Abstract
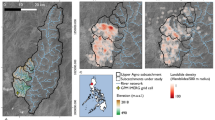
Slope units is an effective mapping unit for rainfall landslides prediction at regional scale. At present, slope units extracted by hydrology and morphological method report very different morphological feature and boundaries. In order to investigate the effect of morphological difference on the prediction performance, this paper presents a general landslide probability analysis model for slope units. Monte Carlo method was used to describe the spatial uncertainties of soil mechanical parameters within slope units, and random search technique was performed to obtain the minimum safety factor; transient hydrological processes simulation was used to provide key hydrological parameters required by the model, thereby achieving landslide prediction driven by quantitative precipitation estimation and forecasting data. The prediction performance of conventional slope units (CSUs) and homogeneous slope units (HSUs) were analyzed in three case studies from Fengjie County, China. The results indicate that the mean missing alarm rate of CSUs and HSUs are 31.4% and 10.6%, respectively. Receiver Operating Characteristics (ROC) analysis also reveals that HSUs is capable of improving the overall prediction performance, and may be used further for rainfall-induced landslide prediction at regional scale.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gutierrez-Martin A (2020) A GIS-physically-based emergency methodology for predicting rainfall-induced shallow landslide zonation. Geomorphology 359:107–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2020.107121
Alvioli M, Guzzetti F, Marchesini I (2020) Parameter-free delineation of slope units and terrain subdivision of Italy. Geomorphology 358:107–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2020.107124
Alemdag S, Kaya A, Karadag M, et al. (2015) Utilization of the limit equilibrium and finite element methods for the stability analysis of the slope debris: an example of the Kalebasi district (NE Turkey). J Afr Earth Sci 106: 134–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2015.03.010
Apip, Takara K, Yamashiki Y, et al. (2010) A distributed hydrological-geotechnical model using satellite-derived rainfall estimates for shallow landslide prediction system at a catchment scale. Landslides 7(3):237–258. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-010-0214-z
ASTM D (2011) Standard Test Method for Direct Shear Test of Soils Under Consolidated Drained Conditions. D3080/D3080M. https://www.astm.org/d3080-98.html
Baum RL, Savage WZ, Godt JW (2002) Trigrs: a fortran program for transient rainfall infiltration and grid-based regional slope-stability analysis. Open-File Report.
Bezak N, Šraj M, Mikoš M (2016) Copula-based IDF curves and empirical rainfall thresholds for flash floods and rainfall-induced landslides. J Hydrol 541: 272–284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2016.02.058
Bogaard TA, Greco R (2018) Hydrological perspectives on precipitation intensity-duration thresholds for a landslide initiation: proposing hydro-meteorological thresholds. Nat Hazards Earth Syst Sci 18(1): 31–39.
Conforti M, Ietto F (2019) An integrated approach to investigate slope instability affecting infrastructures. Bull Eng Geol Environ 78(4):2355–2375. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-018-1311-9
Cruden DM, Varnes DJ (1996) Landslides types and processes. In: Truner AK, Schuster RL (eds.), Landslides: Investigation and Mitigation. Transportation Research Board Special Report 247. National Academy Press, Washington. pp 36–75.
Dai Y, Shangguan W, Duan Q, et al. (2013) Development of a China dataset of soil hydraulic parameters using pedotransfer functions for land surface modeling. J Hydrometeorol 14(3): 869–887. https://doi.org/10.1175/JHM-D-12-0149.!
Dağ S, Akgün A, Kaya A, et al. (2020) Medium scale earthflow susceptibility modelling by remote sensing and geographical information systems based multivariate statistics approach: an example from Northeastern Turkey. Environ Earth Sci 79: 1–21. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-020-09217-7
Di Biagio E, Kjekstad O (2007) Early warning, instrumentation and monitoring landslides. 2nd Regional Training Course, RECLAIM II, 29th January-3rd February.
