Abstract
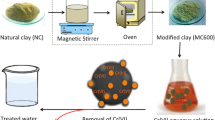
Chemically modified clay (CMC) was used as an adsorbent for the removal of Astrazon Golden Yellow 7GL (AGY-7GL), which is a basic dye from wastewater. For this purpose, the chemically modified clay was first characterized by determining zero point of charge (pHzpc), and using BET, SEM and FTIR. Then effects of operational parameters on adsorption of AGY-7GL were studied in a batch system. The effect of various parameters such as contact time (0−180 min), pH (2−8), temperature (293−323 K), CMC concentration (0.075−0.5 mg/L) and initial AGY-7GL concentration (75−250 mg/L) were investigated on the adsorption efficiency and capacity adsorption of CMC for the removal of AGY-7GL. Thermodynamic and kinetic parameters were calculated from the results of the adsorption experiment. The evaluation of kinetic models shows that this data best fits the pseudo-second-order model. It is determined that the adsorption equilibrium data works very well with the nonlinear Freundlich isotherm model. Thermodynamic parameters such as ΔH 0 (19.0 kJ/mol), ΔG 0 (−28.8 kJ/mol) and ΔS 0 (0.148 kJ/mol) were also determined. According to the experimental results, it is concluded that CMC could be used as an alternative low cost potential adsorbent for the removal of AGY-7GL from wastewater.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
GONG R M, LI M, YANG C, SUN Y Z, CHEN J. Removal of cationic dyes from aqueous solution by adsorption on peanut hull [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2005, 121(1–3): 247–250.
CHHABRA M, MISHRA S, SREEKRISHNAN T R. Combination of chemical and enzymatic treatment for efficient decolorization/ degradation of textile effluent: High operational stability of the continuous process [J]. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 2015, 93: 17–24.
DIZGE N, AYDINER C, DEMIRBAS E, KOBYA M, KARA S. Adsorption of reactive dyes from aqueous solutions by fly ash: Kinetic and equilibrium studies [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2008, 150(3): 737–746.
LEE J W, CHOI S P, THIRUVENKATACHARI R, SHIM W G, MOON H. Evaluation of the performance of adsorption and coagulation processes for the maximum removal of reactive dyes [J]. Dyes and Pigments, 2006, 69(3): 196–203.
AKSAKAL O, UCUN H. Equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies of the biosorption of textile dye (Reactive Red 195) onto Pinus sylvestris L [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2010, 181(1–3): 666–672.
GONZALEZ J A, VILLANUEVA M E, PIEHL L L, COPELLO G J. Development of a chitin/graphene oxide hybrid composite for the removal of pollutant dyes: Adsorption and desorption study [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2015, 280: 41–48.
ANNADURAI G, LING L Y, LEE J F. Adsorption of reactive dye from an aqueous solution by chitosan: Isotherm, kinetic and thermodynamic analysis [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2008, 152(1): 337–346.
AMIN N K. Removal of direct blue-106 dye from aqueous solution using new activated carbons developed from pomegranate peel: Adsorption equilibrium and kinetics [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2009, 165(1–3): 52–62.
TURGAY O, ERSOZ G, ATALAY S, FORSS J, WELANDER U. The treatment of azo dyes found in textile industry wastewater by anaerobic biological method and chemical oxidation [J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2011, 79(1): 26–33.
KIM T H, PARK C, KIM S. Water recycling from desalination and purification process of reactive dye manufacturing industry by combined membrane filtration [J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2005, 13(8): 779–786.
MOGHADDAM S S, MOGHADDAM M R A, ARAMI M. Coagulation/flocculation process for dye removal using sludge from water treatment plant: Optimization through response surface methodology [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2010, 175(1–3): 651–657.
NATARAJ S K, HOSAMANI K M, AMINABHAVI T M. Nanofiltration and reverse osmosis thin film composite membrane module for the removal of dye and salts from the simulated mixtures [J]. Desalination, 2009, 249(1): 12–17.
DULMAN V, CUCU-MAN S M. Sorption of some textile dyes by beech wood sawdust [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2009, 162(2–3): 1457–1464.
MAHMOODI N M, SALEHI R, ARAMI M, BAHRAMI H. Dye removal from colored textile wastewater using chitosan in binary systems [J]. Desalination, 2011, 267(1): 64–72.
AHMED S A S, KHALIL L B, EL-NABARAWY T. Removal of reactive blue 19 dye from aqueous solution using natural and modified orange peel [J]. Carbon Letters, 2012, 13(4): 212–220.
