Abstract
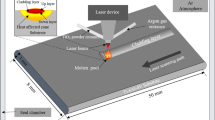
In this study, nano-graphene reinforced titanium matrix composites (GNPs/Ti) with a honeycomb porous structure were fabricated by selective laser melting (SLM). The effects of graphene on the microstructure, mechanical properties and corrosion performance of the SLM GNPs/Ti were systematically investigated. Results of microstructure characterization show that: 1) the density of the SLM GNPs/Ti was improved as compared to that of the SLM Ti; 2) abundant TiC particles were formed in the SLM GNPs/Ti. The hardness and compressive strength of the composite increased by 90% (from HV 236 to HV 503) and 14% (from 277 MPa to 316 MPa), respectively, attributed to the uniformly distributed TiC and fine GNPs in the Ti matrix. Electrochemical tests reveal that the corrosion current density of the SLM GNPs/Ti is only 0.328 μA/cm2, that is about 25% less than that of the SLM Ti. The results indicate that the incorporation of nano-graphene is a potential method to strengthen the Ti by SLM.
摘要
本研究采用激光选区熔化技术(SLM)制备了具有蜂窝多孔结构的纳米石墨烯增强钛基复合材料 (GNPs/Ti),系统研究了石墨烯对SLM GNPs/Ti 微观结构、力学与腐蚀性能的影响。结果表明:1)与 SLM Ti 相比,SLM GNPs/Ti 的密度有所提高;2)在SLM GNPs/Ti 中形成了明显的TiC 颗粒。钛基体 中弥散分布的TiC 和细小的GNPs 颗粒使得SLM GNPs/Ti 的硬度和抗压强度相比SLM Ti 分别提高了 90%(从HV 236 增加到HV 503)和14%(从277 MPa 增加至316 MPa)。电化学腐蚀测试结果表明,SLM GNPs/Ti 的腐蚀电流密度仅为0.328 μA/cm2,相比SLM Ti 降低了约25%。研究工作表明,添加纳米石 墨烯是一种强化SLM Ti 材料的潜在方法。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
LI Zhong-jie, DONG An-ping, XING Hui, XU Hao, DU Dafan, ZHANG Ting, SHE Huan, WANG Dong-hong, ZHU Guo-liang. Microstructure and mechanical properties of bimodal Ti-Bi alloys fabricated by mechanical alloying and spark plasma sintering for biomedical applications [J]. Materials Characterization, 2020, 161: 110134. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2020.110134.
FERRERI N C, SAVAGE D J, KNEZEVIC M. Non-acid, alcohol-based electropolishing enables high-quality electron backscatter diffraction characterization of titanium and its alloys: Application to pure Ti and Ti-6Al-4V [J]. Materials Characterization, 2020, 166: 110406. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2020.110406.
ZHANG Fa-ming, LIU Su-li, ZHAO Pei-pei, LIU Teng-fei, SUN Jing. Titanium/nanodiamond nanocomposites: Effect of nanodiamond on microstructure and mechanical properties of titanium [J]. Materials & Design, 2017, 131: 144–155. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2017.06.015.
HOU Yu-hang, LIU Bin, LIU Yong, ZHOU Ying-hao, SONG Ting-ting, ZHOU Qi, SHA Gang, YAN Ming. Ultra-low cost Ti powder for selective laser melting additive manufacturing and superior mechanical properties associated [J]. Opto-Electronic Advances, 2019, 2(5): 18002801–18002808. DOI: https://doi.org/10.29026/oea.2019.180028.
BOLZONI L, RUIZ-NAVAS E M, GORDO E. Powder metallurgy CP-Ti performances: Hydride-dehydride vs. sponge [J]. Materials & Design, 2014, 60: 226–232. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2014.04.005.
YAN M, DARGUSCH M S, EBEL T, QIAN M. A transmission electron microscopy and three-dimensional atom probe study of the oxygen-induced fine microstructural features in as-sintered Ti-6Al-4V and their impacts on ductility [J]. Acta Materialia, 2014, 68: 196–206. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2014.01.015.
