Abstract
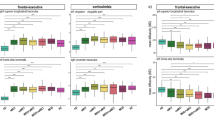
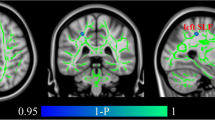
Cognitive deficit is a key feature of late-onset depression (LOD) and remains after clinical recovery. LOD has been associated with widespread neurobiological difficulties, including atrophy in gray and white matter (WM) tissue in areas distributed throughout the brain. However, little is known about the topological pattern changes of WM structural networks in LOD in the remitted state and its relationship to cognitive deficits. We acquired diffusion tensor images in 37 remitted LOD (rLOD) patients and 30 healthy controls. The tract-based spatial statistics method was employed to investigate WM tract integrity in rLOD. Graph-theory based network models were further used to characterize the topological organization of WM structural networks between the two groups. Compared with controls, rLOD patients showed decreased fractional anisotropy values in the left posterior cingulate bundle, right inferior fronto-occipital fasciculus and superior longitudinal fasciculus. Moreover, rLOD patients showed abnormal small-world architecture (i.e., increased path length and decreased network efficiency) in the WM structural networks. rLOD patients also showed reduced nodal efficiencies predominantly in the frontal-striatal-occipital and posterior default-mode regions. Importantly, these structural connectomic changes significantly correlated with cognitive deficits in the rLOD patients. Finally, rLOD networks showed more vulnerable to targeted attacks compared with healthy controls. These findings provide structural evidence to support the concept of rLOD that the core aspects of the pathophysiology of this disease are associated with disruptive alterations in the coordination of large-scale brain networks and advance our understanding of the neurobiological mechanism underlying cognitive deficits in the rLOD patients.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achard, S., Salvador, R., Whitcher, B., Suckling, J., & Bullmore, E. (2006). A resilient, low-frequency, small-world human brain functional network with highly connected association cortical hubs. The Journal of Neuroscience, 26(1), 63–72.
Aggleton, J. P., Wright, N. F., Vann, S. D., & Saunders, R. C. (2012). Medial temporal lobe projections to the retrosplenial cortex of the macaque monkey. Hippocampus, 22(9), 1883–1900.
Ajilore, O., Lamar, M., & Kumar, A. (2014a). Association of brain network efficiency with aging, depression, and cognition. The American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry, 22(2), 102–110.
Ajilore, O., Lamar, M., Leow, A., Zhang, A., Yang, S., & Kumar, A. (2014b). Graph theory analysis of cortical-subcortical networks in late-life depression. The American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry, 22(2), 195–206.
Bai, F., Shu, N., Yuan, Y., Shi, Y., Yu, H., Wu, D., Wang, J., Xia, M., He, Y., & Zhang, Z. (2012). Topologically convergent and divergent structural connectivity patterns between patients with remitted geriatric depression and amnestic mild cognitive impairment. The Journal of Neuroscience, 32(12), 4307–4318.
Ballmaier, M., Kumar, A., Elderkin-Thompson, V., Narr, K. L., Luders, E., Thompson, P. M., Hojatkashani, C., Pham, D., Heinz, A., & Toga, A. W. (2008a). Mapping callosal morphology in early- and late-onset elderly depression: an index of distinct changes in cortical connectivity. Neuropsychopharmacology, 33(7), 1528–1536.
Ballmaier, M., Narr, K. L., Toga, A. W., Elderkin-Thompson, V., Thompson, P. M., Hamilton, L., et al. (2008b). Hippocampal morphology and distinguishing late-onset from early-onset elderly depression. The American Journal of Psychiatry, 165(2), 229–237.
Bhalla, R. K., Butters, M. A., Mulsant, B. H., Begley, A. E., Zmuda, M. D., Schoderbek, B., Pollock, B. G., Reynolds, C. F., III, & Becker, J. T. (2006). Persistence of neuropsychologic deficits in the remitted state of late-life depression. The American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry, 14(5), 419–427.
Bohr, I. J., Kenny, E., Blamire, A., O'Brien, J. T., Thomas, A. J., Richardson, J., et al. (2012). Resting-state functional connectivity in late-life depression: higher global connectivity and more long distance connections. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 3, 116.
Brodaty, H., Luscombe, G., Anstey, K. J., Cramsie, J., Andrews, G., & Peisah, C. (2003). Neuropsychological performance and dementia in depressed patients after 25-year follow-up: a controlled study. Psychological Medicine, 33(7), 1263–1275.
