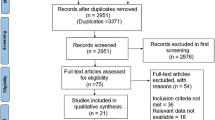
Abstract
The association among plasma trimethylamine-N-oxide (TMAO), FMO3 polymorphisms, and chronic heart failure (CHF) remains to be elucidated. TMAO is a microbiota-dependent metabolite from dietary choline and carnitine. A prospective study was performed including 955 consecutively diagnosed CHF patients with reduced ejection fraction, with the longest follow-up of 7 years. The concentrations of plasma TMAO and its precursors, namely, choline and carnitine, were determined by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry, and the FMO3 E158K polymorphisms (rs2266782) were genotyped. The top tertile of plasma TMAO was associated with a significant increment in hazard ratio (HR) for the composite outcome of cardiovascular death or heart transplantation (HR = 1.47, 95% CI = 1.13–1.91, P = 0.004) compared with the lowest tertile. After adjustments of the potential confounders, higher TMAO could still be used to predict the risk of the primary endpoint (adjusted HR = 1.33, 95% CI = 1.01–1.74, P = 0.039). This result was also obtained after further adjustment for carnitine (adjusted HR = 1.33, 95% CI = 1.01–1.74, P = 0.039). The FMO3 rs2266782 polymorphism was associated with the plasma TMAO concentrations in our cohort, and lower TMAO levels were found in the AA-genotype. Thus, higher plasma TMAO levels indicated increased risk of the composite outcome of cardiovascular death or heart transplantation independent of potential confounders, and the FMO3 AA-genotype in rs2266782 was related to lower plasma TMAO levels.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Huffman MD, Berry JD, Ning H, Dyer AR, Garside DB, Cai X, Daviglus ML, Lloyd-Jones DM. Lifetime risk for heart failure among white and black Americans: cardiovascular lifetime risk pooling project. J Am Coll Cardiol 2013; 61(14): 1510–1517
Sato N. Epidemiology of heart failure in Asia. Heart Fail Clin 2015; 11(4): 573–579
Wang Z, Klipfell E, Bennett BJ, Koeth R, Levison BS, Dugar B, Feldstein AE, Britt EB, Fu X, Chung YM, Wu Y, Schauer P, Smith JD, Allayee H, Tang WH, DiDonato JA, Lusis AJ, Hazen SL. Gut flora metabolism of phosphatidylcholine promotes cardiovascular disease. Nature 2011; 472(7341): 57–63
Tang WH, Wang Z, Levison BS, Koeth RA, Britt EB, Fu X, Wu Y, Hazen SL. Intestinal microbial metabolism of phosphatidylcholine and cardiovascular risk. N Engl J Med 2013; 368(17): 1575–1584
Tang WH, Wang Z, Fan Y, Levison B, Hazen JE, Donahue LM, Wu Y, Hazen SL. Prognostic value of elevated levels of intestinal microbe-generated metabolite trimethylamine-N-oxide in patients with heart failure: refining the gut hypothesis. J Am Coll Cardiol 2014; 64(18): 1908–1914
Wang Z, Tang WH, Buffa JA, Fu X, Britt EB, Koeth RA, Levison BS, Fan Y, Wu Y, Hazen SL. Prognostic value of choline and betaine depends on intestinal microbiota-generated metabolite trimethylamine-N-oxide. Eur Heart J 2014; 35(14): 904–910
Senthong V, Li XS, Hudec T, Coughlin J, Wu Y, Levison B, Wang Z, Hazen SL, Tang WH. Plasma trimethylamine N-oxide, a gut microbe-generated phosphatidylcholine metabolite, is associated with atherosclerotic burden. J Am Coll Cardiol 2016; 67(22): 2620–2628
Li XS, Obeid S, Klingenberg R, Gencer B, Mach F, Räber L, Windecker S, Rodondi N, Nanchen D, Muller O, Miranda MX, Matter CM, Wu Y, Li L, Wang Z, Alamri HS, Gogonea V, Chung YM, Tang WH, Hazen SL, Lüscher TF. Gut microbiota-dependent trimethylamine N-oxide in acute coronary syndromes: a prognostic marker for incident cardiovascular events beyond traditional risk factors. Eur Heart J 2017; 38(11): 814–824
Bennett BJ, de Aguiar Vallim TQ, Wang Z, Shih DM, Meng Y, Gregory J, Allayee H, Lee R, Graham M, Crooke R, Edwards PA, Hazen SL, Lusis AJ. Trimethylamine-N-oxide, a metabolite associated with atherosclerosis, exhibits complex genetic and dietary regulation. Cell Metab 2013; 17(1): 49–60