ZHANG X Z, LEARY M, TANG H P, SONG T, QIAN M. Selective electron beam manufactured Ti-6Al-4V lattice structures for orthopedic implant applications: Current status and outstanding challenges [J]. Current Opinion in Solid State and Materials Science, 2018, 22(3): 75–99. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cossms.2018.05.002.
HACISALIHOĞLU I, YILDIZ F, ÇELIK A. The effects of build orientation and hatch spacing on mechanical properties of medical Ti-6Al-4V alloy manufactured by selective laser melting [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2021, 802: 140649. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2020.140649.
YANG Xin, MA Wen-jun, REN Yao-jia, LIU Shi-feng, WANG Yan, WANG Wan-lin, TANG Hui-ping. Subgrain microstructures and tensile properties of 316L stainless steel manufactured by selective laser melting [J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research International, 2021, 28: 1159–1167. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-021-00561-x.
ZHENG Jing-pu, CHEN Liang-jian, CHEN Dai-yuan, SHAO Chun-sheng, YI Man-fei, ZHANG Bo. Effects of pore size and porosity of surface-modified porous titanium implants on bone tissue ingrowth [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2019, 29(12): 2534–2545. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(19)65161-7.
WANG Di, YANG Yong-qiang, LIU Rui-cheng, XIAO Dongming, SUN Jian-feng. Study on the designing rules and processability of porous structure based on selective laser melting (SLM) [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2013, 213(10): 1734–1742. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2013.05.001.
CHANG Cheng, HUANG Jian, YAN Xing-chen, LI Qing, LIU Min, DENG Si-hao, GARDAN J, BOLOT R, CHEMKHI M. Microstructure and mechanical deformation behavior of selective laser melted Ti6Al4V ELI alloy porous structures [J]. Materials Letters, 2020, 277: 128366. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2020.128366.
FARÍAS I, OLMOS L, JIMÉNEZ O, FLORES M, BRAEM A, VLEUGELS J. Wear modes in open porosity titanium matrix composites with TiC addition processed by spark plasma sintering [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2019, 29(8): 1653–1664. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(19)65072-7.
YABLOKOVA G, SPEIRS M, van HUMBEECK J, KRUTH J P, SCHROOTEN J, CLOOTS R, BOSCHINI F, LUMAY G, LUYTEN J. Rheological behavior of β-Ti and NiTi powders produced by atomization for SLM production of open porous orthopedic implants [J]. Powder Technology, 2015, 283: 199–209. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2015.05.015.
MACONACHIE T, LEARY M, LOZANOVSKI B, ZHANG Xue-zhe, QIAN Ma, FARUQUE O, BRANDT M. SLM lattice structures: Properties, performance, applications and challenges [J]. Materials & Design, 2019, 183: 108137. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2019.108137.
KORZNIKOVA G, CZEPPE T, KHALIKOVA G, GUNDEROV D, KORZNIKOVA E, LITYNSKA-DOBRZYNSKA L, SZLEZYNGER M. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Cu-graphene composites produced by two high pressure torsion procedures [J]. Materials Characterization, 2020, 161: 110122. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2020.110122.
XIONG Jun-jie, YAN Hong. Microstructure and mechanical properties of ADC12 composites reinforced with graphene nanoplates prepared by ultrasonic assisted casting [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2020, 30(12): 3210–3225. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(20)65455-3.
KHOSHGHADAM-PIREYOUSEFAN M, RAHMANIFARD R, OROVCIK L, ŠVEC P, KLEMM V. Application of a novel method for fabrication of graphene reinforced aluminum matrix nanocomposites: Synthesis, microstructure, and mechanical properties [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2020, 772: 138820. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2019.138820.
GÜLER Ö, BAĞCI N. A short review on mechanical properties of graphene reinforced metal matrix composites [J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2020, 9(3): 6808–6833. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2020.01.077.