Buckner, R. L., Snyder, A. Z., Shannon, B. J., LaRossa, G., Sachs, R., Fotenos, A. F., Sheline, Y. I., Klunk, W. E., Mathis, C. A., Morris, J. C., & Mintun, M. A. (2005). Molecular, structural, and functional characterization of Alzheimer’s disease: evidence for a relationship between default activity, amyloid, and memory. The Journal of Neuroscience, 25(34), 7709–7717.
Bullmore, E., & Sporns, O. (2012). The economy of brain network organization. Nature Reviews. Neuroscience, 13(5), 336–349.
Bullmore, E. T., Suckling, J., Overmeyer, S., Rabe-Hesketh, S., Taylor, E., & Brammer, M. J. (1999). Global, voxel, and cluster tests, by theory and permutation, for a difference between two groups of structural MR images of the brain. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 18(1), 32–42.
Chen, P. S., McQuoid, D. R., Payne, M. E., & Steffens, D. C. (2006). White matter and subcortical gray matter lesion volume changes and late-life depression outcome: a 4-year magnetic resonance imaging study. International Psychogeriatrics, 18(3), 445–456.
Dai, Z., & He, Y. (2014). Disrupted structural and functional brain connectomes in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroscience Bulletin, 30(2), 217–232.
Delaloye, C., Moy, G., de Bilbao, F., Baudois, S., Weber, K., Hofer, F., Paquier, C. R., Donati, A., Canuto, A., Giardini, U., von Gunten, A., Stancu, R. I., Lazeyras, F., Millet, P., Scheltens, P., Giannakopoulos, P., & Gold, G. (2010). Neuroanatomical and neuropsychological features of elderly euthymic depressed patients with early- and late-onset. Journal of the Neurological Sciences, 299(1–2), 19–23.
Geda, Y. E., Knopman, D. S., Mrazek, D. A., Jicha, G. A., Smith, G. E., Negash, S., Boeve, B. F., Ivnik, R. J., Petersen, R. C., Pankratz, V. S., & Rocca, W. A. (2006). Depression, apolipoprotein E genotype, and the incidence of mild cognitive impairment: a prospective cohort study. Archives of Neurology, 63(3), 435–440.
Gong, Q., & He, Y. (2015). Depression, neuroimaging and connectomics: a selective overview. Biological Psychiatry, 77(3), 223–235.
Gong, G., He, Y., Concha, L., Lebel, C., Gross, D. W., Evans, A. C., & Beaulieu, C. (2009). Mapping anatomical connectivity patterns of human cerebral cortex using in vivo diffusion tensor imaging tractography. Cerebral Cortex, 19(3), 524–536.
Greicius, M. D., Flores, B. H., Menon, V., Glover, G. H., Solvason, H. B., Kenna, H., Reiss, A. L., & Schatzberg, A. F. (2007). Resting-state functional connectivity in major depression: abnormally increased contributions from subgenual cingulate cortex and thalamus. Biological Psychiatry, 62(5), 429–437.
Guo, H., Cao, X., Liu, Z., Li, H., Chen, J., & Zhang, K. (2012). Machine learning classifier using abnormal brain network topological metrics in major depressive disorder. Neuroreport, 23(17), 1006–1011.
Guo, W., Liu, F., Xun, G., Hu, M., Guo, X., Xiao, C., Chen, H., Chen, J., & Zhao, J. (2014). Disrupted white matter integrity in first-episode, drug-naive, late-onset depression. Journal of Affective Disorders, 163, 70–75.
Haldane, M., Cunningham, G., Androutsos, C., & Frangou, S. (2008). Structural brain correlates of response inhibition in bipolar disorder I. Journal of Psychopharmacology, 22(2), 138–143.
He, Y., Chen, Z., & Evans, A. (2008). Structural insights into aberrant topological patterns of large-scale cortical networks in Alzheimer's disease. The Journal of Neuroscience, 28(18), 4756–4766.
Herrmann, L. L., Goodwin, G. M., & Ebmeier, K. P. (2007). The cognitive neuropsychology of depression in the elderly. Psychological Medicine, 37(12), 1693–1702.
Kohler, S., Thomas, A. J., Barnett, N. A., & O'Brien, J. T. (2010). The pattern and course of cognitive impairment in late-life depression. Psychological Medicine, 40(4), 591–602.
Li, X., Steffens, D. C., Potter, G. G., Guo, H., Song, S., & Wang, L. (2017). Decreased between-hemisphere connectivity strength and network efficiency in geriatric depression. Human Brain Mapping, 38(1), 53–67.