Domènech G, Alvioli M, Corominas J (2020) Preparing firsttime slope failures hazard maps: from pixel-based to slope unit-based. Landslides 17(2): 249–265. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-019-01279-4
Fawcett T (2006) An introduction to ROC analysis. Pattern Recognit Lett 27(8): 861–874. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2005.10.010
Farias MM, Llano S (2016) Simple Methodology to Obtain Critical State Parameters of Remolded Clays Under Normally Consolidated Conditions Using the Fall-Cone Test. Geotech Test J. 39. 20150207. https://doi.org/10.1520/GTJ20150207
Greco VR (1996) Efficient Monte Carlo technique for locating critical slip surface. J Geotech Eng 122(7): 517–525. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)0733-9410(1996)122:7(517)
Gu T, Wang J, Fu X, et al. (2015) GIS and limit equilibrium in the assessment of regional slope stability and mapping of landslide susceptibility. B Eng Geol Environ 74(4): 1105–1115. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-014-0689-2
Guzzetti F, Carrara A, Cardinali M, et al. (1999) Landslide hazard evaluation: a review of current techniques and their application in a multi-scale study, Central Italy. Geomorphology 31(1–4): 181–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-555X(99)00078-1
Guzzetti F, Gariano SL, Peruccacci S, et al. (2020) Geographical landslide early warning systems. Earth-Sci Rev 200: 102973. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2019.102973
Intrieri E, Carlà T, Gigli G (2019) Forecasting the time of failure of landslides at slope-scale: A literature review. Earth-Sci Rev 193: 333–349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2019.03.019
Jia N, Mitani Y, Xie M, et al. (2012) Shallow landslide hazard assessment using a three-dimensional deterministic model in a mountainous area. Comput Geotech 45: 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2012.04.007
Jacobs L, Kervyn M, Reichenbach P, et al. (2020) Regional susceptibility assessments with heterogeneous landslide information: Slope unit- vs. pixel-based approach. Geomorphology 356: 107084.. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2020.107084
Kaya A, Alemdağ S, Dağ S, et al. (2016) Stability assessment of high-steep cut slope debris on a landslide (Gumushane, NE Turkey). B Eng Geol Environ 75: 89–99. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-015-0753-6
Lee JH, Park HJ (2016) Assessment of shallow landslide susceptibility using the transient infiltration flow model and GIS-based probabilistic approach. Landslides 13(5): 885–903. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-015-0646-6
Liu W, Luo Y, Sun L, et al. (2013) Fabrication of the superhydrophobic surface on aluminum alloy by anodizing and polymeric coating. Appl Surf Sci 872–878. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2012.10.167
Marin RJ, García EF, Aristizábal E (2020) Effect of basin morphometric parameters on physically-based rainfall thresholds for shallow landslides. Eng Geol 278:105855. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2020.105855
Muntohar AS, Liao HJ (2009) Analysis of rainfall-induced infinite slope failure during typhoon using a hydrological-geotechnical model. Environmental Geology 56(6): 1145–1159. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-008-1215-2
Nery TD, Vieira BC (2015) Susceptibility to shallow landslides in a drainage basin in the Serra do Mar, São Paulo, Brazil, predicted using the SINMAP mathematical model. B Eng Geol Environ 74(2): 369–378. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-014-0622-8
O’kelly BC, Vardanega PJ, Haigh SK (2018) Use of fall cones to determine Atterberg limits: a review. Géotechnique 68(10): 843–856. https://doi.org/10.1680/jgeot.17.R.039
Park HJ, Lee JH, Woo I (2013) Assessment of rainfall-induced shallow landslide susceptibility using a GIS-based probabilistic approach. Eng Geol 161: 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2013.04.011
Park JY, Lee SR, Lee DH, et al. (2019) A regional-scale landslide early warning methodology applying statistical and physically based approaches in sequence. Eng Geol 260: 105193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2019.105193
Polidori E (2007) Relationship between the Atterberg limits and clay content. Soils Found 47(5): 887–896. https://doi.org/10.3208/sandf.47.887
Pradhan AM, Lee S, Kim Y (2019) A shallow slide prediction model combining rainfall threshold warnings and shallow slide susceptibility in Busan, Korea. Landslides 16(3): 647–659. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-018-1112-z
Raia S, Alvioli M, Rossi M, et al. (2013) Improving predictive power of physically based rainfall-induced shallow landslide models: a probabilistic approach. Geosci Model Dev 7(2): 495–514. https://doi.org/10.5194/gmd-7-495-2014
Roccati A, Faccini F, Luino F, et al. (2019) Heavy rainfall triggering shallow landslides: a susceptibility assessment by a GIS-approach in a Ligurian Apennine Catchment (Italy). Water 11(3): 605. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11030605
Rossi G, Catani F, Leoni L, et al. (2013) HIRESSS: a physically based slope stability simulator for HPC applications. Nat Hazard Earth Sys 13(1): 151–166. https://doi.org/10.5194/nhess-13-151-2013
Salvatici T, Tofani V, Rossi G (2018) Application of a physically based model to forecast shallow landslides at a regional scale. Nat Hazard Earth Sys 18(7): 1919–1935. https://doi.org/10.5194/nhess-18-1919-2018
Schmidt J, Turek G, Clark MP, et al. (2008) Probabilistic forecasting of shallow, rainfall-triggered landslides using realtime numerical weather predictions. Nat Hazard Earth Sys 8(2): 349–357. https://doi.org/10.5194/nhess-8-349-2008
Seibert J, McGlynn B L (2007) A new triangular multiple flow direction algorithm for computing upslope areas from gridded digital elevation models. Water Resour Res 43(4): 306–320. https://doi.org/10.1029/2006WR005128
Sorensen KK, Okkels N (2013) Correlation between drained shear strength and plasticity index of undisturbed over consolidated clays. In: Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, Paris. Vol. 1, pp 423–428.