Warrier M, Shih DM, Burrows AC, Ferguson D, Gromovsky AD, Brown AL, Marshall S, McDaniel A, Schugar RC, Wang Z, Sacks J, Rong X, Vallim TA, Chou J, Ivanova PT, Myers DS, Brown HA, Lee RG, Crooke RM, Graham MJ, Liu X, Parini P, Tontonoz P, Lusis AJ, Hazen SL, Temel RE, Brown JM. The TMAO-generating enzyme flavin monooxygenase 3 is a central regulator of cholesterol balance. Cell Rep 2015; 10(3): 326–338
Schugar RC, Shih DM, Warrier M, Helsley RN, Burrows A, Ferguson D, Brown AL, Gromovsky AD, Heine M, Chatterjee A, Li L, Li XS, Wang Z, Willard B, Meng Y, Kim H, Che N, Pan C, Lee RG, Crooke RM, Graham MJ, Morton RE, Langefeld CD, Das SK, Rudel LL, Zein N, McCullough AJ, Dasarathy S, Tang WHW, Erokwu BO, Flask CA, Laakso M, Civelek M, Naga Prasad SV, Heeren J, Lusis AJ, Hazen SL, Brown JM. The TMAO-producing enzyme flavin-containing monooxygenase 3 regulates obesity and the beiging of white adipose tissue. Cell Rep 2017; 20(1): 279
Koukouritaki SB, Poch MT, Cabacungan ET, McCarver DG, Hines RN. Discovery of novel flavin-containing monooxygenase 3 (FMO3) single nucleotide polymorphisms and functional analysis of upstream haplotype variants. Mol Pharmacol 2005; 68(2): 383–392
Türkanoğlu Özçelik A, Can Demirdöğen B, Demirkaya S, Adali O. Flavin containing monooxygenase 3 genetic polymorphisms Glu158Lys and Glu308Gly and their relation to ischemic stroke. Gene 2013; 521(1): 116–121
Yancy CW, Jessup M, Bozkurt B, Butler J, Casey DE Jr, Drazner MH, Fonarow GC, Geraci SA, Horwich T, Januzzi JL, Johnson MR, Kasper EK, Levy WC, Masoudi FA, McBride PE, McMurray JJ, Mitchell JE, Peterson PN, Riegel B, Sam F, Stevenson LW, Tang WH, Tsai EJ, Wilkoff BL; American College of Cardiology Foundation; American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. 2013 ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of heart failure: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol 2013; 62(16): e147–e239
Koeth RA, Wang Z, Levison BS, Buffa JA, Org E, Sheehy BT, Britt EB, Fu X, Wu Y, Li L, Smith JD, DiDonato JA, Chen J, Li H, Wu GD, Lewis JD, Warrier M, Brown JM, Krauss RM, Tang WH, Bushman FD, Lusis AJ, Hazen SL. Intestinal microbiota metabolism of L-carnitine, a nutrient in red meat, promotes atherosclerosis. Nat Med 2013; 19(5): 576–585
Zhu Y, Jameson E, Crosatti M, Schäfer H, Rajakumar K, Bugg TD, Chen Y. Carnitine metabolism to trimethylamine by an unusual Rieske-type oxygenase from human microbiota. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2014; 111(11): 4268–4273
Koeth RA, Levison BS, Culley MK, Buffa JA, Wang Z, Gregory JC, Org E, Wu Y, Li L, Smith JD, Tang WHW, DiDonato JA, Lusis AJ, Hazen SL. γ-Butyrobetaine is a proatherogenic intermediate in gut microbial metabolism of L-carnitine to TMAO. Cell Metab 2014; 20 (5): 799–812
Cho CE, Caudill MA. Trimethylamine-N-oxide: friend, foe, or simply caught in the cross-fire? Trends Endocrinol Metab 2017; 28 (2): 121–130
Stubbs JR, House JA, Ocque AJ, Zhang S, Johnson C, Kimber C, Schmidt K, Gupta A, Wetmore JB, Nolin TD, Spertus JA, Yu AS. Serum trimethylamine-N-oxide is elevated in CKD and correlates with coronary atherosclerosis burden. J Am Soc Nephrol 2016; 27 (1): 305–313
Shafi T, Powe NR, Meyer TW, Hwang S, Hai X, Melamed ML, Banerjee T, Coresh J, Hostetter TH. Trimethylamine N-oxide and cardiovascular events in hemodialysis patients. J Am Soc Nephrol 2017; 28(1): 321–331
Westerterp M, Bochem AE, Yvan-Charvet L, Murphy AJ, Wang N, Tall AR. ATP-binding cassette transporters, atherosclerosis, and inflammation. Circ Res 2014; 114(1): 157–170
Kathirvel E, Morgan K, Nandgiri G, Sandoval BC, Caudill MA, Bottiglieri T, French SW, Morgan TR. Betaine improves nonalcoholic fatty liver and associated hepatic insulin resistance: a potential mechanism for hepatoprotection by betaine. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2010; 299(5): G1068–G1077