SELEN V, OZER D, OZER A. A study on the removal of Cr(VI) ions by sesame (sesamum indicum) stems dehydrated with sulfuric acid [J]. Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering, 2014, 39(8): 5895–5904.
CICEK F, OZER D, OZER A, OZER A. Low cost removal of reactive dyes using wheat bran [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2007, 146(1, 2): 408–416.
ZHANG Z Y, ZHANG Z B, FERNANDEZ Y, MENENDEZ J A, NIU H, PENG J H, ZHANG L B, GUO S H. Adsorption isotherms and kinetics of methylene blue on a low-cost adsorbent recovered from a spent catalyst of vinyl acetate synthesis [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2010, 256(8): 2569–2576.
AKSU Z, ISOGLU I A. Us of agricultural waste sugar beet pulp for the removal of Gemazol turquoise blue-G reactive dye from aqueous solution [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2006, 137(1): 418–430.
SILVA J P, SOUSA S, RODRIGUES J, ANTUNES H, PORTER J J, GONCALVES I, FERREIRA-DIAS S. Adsorption of acid orange 7 dye in aqueous solutions by spent brewery grains [J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2004, 40(3): 309–315.
WANG S B, BOYJOO Y, CHOUEIB A, ZHU Z H. Removal of dyes from aqueous solution using fly ash and red mud [J]. Water Research, 2005, 39(1): 129–138.
SANTHY K, SELVAPATHY P. Removal of reactive dyes from wastewater by adsorption on coir pith activated carbon [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2006, 97(11): 1329–1336.
OZER A, AKKAYA G, TURABIK M. Biosorption of Acid Blue 290 (AB 290) and Acid Blue 324 (AB 324) dyes on Spirogyra rhizopus [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2006, 135(1–3): 355–364.
KARAGOZ S, TAY T, UCAR S, ERDEM M. Activated carbons from waste biomass by sulfuric acid activation and their use on methylene blue adsorption [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2008, 99(14): 6214–6222.
MADEJOVA J, KOMADEL P. Baseline studies of the clay minerals society source clays: Infrared methods [J]. Clays and Clay Minerals, 2001, 49(5): 410–432.
LIU H M, YUAN P, QIN Z H, LIU D, TAN D Y, ZHU J X, HE H P. Thermal degradation of organic matter in the interlayer clay-organic complex: A TG-FTIR study on a montmorillonite/12-aminolauric acid system [J]. Applied Clay Science, 2013, 80–81: 398–406.
DANISH M, HASHIM R, IBRAHIM M N M, SULAIMAN O. Characterization of physically activated acacia mangium wood-based carbon for the removal of methyl orange dye [J]. Bioresources, 2013, 8(3): 4323–4339.
LOPEZ-RAMON M V, STOECKLI F, MORENO-CASTILLA C, CARRASCO-MARIN F. On the characterization of acidic and basic surface sites on carbons by various techniques [J]. Carbon, 1999, 37(8): 1215–1221.
JIA Y F, XIAO B, THOMAS K M. Adsorption of metal ions on nitrogen surface functional groups in activated carbons [J]. Langmuir, 2002, 18(2): 470–478.
YAO Y J, HE B, XU F F, CHEN X F. Equilibrium and kinetic studies of methyl orange adsorption on multiwalled carbon nanotubes [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2011, 170(1): 82–89.
WANG P F, CAO M H, WANG C, AO Y H, HOU J, QIAN J. Kinetics and thermodynamics of adsorption of methylene blue by a magnetic graphene-carbon nanotube composite [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2014, 290: 116–124.
VIJAYARAGHAVAN K, YUN Y S. Bacterial biosorbents and biosorption [J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2008, 26(3): 266–291.
AKSU Z, TEZER S. Equilibrium and kinetic modelling of biosorption of Remazol Black B by Rhizopus arrhizus in a batch system: Effect of temperature [J]. Process Biochemistry, 2000, 36(5): 431–439.
OZER D, DURSUN G, OZER A. Methylene blue adsorption from aqueous solution by dehydrated peanut hull [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2007, 144(1, 2): 171–179.
FRANCA A S, OLIVEIRA L S, FERREIRA M E. Kinetics and equilibrium studies of methylene blue adsorption by spent coffee grounds [J]. Desalination, 2009, 249(1): 267–272.
ALKAN M, CELIKCAPA S, DEMIRBAS O, DOGAN M. Removal of reactive blue 221 and acid blue 62 anionic dyes from aqueous solutions by sepiolite [J]. Dyes and Pigments, 2005, 65(3): 251–259.
