(2019):345–356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.05.379
Dmowska R, Holton JR, Thomas Rossby H (2000) Paleomagnetism: continents and oceans. In: International geophysics, vol 73. Academic Press, 86, p 383. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0074-6142(00)80103-5
Dystłowa S, Winklerb A, Górka-Kostrubieca B, Sagnottib L (2019) Magnetic, geochemical and granulometric properties of street dust from Warsaw (Poland). J Appl Geophys 169:58–73
Frank U, Nowaczyk N (2008) Mineral magnetic properties of artificial samples systematically mixed from haematite and magnetite. Geophys J Int 175:449–461
Górka-Kostrubiec B, Szczepaniak-Wnuk I (2017) Magnetic study of a mixture of magnetite and metallic iron in indoor dust samples. Air Qual Atmos Health 10(1):105–116. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11869-016-0412-5
Górka-Kostrubiec B, Werner T, Dytłow S, Szczepaniak-Wnuk I, Jeleńska M, Hanc-Kuczkowska A (2019) Detection of metallic Iron in urban dust by using high-temperature measurements supplemented with microscopic observations and Mössbauer spectra. J Appl Geophys 166:89–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jappgeo.2019.04.022
Guvenç N, Alagha O, Tuncel G (2003) Investigation of soil multi-element composition in Antalya, Turkey. Environ Int 29(5):631–640. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0160-4120(03)00046-1
Keshavarzi B, Tazarvi Z, Rajabzadeh MA, Najmeddin A (2015) Chemical speciation, human health risk assessment and pollution level of selected heavy metals in urban street dust of Shiraz, Iran. Atmos Environ 119(August):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2015.08.001
Kruiver PP, Passier HF (2001) Coercivity analysis of magnetic phases in sapropel S1 related to variations in redox conditions, including an investigation of the S ratio. Geochem Geophys Geosyst 2(12). https://doi.org/10.1029/2001GC000181
Li N, Georas S, Alexis N, Fritz P, Xia T, Williams MA, Horner E, Nel A (2016) A work group report on ultrafine particles (American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology): why ambient ultrafine and engineered nanoparticles should receive special attention for possible adverse health outcomes in human subjects. J Allergy Clin Immunol 138(2):386–396. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2016.02.023
Liu Q, Roberts AP, Torrent J, Horng CS, Larrasoaña JC (2007) What do the HIRM and S-ratio really measure in environmental magnetism? Geochem Geophys Geosyst 8(9). https://doi.org/10.1029/2007GC001717
Liu Q, Roberts AP, Larrasoaña JC, Banerjee SK, Guyodo Y, Tauxe L, Oldfield F (2012) Environmental magnetism: principles and applications. Rev Geophys 50(4):RG4002. https://doi.org/10.1029/2012RG000393
Liu X, Zhai Y, Zhu Y, Liu Y, Chen H, Li P, Peng C, Xu B, Li C, Zeng G (2015) Mass concentration and health risk assessment of heavy metals in size-segregated airborne particulate matter in Changsha. Sci Total Environ 517(June):215–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.02.066
Lozano R, Bernal JP (2005) Characterization of a new set of eight geochemical reference materials for XRF major and trace element analysis. Rev Mex Cien Geol 22(3):329–344
Lu SG, Xue QF, Zhu L, Jin Yan Y (2008) Mineral magnetic properties of a weathering sequence of soils derived from basalt in eastern China. Catena 73(1):23–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2007.08.004
Magiera T, Jabłońska M, Strzyszcz Z, Rachwal M (2011) Morphological and mineralogical forms of technogenic magnetic particles in industrial dusts. Atmos Environ 45(25):4281–4290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2011.04.076
Maher BA, Ahmed IAM, Karloukovski V, MacLaren DA, Foulds PG, Allsop D, Mann DMA, Torres-Jardón R, Calderon-Garciduenas L (2016) Magnetite pollution nanoparticles in the human brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci 113(39):10797–10801. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1605941113
Pérez-Martínez I, Romero FM (2015) Uso de Parámetros Indirectos Para La Evaluación de La Contaminación de Suelos Por Metales Pesados En Una Zona Minera de San Luis Potosí , México. Bol Soc Geol Mex 67(1):12