Wang LJ, Zhang HW, Zhou JY, Liu Y, Yang Y, Chen XL, Zhu CH, Zheng RD, Ling WH, Zhu HL. Betaine attenuates hepatic steatosis by reducing methylation of the MTTP promoter and elevating genomic methylation in mice fed a high-fat diet. J Nutr Biochem 2014; 25(3): 329–336
Lim GB. Gut flora—pathogenic role in chronic heart failure. Nat Rev Cardiol 2016; 13(2): 61
Tang WH. We are not alone: understanding the contributions of intestinal microbial communities and the congested gut in heart failure. JACC Heart Fail 2016; 4(3): 228–229
Pasini E, Aquilani R, Testa C, Baiardi P, Angioletti S, Boschi F, Verri M, Dioguardi F. Pathogenic gut flora in patients with chronic heart failure. JACC Heart Fail 2016; 4(3): 220–227
Shih DM, Wang Z, Lee R, Meng Y, Che N, Charugundla S, Qi H, Wu J, Pan C, Brown JM, Vallim T, Bennett BJ, Graham M, Hazen SL, Lusis AJ. Flavin containing monooxygenase 3 exerts broad effects on glucose and lipid metabolism and atherosclerosis. J Lipid Res 2015; 56(1): 22–37
Miao J, Ling AV, Manthena PV, Gearing ME, Graham MJ, Crooke RM, Croce KJ, Esquejo RM, Clish CB, Morbid Obesity Study Group; Vicent D, Biddinger SB. Flavin-containing monooxygenase 3 as a potential player in diabetes-associated atherosclerosis. Nat Commun 2015; 6(1): 6498
Yamazaki H, Shimizu M. Survey of variants of human flavin-containing monooxygenase 3 (FMO3) and their drug oxidation activities. Biochem Pharmacol 2013; 85(11): 1588–1593
Lambert DM, Mamer OA, Akerman BR, Choinière L, Gaudet D, Hamet P, Treacy EP. In vivo variability of TMA oxidation is partially mediated by polymorphisms of the FMO3 gene. Mol Genet Metab 2001; 73(3): 224–229
Morandi A, Zusi C, Corradi M, Olivieri F, Piona C, Fornari E, Maffeis C. Minor diplotypes of FMO3 might protect children and adolescents from obesity and insulin resistance. Int J Obes 2018; 42 (6): 1243–1248
Shan Z, Sun T, Huang H, Chen S, Chen L, Luo C, Yang W, Yang X, Yao P, Cheng J, Hu FB, Liu L. Association between microbiota-dependent metabolite trimethylamine-N-oxide and type 2 diabetes. Am J Clin Nutr 2017; 106(3): 888–894
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Key R&D Program of China (Nos. 2017YFC0909400 and 2017YFC1307700), Projects from National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 81630010, 91639108, 81770272, 81873506, 82070235, and 81790624), the Beijing Municipal Natural Science Foundation (No. 7191013), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 2020M680261), National Postdoctoral Program for Innovative Talents (No. BX20200022) and Integrated Innovative Team for Human Disease Program of Tongji Medical College, HUST (No. 2015ZDTD044).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Compliance with ethics guidelines
Haoran Wei, Mingming Zhao, Man Huang, Chenze Li, Jianing Gao, Ting Yu, Qi Zhang, Xiaoqing Shen, Liang Ji, Li Ni, Chunxia Zhao, Zeneng Wang, Erdan Dong, Lemin Zheng, and Dao Wen Wang declare that they have no conflict of interest. This study was approved by the ethics committee of Tongji Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China. This research was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and the International Conference on Harmonization Guidelines for Good Clinical Practice. Written informed consent was obtained from all individuals at admission.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, H., Zhao, M., Huang, M. et al. FMO3-TMAO axis modulates the clinical outcome in chronic heart-failure patients with reduced ejection fraction: evidence from an Asian population. Front. Med. 16, 295–305 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11684-021-0857-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11684-021-0857-2