Abstract
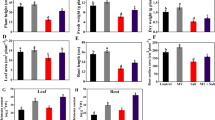
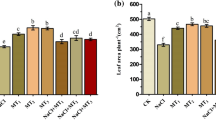
Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) is the most cultivated forage plant as a model in legumes. The growth and development of alfalfa root limited by salt stress. Growth regulator is an essential role of melatonin in plants, especially in root involved in stress tolerance. In this study, alfalfa root under in vitro culture was treated with salinity (150 and 200 mM NaCl) as well as different concentrations of melatonin (0.1, 10 and 15 µM). Treated plants by using melatonin increased compatible solutes such as glycine betaine, soluble carbohydrate and K+ under salt stress in alfalfa root. In contrast, melatonin decreased reactive oxygen species (ROS), hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), superoxide anion (O2−), malondialdehyde (MDA), electrolyte leakage (EL) and Na+ content in root treated with salinity. Interestingly, melatonin increased endogenous melatonin, indole-3-acetic acid (IAA), fresh and dry weight of the alfalfa root. According to our findings, all of the melatonin concentrations had a positive effect as a growth regulator but looking at the overall data 0.1 µM melatonin was the best candidate for increasing salt tolerance and reducing oxidative stress in alfalfa root.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
In case of request, it would be available.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Change history
09 May 2023
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11756-023-01425-3
Abbreviations
- GB:
-
Glycin betaine
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- H2O2 :
-
Hydrogen peroxide
- DAB:
-
3,3′-diaminobenzidine
- O2−:
-
Superoxide anion
- NBT:
-
Nitroblue tetrazolium
- MDA:
-
Malondialdehyde
- EL:
-
Electrolyte leakage
- EC:
-
Electrical conductivity
- IAA:
-
Indole-3-acetic acid
- MS:
-
Murashige Skoog
- TBARS:
-
Thiobarbituric acid
- TCA:
-
Trichloroacetic acid
- TBA:
-
Thiobarbituric acid
- DCFDA:
-
2’,7’-dichlorofluorescin diacetate
- DCF:
-
2’,7’-dichlorofluorescein
- HPLC:
-
High-performance liquid chromatography
- PCA:
-
Principal component analysis
- ABA:
-
Abscisic acid
- GA:
-
Gibberellic acids
- CK:
-
Cytokinins
- TDC:
-
Tryptophan decarboxylase
- SNAT:
-
Serotonin N-acetyltransferase
- ASMT:
-
N-acetylserotonin methyltransferase
References
Ahmad S, Wang G-Y, Muhammad I, Zeeshan M, Zhou X-B (2022) Melatonin and KNO3 application improves growth, physiological and biochemical characteristics of Maize seedlings under waterlogging stress conditions. Biology 11:99. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11010099
Altaf MA, Shahid R, Ren M-X, Naz S, Altaf MM, Khan LU, Tiwari RK, Lal MK, Shahid MA, Kumar R (2022) Melatonin improves drought stress tolerance of tomato by modulating plant growth, root architecture, photosynthesis, and antioxidant defense system. Antioxidants 11:309. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11020309
Arnao M, Hernández-Ruiz J (2017) Growth activity, rooting capacity, and tropism: three auxinic precepts fulfilled by melatonin. Acta Physiol Plant 39:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-017-2428-3
Arnao MB, Hernández-Ruiz J (2018) Melatonin and its relationship to plant hormones. Ann Bot 121:195–207. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcx114
Arnao MB, Hernández-Ruiz J (2021) Melatonin against environmental plant stressors: a review. Curr Protein Pept Sci 22:413–429. https://doi.org/10.2174/1389203721999210101235422
Arnao MB, Hernández-Ruiz J, Cano A, Reiter RJ (2021) Melatonin and carbohydrate metabolism in plant cells. Plants 10:1917. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10091917
Bates LS, Waldren RP, Teare ID (1973) Rapid determination of free proline for water-stress studies. Plant Soil 39(1):205–207. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00018060
Bhattarai S, Biswas D, Fu Y-B, Biligetu B (2020) Morphological, physiological, and genetic responses to salt stress in alfalfa: a review. Agronomy 10:577. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10040577
Bündig C, Vu T, Meise P, Seddig S, Schum A, Winkelmann T (2017) Variability in osmotic stress tolerance of starch potato genotypes (Solanum tuberosum L.) as revealed by an in vitro screening: role of proline, osmotic adjustment and drought response in pot trials. J Agron Crop Sci 203:206–218. https://doi.org/10.1111/jac.12186
Cen H, Wang T, Liu H, Tian D, Zhang Y (2020) Melatonin application improves salt tolerance of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) by enhancing antioxidant capacity. Plants 9:220. https://dx.doi.org/10.3390%2Fplants9020220
Chen L, Lu B, Liu L, Duan W, Jiang D, Li J, Zhang K, Sun H, Zhang Y, Li C (2021) Melatonin promotes seed germination under salt stress by regulating ABA and GA3 in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Plant Physiol Biochem 162:506–516. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-27842/v1
Dubois M, Gilles KA, Hamilton JK, Rebers Pt, Smith F (1956) Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal Chem 28:350–356. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac60111a017