NASUHA N, HAMEED B H, DIN A T M. Rejected tea as a potential low-cost adsorbent for the removal of methylene blue [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2010, 175(1–3): 126–132.
PANDAY K K, PRASAD G, SINGH V N. Copper(II) removal from aqueous-solutions by fly-ash [J]. Water Research, 1985, 19(7): 869–873.
HO Y S, MCKAY G. Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes [J]. Process Biochemistry, 1999, 34(5): 451–465.
GIL A, ASSIS F C C, ALBENIZ S, KORILI S A. Removal of dyes from wastewaters by adsorption on pillared clays [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2011, 168(3): 1032–1040.
WAHAB M A, JELLALI S, JEDIDI N. Ammonium biosorption onto sawdust: FTIR analysis, kinetics and adsorption isotherms modeling [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2010, 101(14): 5070–5075.
GAO J F, ZHANG Q, SU K, CHEN R N, PENG Y Z. Biosorption of acid yellow 17 from aqueous solution by non-living aerobic granular sludge [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2010, 174(1–3): 215–225.
LIU Y, LIU Y. Biosorption isotherms, kinetics and thermodynamics [J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2008, 61(3): 229–242.
ALVER E, METIN A U. Anionic dye removal from aqueous solutions using modified zeolite: Adsorption kinetics and isotherm studies [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2012, 200: 59–67.
PANNEERSELVAM P, MORAD N, TAN K A. Magnetic nanoparticle (Fe3O4) impregnated onto tea waste for the removal of nickel(II) from aqueous solution [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2011, 186(1): 160–168.
AL-DEGS Y S, EL-BARGHOUTHI M I, EL-SHEIKH A H, WALKER G M. Effect of solution pH, ionic strength, and temperature on adsorption behavior of reactive dyes on activated carbon [J]. Dyes and Pigments, 2008, 77(1): 16–23.
GURSES A, DOGAR C, YALCIN M, ACIKYILDIZ M, BAYRAK R, KARACA S. The adsorption kinetics of the cationic dye, methylene blue, onto clay [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2006, 131(1–3): 217–228.
KARAGOZOGLU B, TASDEMIR M, DEMIRBAS E, KOBYA M. The adsorption of basic dye (Astrazon Blue FGRL) from aqueous solutions onto sepiolite, fly ash and apricot shell activated carbon: Kinetic and equilibrium studies [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2007, 147(1, 2): 297–306.
TURABIK M. Adsorption of basic dyes from single and binary component systems onto bentonite: Simultaneous analysis of Basic Red 46 and Basic Yellow 28 by first order derivative spectrophotometric analysis method [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2008, 158(1): 52–64.
TAHIR S S, RAUF N. Removal of a cationic dye from aqueous solutions by adsorption onto bentonite clay [J]. Chemosphere, 2006, 63(11): 1842–1848.
OZCAN A, OMEROGLU C, ERDOGAN Y, OZCAN A S. Modification of bentonite with a cationic surfactant: An adsorption study of textile dye Reactive Blue 19 [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2007, 140(1, 2): 173–179.
VIMONSES V, LEI S M, JIN B, CHOWD C W K, SAINT C. Kinetic study and equilibrium isotherm analysis of Congo Red adsorption by clay materials [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2009, 148(2, 3): 354–364.
ALMEIDA C A P, DEBACHER N A, DOWNS A J, COTTET L, MELLO C A D. Removal of methylene blue from colored effluents by adsorption on montmorillonite clay [J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2009, 332(1): 46–53.
PUNJONGHARN P, MEEVASANA K, PAVASANT P. Influence of particle size and salinity on adsorption of basic dyes by agricultural waste: Dried Seagrape (Caulerpa lentillifera) [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences-China, 2008, 20(6): 760–768.
SULAK M T, DEMIRBAS E, KOBYA M. Removal of Astrazon Yellow 7GL from aqueous solutions by adsorption onto wheat bran [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2007, 98(13): 2590–2598.
DEMIRBAS E, KOBYA M, SULAK M T. Adsorption kinetics of a basic dye from aqueous solutions onto apricot stone activated carbon [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2008, 99(13): 5368–5373.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Çakmak, M., Taşar, Ş., Selen, V. et al. Removal of astrazon golden yellow 7GL from colored wastewater using chemically modified clay. J. Cent. South Univ. 24, 743–753 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-017-3476-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-017-3476-y