WU Li-yun, ZHAO Zhan-yong, BAI Pei-kang, ZHAO Wenjie, LI Yu-xin, LIANG Min-jie, LIAO Hai-hong, HUO Pengcheng, LI Jing. Wear resistance of graphene nano-platelets (GNPs) reinforced AlSi10Mg matrix composite prepared by SLM [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2020, 503: 144156. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.144156.
SU Ying, ZUO Qian, YANG Gang, YANG Yi, WEI Can, WANG Lin, LIU Jian. Compressive properties of the grahpene reinforced titanium composites [J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2017, 46(12): 3882–3886. (in Chinese)
KONG Xu, WANG Yu-min, YANG Qing, ZHANG Xu, ZHANG Guo-xing, YANG Li-na, WU Ying, YANG Rui. Low-cycle fatigue behavior and damage progression of a fiber reinforced titanium matrix composite [J]. International Journal of Lightweight Materials and Manufacture, 2021, 4(1): 9–17. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijlmm.2020.07.005.
ZHANG Z Y, LIANG Y L. Preparation of graphene/titanium matrix composites and their conductive properties [J]. Journal of Yunnan University: Natural Science Edition, 2019, 41(3): 551–556. http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-YNDZ201903018.htm. (in Chinese)
JIN Jian-bo, ZHOU Sheng-feng, ZHAO Yu, ZHANG Qiang, WANG Xiao-jian, LI Wei, CHEN Dong-chu, ZHANG Laichang. Refined microstructure and enhanced wear resistance of titanium matrix composites produced by selective laser melting [J]. Optics & Laser Technology, 2021, 134: 106644. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2020.106644.
MU X N, CHEN P W, ZHANG H M, CHENG X W, LIU L, GE Y X. Interface-dependent failure behaviors in graphene nanoflakes reinforced Ti matrix composites [J]. Materials Letters, 2021, 289: 129422. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2021.129422.
MANAM N S, HARUN W S W, SHRI D N A, GHANI S A C, KURNIAWAN T, ISMAIL M H, IBRAHIM M H I. Study of corrosion in biocompatible metals for implants: A review [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2017, 701: 698–715. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.01.196.
PRAVEEN B, SURESH S, PETHURAJAN V. Heat transfer performance of graphene nano-platelets laden micro-encapsulated PCM with polymer shell for thermal energy storage based heat sink [J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2019, 156: 237–249. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2019.04.072.
MITTAL G, DHAND V, RHEE K Y, PARK S J, LEE W R. A review on carbon nanotubes and graphene as fillers in reinforced polymer nanocomposites [J]. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 2015, 21: 11–25. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2014.03.022.
ALMANGOUR B, GRZESIAK D, YANG J M. In situ formation of TiC-particle-reinforced stainless steel matrix nanocomposites during ball milling: Feedstock powder preparation for selective laser melting at various energy densities [J]. Powder Technology, 2018, 326: 467–478. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2017.11.064.
KAZANTSEVA N, KRAKHMALEV P, THUVANDER M, YADROITSEV I, VINOGRADOVA N, EZHOV I. Martensitic transformations in Ti-6Al-4V (ELI) alloy manufactured by 3D printing [J]. Materials Characterization, 2018, 146: 101–112. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2018.09.042.
ATTAR H, EHTEMAM-HAGHIGHI S, KENT D, OKULOV I V, WENDROCK H, BÖNISCH M, VOLEGOVA S, CALIN M, ECKERT J. Nanoindentation and wear properties of Ti and Ti-TiB composite materials produced by selective laser melting [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2017, 688: 20–26. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2017.01.096.
MANDAL A, TIWARI J K, SATHISH N, SRIVASTAVA A K. Microstructural and mechanical properties evaluation of graphene reinforced stainless steel composite produced via selective laser melting [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2020, 774: 138936. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2020.138936.