Fryer MJ, Oxborough K, Mullineaux PM, Baker NR (2002) Imaging of photo-oxidative stress responses in leaves. J Exp Bot 53:1249–1254. https://doi.org/10.1093/jexbot/53.372.1249
Grieve C, Grattan S (1983) Rapid assay for determination of water soluble quaternary ammonium compounds. Plant soil 70:303–307. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02374789
Gupta B, Huang B (2014) Mechanism of salinity tolerance in plants: physiological, biochemical, and molecular characterization. Int j genomics 2014. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/701596
Heath RL, Packer L (1968) Photoperoxidation in isolated chloroplasts: I. Kinetics and stoichiometry of fatty acid peroxidation. Arch Biochem Biophys 125:189–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-9861(68)90654-1
Hniličková H, Hnilička F, Orsák M, Hejnák V (2019) Effect of salt stress on growth, electrolyte leakage, Na+ and K+ content in selected plant species. Plant Soil Environ 65:90–96. https://doi.org/10.17221/620/2018-PSE
Hossain M, Li J, Sikdar A, Hasanuzzaman M, Uzizerimana F, Muhammad I, Yuan Y, Zhang C, Wang C, Feng B (2020) Exogenous melatonin modulates the physiological and biochemical mechanisms of drought tolerance in tartary buckwheat (Fagopyrum tataricum (L.) Gaertn). Molecules 25:2828. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25122828
Iriti M, Rossoni M, Faoro F (2006) Melatonin content in grape: myth or panacea? J Sci Food Agric 86:1432–1438. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.2537
Khan A, Numan M, Khan AL, Lee I-J, Imran M, Asaf S, Al-Harrasi A (2020) Melatonin: awakening the defense mechanisms during plant oxidative stress. Plants 9:407. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9040407
Kobylińska A, Borek S, Posmyk MM (2018) Melatonin redirects carbohydrates metabolism during sugar starvation in plant cells. J Pineal Res 64:e12466. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12466
Li H, Chang J, Chen H, Wang Z, Gu X, Wei C, Zhang Y, Ma J, Yang J, Zhang X (2017) Exogenous melatonin confers salt stress tolerance to watermelon by improving photosynthesis and redox homeostasis. Front plant sci 8:295. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.00295
Li J, Liu Y, Zhang M, Xu H, Ning K, Wang B, Chen M (2022) Melatonin increases growth and salt tolerance of Limonium bicolor by improving photosynthetic and antioxidant capacity. BMC Plant Biol 22:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-021-03402-x
Liang C, Li A, Yu H, Li W, Liang C, Guo S, Zhang R, Chu C (2017) Melatonin regulates root architecture by modulating auxin response in rice. Front Plant Sci 8:134. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.00134
Lutts S, Kinet J, Bouharmont J (1995) Changes in plant response to NaCl during development of rice (Oryza sativa L.) varieties differing in salinity resistance. J Exp Bot 46:1843–1852. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/46.12.1843
MA X-h CHEN, R-m LIU, X-q ZHAOJ, ZHANG X (2021) Effects of melatonin on root growth and drought tolerance of maize seedlings. Biotechnol Bull 37:1. https://doi.org/10.13560/j.cnki.biotech.bull.1985.2020-0575
Ma Z, Ge L, Lee AS, Yong JWH, Tan SN, Ong ES (2008) Simultaneous analysis of different classes of phytohormones in coconut (Cocos nucifera L.) water using high-performance liquid chromatography and liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry after solid-phase extraction. Anal Chim Acta 610:274–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2008.01.045
Mahalingam R, Jambunathan N, Gunjan SK, Faustin E, Weng H, Ayoubi P (2006) Analysis of oxidative signalling induced by ozone in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Environ 29:1357–1371. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3040.2006.01516.x
Mao J, Niu C, Li K, Chen S, Tahir MM, Han M, Zhang D (2020) Melatonin promotes adventitious root formation in apple by promoting the function of MdWOX11. BMC Plant Biol 20:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-020-02747-z
Moustafa-Farag M, Almoneafy A, Mahmoud A, Elkelish A, Arnao MB, Li L, Ai S (2019) Melatonin and its protective role against biotic stress impacts on plants. Biomolecules 10:54. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10010054
Mukhopadhyay R, Sarkar B, Jat HS, Sharma PC, Bolan NS (2021) Soil salinity under climate change: Challenges for sustainable agriculture and food security. J Environ Manage 280:111736. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111736
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bio assays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–497. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-3054.1962.tb08052.x
Murch SJ, Erland LA (2021) A systematic review of melatonin in plants: an example of evolution of literature. Front Plant Sci 12:1060. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2021.683047
Nawaz K, Chaudhary R, Sarwar A, Ahmad B, Gul A, Hano C, Abbasi BH, Anjum S (2020) Melatonin as master regulator in plant growth, development and stress alleviator for sustainable agricultural production: current status and future perspectives. Sustainability 13:294. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13010294