Liao, W., Wang, Z., Zhang, X., Shu, H., Wang, Z., Liu, D., & Zhang, Z. (2017). Cerebral blood flow changes in remitted early- and late-onset depression patients. Oncotarget, 8(44), 76214–76222.
Lim, H. K., Jung, W. S., Ahn, K. J., Won, W. Y., Hahn, C., Lee, S. Y., Kim, I. S., & Lee, C. U. (2012). Regional cortical thickness and subcortical volume changes are associated with cognitive impairments in the drug-naive patients with late-onset depression. Neuropsychopharmacology, 37(3), 838–849.
Lim, H. K., Jung, W. S., & Aizenstein, H. J. (2013). Aberrant topographical organization in gray matter structural network in late life depression: a graph theoretical analysis. International Psychogeriatrics, 25(12), 1929–1940.
Lo, C. Y., Wang, P. N., Chou, K. H., Wang, J., He, Y., & Lin, C. P. (2010). Diffusion tensor tractography reveals abnormal topological organization in structural cortical networks in Alzheimer’s disease. The Journal of Neuroscience, 30(50), 16876–16885.
Lui, S., Zhou, X. J., Sweeney, J. A., & Gong, Q. (2016). Psychoradiology: the frontier of Neuroimaging in psychiatry. Radiology, 281(2), 357–372.
Ma, N., Li, L., Shu, N., Liu, J., Gong, G., He, Z., et al. (2007). White matter abnormalities in first-episode, treatment-naive young adults with major depressive disorder. The American Journal of Psychiatry, 164(5), 823–826.
Mai, N., Zhong, X., Chen, B., Peng, Q., Wu, Z., Zhang, W., Ouyang, C., & Ning, Y. (2017). Weight Rich-Club analysis in the white matter network of late-life depression with memory deficits. Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience, 9, 279.
Mak, E., Colloby, S. J., Thomas, A., & O'Brien, J. T. (2016). The segregated connectome of late-life depression: a combined cortical thickness and structural covariance analysis. Neurobiology of Aging, 48, 212–221.
Nielsen, F. A., Balslev, D., & Hansen, L. K. (2005). Mining the posterior cingulate: segregation between memory and pain components. Neuroimage, 27(3), 520–532.
Perez, D. L., Matin, N., Williams, B., Tanev, K., Makris, N., LaFrance, W. C., Jr., et al. (2017). Cortical thickness alterations linked to somatoform and psychological dissociation in functional neurological disorders. Human Brain Mapping, 39(1), 428–439.
Phillips, D. J., McGlaughlin, A., Ruth, D., Jager, L. R., Soldan, A., & Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging, I. (2015). Graph theoretic analysis of structural connectivity across the spectrum of Alzheimer's disease: The importance of graph creation methods. Neuroimage Clinical, 7, 377–390.
Rubinov, M., & Sporns, O. (2010). Complex network measures of brain connectivity: uses and interpretations. Neuroimage, 52(3), 1059–1069.
Sachs-Ericsson, N., Corsentino, E., Moxley, J., Hames, J. L., Rushing, N. C., Sawyer, K., Joiner, T., Selby, E. A., Zarit, S., Gotlib, I. H., & Steffens, D. C. (2013). A longitudinal study of differences in late- and early-onset geriatric depression: depressive symptoms and psychosocial, cognitive, and neurological functioning. Aging & Mental Health, 17(1), 1–11.
Salloway, S., Malloy, P., Kohn, R., Gillard, E., Duffy, J., Rogg, J., Tung, G., Richardson, E., Thomas, C., & Westlake, R. (1996). MRI and neuropsychological differences in early- and late-life-onset geriatric depression. Neurology, 46(6), 1567–1574.
Sexton, C. E., McDermott, L., Kalu, U. G., Herrmann, L. L., Bradley, K. M., Allan, C. L., le Masurier, M., Mackay, C. E., & Ebmeier, K. P. (2012). Exploring the pattern and neural correlates of neuropsychological impairment in late-life depression. Psychological Medicine, 42(6), 1195–1202.
Sheline, Y. I., Price, J. L., Vaishnavi, S. N., Mintun, M. A., Barch, D. M., Epstein, A. A., et al. (2008). Regional white matter hyperintensity burden in automated segmentation distinguishes late-life depressed subjects from comparison subjects matched for vascular risk factors. The American Journal of Psychiatry, 165(4), 524–532.
