Abstract
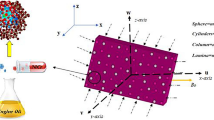
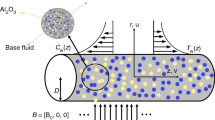
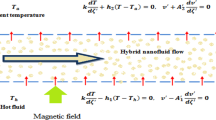
The intention of the current research is to address the conclusion of non-isothermal heterogeneous reaction on the stagnation — point flow of SWCNT — engine oil and MWCNT — engine oil nanofluid over a shrinking/stretching sheet. Further, exemplify the aspect of heat and mass transfer the upshot of magnetohydrodynamics (MHD), thermal radiation, and heat generation/absorption coefficient are exemplified. The bvp4c from Matlab is pledged to acquire the numerical explanation of the problem that contains nonlinear system of ordinary differential equations (ODE). The impacts of miscellaneous important parameters on axial velocity, temperature field, concentration profile, skin friction coefficient, and local Nusselt number, are deliberated through graphical and numerically erected tabulated values. The solid volume fraction diminishes the velocity distribution while enhancing the temperature distribution. Further, the rate of shear stress declines with increasing the magnetic and stretching parameter for both SWCNT and MWCNT.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J H Merkin. A model for isothermal homogeneous-heterogeneous reactions in boundary-layer flow. Math Comput Model, 1996, 24(8): 125–136.
M A Chaudhary, and J H Merkin. A simple isothermal model for homogeneous-heterogeneous reactions in boundary-layer flow. I Equal diffusivities. Fluid Dyn Res, 1995, 16(6): 311.
A Mahdy. Aspects of homogeneous-heterogeneous reactions on natural convection flow of micropolar fluid past a permeable cone, Appl Math Comput, 2019, 352: 59–67.
H Xu. Homogeneous—Heterogeneous Reactions of Blasius Flow in a Nanofluid. J Heat Transfer, 2019, 141(2): 024501.
S Nadeem, N Ullah, A U Khan, T Akbar. Effect of homogeneous-heterogeneous reactions on ferrofluid in the presence of magnetic dipole along a stretching cylinder, Results Phys, 2017, 7: 3574–3582.
S Nadeem, S Ahmad, N Muhammad, M T Mustafa. Chemically reactive species in the flow of a Maxwell fluid, Results Phys, 2017, 7: 2607–2613.
M Khan, L Ahmad, M Ayaz. Numerical simulation of unsteady 3D magneto-Sisko fluid flow with nonlinear thermal radiation and homogeneous—heterogeneous chemical reactions. Pramana, 2018, 91(1): 13.
M Ramzan, S Ahmad, D Lu. Numerical simulation for homogeneous-heterogeneous reactions and Newtonian heating in the silver-water nanofluid flow past a nonlinear stretched cylinder. Phys Scr, 2019, 94(8): 085702.
M M Bhatti, R Ellahi, A Zeeshan, M Marin, N Ijaz. Numerical study of heat transfer and Hall current impact on peristaltic propulsion of particle-fluid suspension with compliant wall properties. Mod Phys Lett B, 2019, 33(35): 1950439.
S U S Choi, J A Eastman. Enhancing thermal conductivity of fluids with nanoparticles, No. ANL/MSD/CP-84938; CONF-951135–29. Argonne National Lab, IL (United States), 1995.
S Nadeem, S Ahmad, and N Muhammad. Computational study of Falkner-Skan problem for a static and moving wedge, Sens Actuators B: Chem, 2018, 263: 69–76.
W A Khan, and I Pop. Boundary-layer flow of a nanofluid past a stretching sheet. Int J Heat Mass Tran, 2010, 53(11–12): 2477–2483.
S Z Heris, M N Esfahany, and S Gh Etemad. Experimental investigation of convective heat transfer of Al2O3/water nanofluid in circular tube. Int J Heat Fluid Fl, 2007, 28(2): 203–210.
Q Li, Y Xuan. Convective heat transfer and flow characteristics of Cu-water nanofluid. Sci China Ser E: Technol Sci, 2002, 45(4): 408–416.
S Nadeem, T Hayat, A U Khan. Numerical study on 3D rotating hybrid SWCNT-MWCNT flow over a convectively heated stretching surface with heat generation/absorption. Phys Scr, 2019, 94(7): 075202.
A Sarlak, A Ahmadpour, M R Hajmohammadi. Thermal design improvement of a double-layered microchannel heat sink by using multi-walled carbon nanotube (MWCNT) nanofluids with non-Newtonian viscosity, Appl Therm Eng, 2019, 147: 205–215.
A Hussanan, I Khan, M R Gorji, W A Khan. CNT S-Water—Based Nanofluid Over a Stretching Sheet, BioNanoScience 2019, 9(1): 21–29.
N Muhammad, and S Nadeem. Ferrite nanoparticles Ni — ZnFe2O4: Mn — ZnFe2O4and Fe2O4in the flow of ferromagnetic nanofluid. Eur Phys J Plus, 2017, 132(9): 377.
L Zhang, M B Arain, M M Bhatti, A Zeeshan, H Hal-Sulami. Effects of magnetic Reynolds number on swimming of gyrotactic microorganisms between rotating circular plates filled with nanofluids. Appl Math Mech-Engl, 2020, 41(4): 637–654.
M M Bhatti, A Shahid, T Abbas, S Z Alamri, R Ellahi. Study of activation energy on the movement of gyrotactic microorganism in a magnetized nanofluids past a porous plate. Processes, 2020, 8(3): 328.
K Hiemenz. Die Grenzschicht an einem in den gleichformigen Flussigkeitsstrom eingetauchten geraden Kreiszylinder, Dinglers Polytech. J, 1911, 326: 321–324.
N S Akbar, Z H Khan, S Nadeem. The combined effects of slip and convective boundary conditions on stagnation-point flow of CNT suspended nanofluid over a stretching sheet, J Mol Liq, 2014, 196: 21–25.
Z Iqbal, E Azhar, E N Maraj. Transport phenomena of carbon nanotubes and bioconvection nanoparticles on stagnation point flow in presence of induced magnetic field, Physica E Low Dimens Syst Nanostruct, 2017, 91: 128–135.
T Hayat, M Farooq, A Alsaedi. Homogeneous-heterogeneous reactions in the stagnation point flow of carbon nanotubes with Newtonian heating. AIP Adv, 2015, 5(2): 027130.
R U Haq, S Nadeem, Z H Khan, N F M Noor. Convective heat transfer in MHD slip flow over a stretching surface in the presence of carbon nanotubes, Physica B: Condens Matter, 2015, 457: 40–47.
M A Chaudhary, J H Merkin. Free convection boundary layers driven by exothermic surface reactions: critical ambient temperatures. Math Eng Industry, 1995, 5(2): 129–145.
J H Merkin, I Pop. Stagnation point flow past a stretching/shrinking sheet driven by Arrhenius kinetics, Appl Math Comput, 2018, 337: 583–590.
Q Z Xue. Model for thermal conductivity of carbon nanotube-based composites. Physica B: Condens Matter, 2005, 368(1–4): 302–307.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nadeem, S., Ahmad, S., Issakhov, A. et al. MHD stagnation point flow of nanofluid with SWCNT and MWCNT over a stretching surface driven by Arrhenius kinetics. Appl. Math. J. Chin. Univ. 37, 366–382 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11766-022-3966-z
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11766-022-3966-z