Abstract
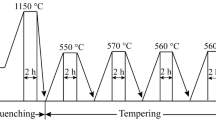
The mechanical properties and microstructures, in particular precipitation in the AISI H13 steel, quenched and tempered from 773 K to 973 K for different periods, were systematically investigated by scanning electron microscopy, electron backscatter diffraction (EBSD) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The results indicate a sharp decrease in hardness at temperatures > 863 K during the first 2 h of tempering. Ultimate tensile strength and yield strength decrease, while elongation and impact energy increase with the increase of tempering temperature. The volume fraction of static recrystallization increases from the EBSD result. Regarding precipitates, the coarsening rate of M23C6 was much faster than that of MC and M2C and was verified by using the Ostwald ripening model. In addition, kinetic modeling of the softening of H13 during tempering from 863 K to 973 K was performed. This model was also applied successfully to predict the hardness of double-tempered H13 steel samples.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Q.C. Zhou, X.C. Wu, N.N. Shi, J.W. Li, and N. Min, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 528, 5696. (2011).
D. Salcedo, C.J. Luis, R. Luri, J. León, I. Puertas, and J.P. Fuertes, Proc. Eng. 132, 1069. (2015).
S.D. Lu, Z.B. Wang, and Lu, J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 26, 258. (2010).
J.G. Ge, T.J. Ma, Y. Chen, T.N. Jin, H.G. Fu, R.S. Xiao, Y.P. Lei, and J. Lin, J. Alloys Compd. 783, 145. (2019).
L.N. Zhou, G.Z. Tang, X.X. Ma, L.Q. Wang, and X.H. Zhang, Mater. Charact. 146, 258. (2018).
X.Q. Wang, Z. Tao, and M.K. Hassan, J. Constr. Steel Res. 164, 105785. (2020).
K. Chen, Z.H. Jiang, F.B. Liu, J. Yu, Y. Li, W. Gong, and C.Y. Chen, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 766, 138272. (2019).
E.J. Mittemeher, L. Cheng, P.J. van der Schaaf, C.M. Brakman, and B.M. Korevaar, Metall. Trans. A 19, 925 (1988).
J.J. Yan, H. Song, Y.P. Dong, W.M. Quach, and M. Yan, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 773, 138845. (2020).
J. Zhu, Z.H. Zhang, and J.X. Xie, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 752, 101. (2019).
Y.L. Wang, X. Song, and Y.M. Zhang, Mater. Res. Express 6, 096513. (2019).
W.W. Song, Y.A. Min, and X.C. Wu, Trans. Mater. Heat Treat. 30, 122. (2009).
N. Mebarki, D. Delagnes, P. Lamesle, F. Delmas, and C. Levaillant, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 387–389, 171. (2004).
N. Mebarki, Ph.D. Thesis, Ecole Nationale Supérieure des Mines deParis, (February 2003).
N. Mebarki, P. Lamesle, D. Delagnes, F. Delmas, and C. Levaillant, in: J. Bergström, G. Fredriksson, M. Johansson, O. Kotik, and F. Thuvander(Eds.), The Use of Tool Steels: Experience and Research, Proceedings of the 6th International Tooling Conference, Karlstad University, Sweden, 10–13 September 2002, pp. 617–632.
A.G. Ning, S. Yue, R. Gao, L.X. Li, and H.J. Guo, Metals 9, 1283. (2019).
G.E. Totten, Steel Heat Treatment: Metallurgy and Technologies (CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006), pp. 171–183.
Z.Q. Cui, and Y.C. Oin, Metal Science and Heat Treatment, (Machinery Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2007), pp. 268–277.
W.Q. Zhang, Phase transformation in solid metals and alloys (National defense Industry Press: 2015), pp. 95–102.
R.J. Seher, H.M. James, G.N. Maniar, Stereology and Quantitative Metallography, Pellissier, G.E., Purdy, S.M., Eds. (ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1972), pp. 119–137.
I.M. Lifshitz, and V.V. Slyozov, J. Phys. Chem. Solids 19, 35. (1961).
J.W. Martin, R.D. Doherty, B. Cantor, Stability of Microstructure in Metallic System, 2nd edn. (Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1997), pp. 102–144.
T. Philippe, and P.W. Voorhees, Acta Mater. 61, 4237 (2013).
A. Umantsev, and G.B. Olson, Scr. Metall. Mater. 29, 1135 (1993).
Q.L. Yong, Secondary Phases in Steels, (Metallurgical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2006), pp. 86–253.
E. Gamsjägera, J. Svobodab, and F.D. Fischerac, Comput. Mater. Sci. 32, 360 (2005).
W.A. Johnson, and R.F. Mehl, Trans. Am. Inst. Min. Metall. Pet. Eng. 135, 416 (1939).
M. Avrami, J. Chem. Phys. 7, 1103 (1939).
M. Avrami, J. Chem. Phys. 8, 212 (1940).
M. Avrami, J. Chem. Phys. 9, 177 (1941).
P. Watté, J. Van Humbeeck, and E. Aernoudt, Scr. Mater. 34, 89 (1996).
Z. Zhang, D. Delagnes, and G. Bernhart, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 380, 222 (2004).
Acknowledgements
This research was funded by the China Scholarship Council under Grant No. 201806935054. This work was also supported by the Scientific and Technological Innovation Programs of Higher Education Institutions in Shanxi, China, under Grant No. 201802035.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ning, A., Liu, Y., Gao, R. et al. Effect of Tempering Condition on Microstructure, Mechanical Properties and Precipitates in AISI H13 Steel. JOM 73, 2194–2202 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-021-04694-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-021-04694-y