Shu, N., Liu, Y., Li, K., Duan, Y., Wang, J., Yu, C., Dong, H., Ye, J., & He, Y. (2011). Diffusion tensor tractography reveals disrupted topological efficiency in white matter structural networks in multiple sclerosis. Cerebral Cortex, 21(11), 2565–2577.
Shu, H., Yuan, Y., Xie, C., Bai, F., You, J., Li, L., Li, S. J., & Zhang, Z. (2014). Imbalanced hippocampal functional networks associated with remitted geriatric depression and apolipoprotein E epsilon4 allele in nondemented elderly: a preliminary study. Journal of Affective Disorders, 164, 5–13.
Smagula, S. F., & Aizenstein, H. J. (2016). Brain structural connectivity in late-life major depressive disorder. Biological Psychiatry. Cognitive Neuroscience and Neuroimaging, 1(3), 271–277.
Sporns, O., & Zwi, J. D. (2004). The small world of the cerebral cortex. Neuroinformatics, 2(2), 145–162.
Tadayonnejad, R., & Ajilore, O. (2014). Brain network dysfunction in late-life depression: a literature review. Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry and Neurology, 27(1), 5–12.
Tzourio-Mazoyer, N., Landeau, B., Papathanassiou, D., Crivello, F., Etard, O., Delcroix, N., Mazoyer, B., & Joliot, M. (2002). Automated anatomical labeling of activations in SPM using a macroscopic anatomical parcellation of the MNI MRI single-subject brain. Neuroimage, 15(1), 273–289.
Wang, Z., Yuan, Y., Bai, F., Shu, H., You, J., Li, L., & Zhang, Z. (2015). Altered functional connectivity networks of hippocampal subregions in remitted late-onset depression: a longitudinal resting-state study. Neuroscience Bulletin, 31(1), 13–21.
Wang, Z., Yuan, Y., Bai, F., You, J., & Zhang, Z. (2016). Altered topological patterns of brain networks in remitted late-onset depression: a resting-state fMRI study. The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, 77(1), 123–130.
Wen, M. C., Steffens, D. C., Chen, M. K., & Zainal, N. H. (2014). Diffusion tensor imaging studies in late-life depression: systematic review and meta-analysis. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry, 29(12), 1173–1184.
Wu, D., Yuan, Y., Bai, F., You, J., Li, L., & Zhang, Z. (2013). Abnormal functional connectivity of the default mode network in remitted late-onset depression. Journal of Affective Disorders, 147(1–3), 277–287.
Yuan, Y., Zhang, Z., Bai, F., Yu, H., Shi, Y., Qian, Y., Zang, Y., Zhu, C., Liu, W., & You, J. (2007). White matter integrity of the whole brain is disrupted in first-episode remitted geriatric depression. Neuroreport, 18(17), 1845–1849.
Yuan, Y., Zhang, Z., Bai, F., Yu, H., Shi, Y., Qian, Y., Liu, W., You, J., Zhang, X., & Liu, Z. (2008). Abnormal neural activity in the patients with remitted geriatric depression: a resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Journal of Affective Disorders, 111(2–3), 145–152.
Yuan, Y., Hou, Z., Zhang, Z., Bai, F., Yu, H., You, J., Shi, Y., Liu, W., & Jiang, T. (2010). Abnormal integrity of long association fiber tracts is associated with cognitive deficits in patients with remitted geriatric depression: a cross-sectional, case-control study. The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, 71(10), 1386–1390.
Yue, Y., Yuan, Y., Hou, Z., Jiang, W., Bai, F., & Zhang, Z. (2013). Abnormal functional connectivity of amygdala in late-onset depression was associated with cognitive deficits. PLoS One, 8(9), e75058.
Zhong, X., Shi, H., Ming, Q., Dong, D., Zhang, X., Zeng, L. L., & Yao, S. (2017). Whole-brain resting-state functional connectivity identified major depressive disorder: a multivariate pattern analysis in two independent samples. Journal of Affective Disorders, 218, 346–352.
Acknowledgements
We thank all the patients and volunteers for participating in this study.
Funding
This study was supported by the Projects of International Cooperation and Exchanges NSFC (grant number 81420108012), the National Key Basic Research Program of China (grant number 2014CB846102), the Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number 81601559), and the Key Program for Clinical Medicine and Science and Technology: Jiangsu Province Clinical Medical Research Center (grant numbers BL2013025, BL2014077).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 8.39 mb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Z., Yuan, Y., You, J. et al. Disrupted structural brain connectome underlying the cognitive deficits in remitted late-onset depression. Brain Imaging and Behavior 14, 1600–1611 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-019-00091-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-019-00091-x