Sun D, Xu J, Wen H, et al. (2021) Assessment of landslide susceptibility mapping based on Bayesian hyperparameter optimization: A comparison between logistic regression and random forest. Eng Geol 281: 105972. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2020.105972
Tanyas H, Rossi M, Alvioli M, et al. (2019) A global slope unit-based method for the near real-time prediction of earthquake-induced landslides. Geomorphology 327: 126–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2018.10.022
Tripathy S, Mishra AK (2011) On the use of Skempton’s compression index equation. Geotech Geol Eng 29(1): 129–135. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-010-9359-8
Tiranti D, Rabuffetti D (2010) Estimation of rainfall thresholds triggering shallow landslides for an operational warning system implementation. Landslides 7(4): 471–481. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-010-0198-8
Turel M, Frost JD (2011) Delineation of slope profiles from digital elevation models for landslide hazard analysis. In Geo-Risk 2011: Risk Assessment and Management 829–836. https://doi.org/10.1061/41183(418)87
Van Genuchten MT (1980) A closed-form equation for predicting the hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 44(5): 892–898. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1980.03615995004400050002x
Wang X, Zhang L, Wang S, et al. (2014) Regional landslide susceptibility zoning with considering the aggregation of landslide points and the weights of factors. Landslides 11(3): 399–409. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-013-0392-6
Wang S, Zhang K, Van Beek LP, et al. (2020) Physically-based landslide prediction over a large region: Scaling low-resolution hydrological model results for high-resolution slope stability assessment. Environ Modell Softw 124: 104607. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2019.104607
Wang K, Wei F (2018) Slope unit profile extraction method and realization for regional slope assessment. Bull Sci Technol 34(9): 242–248. (In Chinese) https://doi.org/10.13774/j.cnki.kjtb.2018.09.050
Wang K, Zhang S, Wei F (2019) Geotechnical mechanical parameters determination of prediction unit based spatial interpolation technique. J Nat Disasters 28(5): 208–219. (In Chinese) https://doi.org/10.13577/j.jnd.2019.0523
Wang K, Zhang S, Delgado-Tellez R, et al. (2019) A new slope unit extraction method for regional landslide analysis based on morphological image analysis. Eng GeolB Eng Geol Environ 78(6): 4139–4151. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-018-1389-0.
Wang K, Xu H, Zhang S, et al. (2020) Identification and Extraction of Geomorphological Features of Landslides Using Slope Units for Landslide Analysis. ISPRS Int J Geo-inf 9(4):274. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi9040274
Wang K, Zhang S (2021) Rainfall-induced landslides assessment in the Fengjie County, three-gorge reservoir area, china. Nat Hazards (11): 1–28. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-021-04691-z
Wei FQ, Gao KC, Jiang YH, et al. (2007) GIS-based prediction of debris flows and landslides in Southwestern China. In: Chen CL, Major JJ (eds.), Proceedings of Debris-Flow Hazards Mitigation: Mechanics, Prediction, and Assessment. Mill Press, the Netherlands. pp 479–490.
Zhang S, Zhao L, Delgado-Tellez R (2018) A physics-based probabilistic forecasting model for rainfall-induced shallow landslides at regional scale. Nat Hazard Earth Sys 18(3): 969–982. https://doi.org/10.5194/nhess-18-969-2018
Zhang SJ, Xu CX, Wei FQ, et al. (2020) A physics-based model to derive rainfall intensity-duration threshold for debris flow. Geomorphology 351: 106930. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2019.106930
Zhang SJ, Ma ZG, Li YJ, et al. (2021) A grid-based physical model to analyze the stability of slope unit. Geomorphology 391: 107887. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.GEOMORPH.2021.107887
Zhuang J, Peng J, Xu Y, et al. (2016) Assessment and mapping of slope stability based on slope units: A case study in Yan’an, China. J Earth Syst Sci 125(7): 1439–1450. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-016-0741-7
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 42271013) and the Chongqing Municipal Bureau of Land, Resources and Housing Administration (Grant No. KJ-2022033), the Young Scholar Training Program of Zhongyuan University of technology (Grant No. 2020XQG13), the strength improvement plan of the advantageous disciplines of Zhongyuan University of Technology (Grant No. SD202231), Natural Science Foundation Project of Zhongyuan University of Technology (Grant No. K2023QN008) and the Science and Technology Support Program of Sichuan Province (2021YFG0258). This work was also supported by the funding of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 41972292), the Innovation Capability Support Program of Shaanxi Province (Grant No. 2021TD-54), the Key Research and Development Program of Shaanxi Province (Grant No. 2022ZDLSF06-03).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, K., Zhang, Sj., Xie, Wl. et al. Prediction of the instability probability for rainfall induced landslides: the effect of morphological differences in geomorphology within mapping units. J. Mt. Sci. 20, 1249–1265 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-022-7789-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-022-7789-4