Reddy INBL, Kim B-K, Yoon I-S, Kim K-H, Kwon T-R (2017) Salt tolerance in rice: focus on mechanisms and approaches. Rice Sci 24:123–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rsci.2016.09.004
Rook G, Steele J, Umar S, Dockrell H (1985) A simple method for the solubilisation of reduced NBT, and its use as a colorimetric assay for activation of human macrophages by γ-interferon. J Immunol Methods 82:161–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1759(85)90235-2
Salemi F, Esfahani MN, Tran L-SP (2019) Mechanistic insights into enhanced tolerance of early growth of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) under low water potential by seed-priming with ascorbic acid or polyethylene glycol solution. Ind Crops Prod 137:436–445. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2019.05.049
Sarker U, Oba S (2020) The response of salinity stress-induced A. tricolor to growth, anatomy, physiology, non-enzymatic and enzymatic antioxidants. Front Plant Sci 1354. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2020.559876
Sarropoulou V, Dimassi-Theriou K, Therios I, Koukourikou-Petridou M (2012) Melatonin enhances root regeneration, photosynthetic pigments, biomass, total carbohydrates and proline content in the cherry rootstock PHL-C (Prunus avium× Prunus cerasus). Plant Physiol Biochem 61:162–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2012.10.001
Shi G, Liu C, Cui M, Ma Y, Cai Q (2012) Cadmium tolerance and bioaccumulation of 18 hemp accessions. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 168:163–173. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-011-9382-0
Thordal-Christensen H, Zhang Z, Wei Y, Collinge DB (1997) Subcellular localization of H2O2 in plants. H2O2 accumulation in papillae and hypersensitive response during the barley—powdery mildew interaction. Plant J 11:1187–1194. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-313X.1997.11061187.x
Velikova V, Yordanov I, Edreva A (2000) Oxidative stress and some antioxidant systems in acid rain-treated bean plants: protective role of exogenous polyamines. Plant sci 151:59–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-9452(99)00197-1
Wang L, Liu J, Wang W, Sun Y (2016) Exogenous melatonin improves growth and photosynthetic capacity of cucumber under salinity-induced stress. Photosynthetica 54:19–27. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11099-015-0140-3
Wang Q, An B, Wei Y, Reiter RJ, Shi H, Luo H, He C (2016) Melatonin regulates root meristem by repressing auxin synthesis and polar auxin transport in Arabidopsis. Front Plant Sci 7:1882. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.01882
Yang H, Dai L, Wei Y, Deng Z, Li D (2020) Melatonin enhances salt stress tolerance in rubber tree (Hevea brasiliensis) seedlings. Ind Crops Prod 145:111990. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2019.111990
Yang L, You J, Li J, Wang Y, Chan Z (2021) Melatonin promotes Arabidopsis primary root growth in an IAA-dependent manner. J Exp Bot 72:5599–5611. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erab196
Yu Y, Wang A, Li X, Kou M, Wang W, Chen X, Xu T, Zhu M, Ma D, Li Z (2018) Melatonin-stimulated triacylglycerol breakdown and energy turnover under salinity stress contributes to the maintenance of plasma membrane H+–ATPase activity and K+/Na+ homeostasis in sweet potato. Front Plant Sci 9:256. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.00256
Zhang Y, Li D, Zhou R, Wang X, Dossa K, Wang L, Zhang Y, Yu J, Gong H, Zhang X (2019) Transcriptome and metabolome analyses of two contrasting sesame genotypes reveal the crucial biological pathways involved in rapid adaptive response to salt stress. BMC Plant Biol 19:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-019-16656
Zuo B, Zheng X, He P, Wang L, Lei Q, Feng C, Zhou J, Li Q, Han Z, Kong J (2014) Overexpression of MzASMT improves melatonin production and enhances drought tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana plants. J Pineal Res 57:408–417. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12180
Acknowledgements
Author would like to thank the Plant Antioxidant Center of Excellence (OACE), the University of Isfahan for their support. We also acknowledge Prof. Acram Taji for extensive english editing of the manuscript.
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Shabnam Jalili carried out the experimental lab analysis and wrote the first draft of the manuscript, Ali Akbar Ehsanpour edited, organized and submitted the manuscript and Seyed Morteza Javadirad helped us for designing of some parts of the experiments.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest/competing interests
No competing interest for the manuscript exist.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jalili, S., Ehsanpour, A. & Morteza Javadirad, S. Melatonin improves salt tolerance of in vitro root culture of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). Biologia 78, 961–970 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11756-022-01275-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11756-022-01275-5