Pérez-Vázquez FJ, Flores-Ramírez R, Ochoa-Martínez AC, Carrizales-Yáñez L, Ilizaliturri-Hernández CA, Moctezuma-González J, Pruneda-Álvarez LG, Ruiz-Vera T, Orta-García ST, González-Palomo AK, Pérez-Maldonado IN (2015) Human health risks associated with heavy metals in soil in different areas of San Luis Potosí, México. Hum Ecol Risk Assess 7039(September):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2015.1064760
Qian P, Zhou L, Zheng X, Dong Y, Wang Y (2014) Magnetic properties of airborne particulate matter in Shanghai during dust storm events and the implications for heavy metal contaminant sources. Environ Earth Sci 72(10):4167–4178. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3313-7
Qiao, Qingqing, Chunxia Zhang, Baochun Huang, and John D. A. Piper. 2011. “Evaluating the environmental quality impact of the 2008 Beijing Olympic Games: magnetic monitoring of street dust in Beijing Olympic Park.” Geophys J Int 187 (3): 1222–1236. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-246X.2011.05195.x
Reyes A, Bertha FB, Rosas-Elguera J, Gogichaishvili A, Cejudo R, Morales J (2011) Evaluación de La Contaminación Ambiental Por Métodos Magnéticos En Las Ciudades de Morelia y Guadalajara, México. Latinmag Lett 3(Special Issue):1–6
Ruxton GD, Beauchamp G (2008) Some suggestions about appropriate use of the Kruskal-Wallis test. Anim Behav 76(3):1083–1087. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anbehav.2008.04.011
Sánchez-Duque A, Bautista F, Goguitchaichvili A, Cejudo-Ruiz R, Reyes-López JA, Solís-Domínguez FA, Morales-Contreras JJ (2015) Evaluación de La Contaminación Ambiental a Partir Del Aumento Magnético En Polvos Urbanos. Caso de Estudio Para La Ciudad de Mexicali, México. Rev Mex Cien Geol 32(3):501–513
Solomon PA, Costantini M, Grahame TJ, Gerlofs-Nijland ME, Cassee FR, Russell AG, Brook JR et al (2012a) Air pollution and health: bridging the gap from sources to health outcomes: conference summary. Air Qual Atmos Health 5. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11869-011-0161-4
Solomon PA, Gehr P, Bennett DH, Phalen RF, Méndez LB, Rothen-Rutishauser B, Clift M, Brandenberger C, Mühlfeld C (2012b) Macroscopic to microscopic scales of particle dosimetry: from source to fate in the body. Air Qual Atmos Health 5(2):169–187. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11869-011-0167-y
Wang XS (2016) Investigation of the pollution in the street dust at Xuzhou, China, using magnetic, micro-morphological and Mössbauer spectra analyses. Environ Earth Sci 75(10):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5731-1
Wang G, Chen J, Zhang W, Ren F, Chen Y, Fang A, Ma L (2019) Magnetic properties of street dust in Shanghai, China and its relationship to anthropogenic activities. Environ Pollut 255:113214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113214
Xia D, Wang B, Yu Y, Jia J, Nie Y, Wang X, Shujing X (2014) Combination of magnetic parameters and heavy metals to discriminate soil-contamination sources in Yinchuan--a typical oasis city of northwestern China. Sci Total Environ 485–486(July):83–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.03.070
Acknowledgments
Thanks are due to José Luis Cortés, Ruben Cejudo-Ruíz, Marco Anyelo Cazarez-Barboza, Alexander Sanchez-Duque, and Daniel Aguilar for their help in the field and laboratory work. Anahi Aguilera appreciates the economic support of CONACYT for the master’s program fellowship.
Funding
This study was financially supported by the National Council of Science and Technology project CB-2016-283135 and the projects PAPIIT IA203713 and IN209218.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Anahi Aguilera performed material preparation, data collection, and analysis. Anahi Aguilera wrote the first draft of the manuscript, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aguilera, A., Morales, J.J., Goguitchaichvili, A. et al. Spatial distribution of magnetic material in urban road dust classified by land use and type of road in San Luis Potosí, Mexico. Air Qual Atmos Health 13, 951–963 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11869-020-00851-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11869-020-00851-5