BELYAKOV A, WEI F G, TSUZAKI K, KIMURA Y, MISHIMA Y. Incomplete recrystallization in cold worked steel containing TiC [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2007, 471(1,2): 50–56. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2007.04.022.
WANG Z J, QIU Z X, SUN H Y, LIU W C. Effect of TiC content on the microstructure, texture and mechanical properties of 1060/Al-TiC/1060 laminated composites [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2019, 806: 788–797. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.07.317.
WEI Ying-kang, LUO Xiao-tao, CHU Xin, HUANG Guosheng, LI Chang-jiu. Solid-state additive manufacturing high performance aluminum alloy 6061 enabled by an in situ micro-forging assisted cold spray [J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2020, 776: 139024. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2020.139024.
ARABNEJAD S, BURNETT JOHNSTON R, PURA J A, SINGH B, TANZER M, PASINI D. High-strength porous biomaterials for bone replacement: A strategy to assess the interplay between cell morphology, mechanical properties, bone ingrowth and manufacturing constraints [J]. Acta Biomaterialia, 2016, 30: 345–356. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2015.10.048.
BENEDETTI M, DU PLESSIS A, RITCHIE R O, DALLAGO M, RAZAVI S M J, BERTO F. Architected cellular materials: A review on their mechanical properties towards fatigue-tolerant design and fabrication [J]. Materials Science and Engineering R: Reports, 2021, 144: 100606. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mser.2021.100606.
WEI Ying-kang, LUO Xiao-tao, GE Yi, CHU Xin, HUANG Guo-sheng, LI Chang-jiu. Deposition of fully dense Al-based coatings via in situ micro-forging assisted cold spray for excellent corrosion protection of AZ31B magnesium alloy [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2019, 806: 1116–1126. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.07.279.
KRISHNA N G, GEORGE R P, PHILIP J. Anomalous enhancement of corrosion resistance and antibacterial property of commercially pure Titanium (CP-Ti) with nanoscale rutile titania film [J]. Corrosion Science, 2020, 172: 108678. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2020.108678.
WEI Ying-kang, LUO Xiao-tao, CHU Xin, GE Yi, HUANG Guo-sheng, XIE Ying-chun, HUANG Ren-zhong, LI Chang-jiu. Ni coatings for corrosion protection of Mg alloys prepared by an in situ micro-forging assisted cold spray: Effect of powder feedstock characteristics [J]. Corrosion Science, 2021, 184: 109397. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2021.109397.
HAN Bin, ZHU Shi-gen, DONG Wei-wei, BAI Yun-feng, DING Hao, LUO Yi-lan, DI Ping. Improved mechanical performance and electrochemical corrosion of WC-Al2O3 composite in NaCl solution by adding the TiC additives [J]. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials, 2021, 99: 105566. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2021.105566.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YANG Xin: Funding acquisition, supervision, writing-review and edition; ZHANG Zhao-yang: Data curation, writing-original draft; WANG Ben, MA Wen-jun and WANG Wan-lin: Methodology; CHEN Wen-ge and KANG Ning-ning: Funding acquisition, investigation; LIU Shi-feng: Writingreview and editing.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Foundation item: Projects(51504191, 51671152, 51874225) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(2019GY-188) supported by the Key R&D Projects of Shaanxi, China; Project(18JC019) supported by the Industrialization Project of Shaanxi Education Department, China; Project(PMMSLKL-901) supported by the State Key Laboratory of Metal Porous Materials, China; Project(2020ZDLGY13-10) supported by the Science & Technology Project of Shaanxi, China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, X., Zhang, Zy., Wang, B. et al. Microstructure, mechanical properties and corrosion performance of selective laser melting Ti/GNPs composite with a porous structure. J. Cent. South Univ. 28, 2257–2268 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-021-4767-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-021-4767-x
Key words
- porous GNPs/Ti composites
- selective laser melting
- microstructure
- mechanical properties
- corrosion properties