Abstract
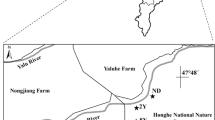
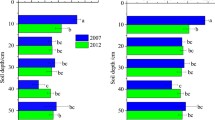
Wetland is an important carbon pool, and the degradation of wetlands causes the loss of organic carbon and total nitrogen. This study aims to explore how wetland degradation succession affects soil organic carbon (SOC) and total nitrogen (TN) contents in alpine wetland. A field survey of 180 soil-sampling profiles was conducted in an alpine wetland that has been classified into three degradation succession stages. The SOC and TN contents of soil layers from 0 to 200 cm depth were studied, including their distribution characteristics and the relationship between soil water content (SWC) and microtopography. The results showed that SOC and TN of different degradation succession gradients followed the ranked order of Non Degradation (ND) > Light Degradation (LD) > Heavy Degradation (HD). SWC was positively correlated with SOC and TN (p<0.05). As the degree of degradation succession worsened, SOC and TN became more sensitive to the SWC. Microtopography was closely related to the degree of wetland degradation succession, SWC, SOC and TN, especially in the topsoil (0–30 cm). This result showed that SWC was an important indicator of SOC/TN in alpine wetland. It is highly recommended to strengthen water injection into the wetland as a means of effective restoration to reverse alpine meadow back to marsh alpine wetland.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amador JA Gorres JH, Savin MC (2005) Role of soil water content in the carbon and nitrogen dynamics of Lumbricusterrestris Lburrow soil. Appl Soil Ecol 28:15–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2004.06.009
Bai JH, Ouyang H, Deng W, et al. (2005) Spatial distribution characteristics of organic matter and total nitrogen of marsh soils in River Marginal Wetlands. Geoderma 124(1/2):181–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2004.04.012
Bai JH, Ouyang H, Xiao R, et al. (2010) Spatial variability of soil carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus content and storage in an alpine wetland in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China. Aust J Soil Res 48(8): 730–736.
Dang JJ, Zhao CZ, Dong XG, et al. (2014) Response of spatial distribution patterns of Kobresia tibetiana and Kobresia humilis populations to water. J Ecol 33(7):1734–1740.(In Chinese)
Fu MY, Yang N, Yang MY, et al. (2015) Coupling relationship between soil microbe with soil nutrient in re-vegetation stages on sloping-land with purple soils in Hengyang of Hunan Province, South-central China. Ecol Environ Sci 24: 41–48. (In Chinese) https://doi.org/10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2015.01.007
Gao J, Li XL (2016) Degradation of frigid swampy meadows on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau: Current status and future directions of research. Prog Phys Geogr 40(6):794–810. https://doi.org/10.1177/0309133316659283
GAO J, Li XL, Gary B (2012) Topographic influence on wetland distribution and change in Maduo County, Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China. J Mt Sci 9:362–371. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-009-2263-0
Gao J, Li XL, Gary B (2013) Geomorphic-centered classification of wetlands on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, Western China. Journal of Mountain Science 10(4):632–642. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11629-013-2561-4
Huang CY (2000) Soil. Science Beijing: China Agricultural Press.
Khaznadar M, Vogiatzakis IN, Griffiths GH (2009) Land degradation and vegetation distribution in Chott El Beida wetland, Algeria. J Arid Environ 73(3):0–377. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaridenv.2008.09.026
Li C, Cui J, Sun G, Trettin C (2004) Modelling impacts of management on carbon sequestration and trace gas emissions in forested wetland ecosystems. Environmental Management 33(Suppl. 1): S176–S186. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00267-003-9128-Z
Li F, Liu ZH, Jia TH, et al. (2018) Functional diversity of soil microbial community carbon metabolism with the degradation and restoration of alpine wetlands and meadows. Acta Ecol Sin 38(17):6006–6015.https://doi.org/10.5846/stxb201706161096
Li I, Qing FQ, Jiang IN, et al. (2019) Vertical distribution of soil organic carbon content and its influencing factors in Aaohan, Chifeng. Acta Ecol Sin 39:345–354. https://doi.org/10.5846/stxb201710081779
Li X, Xie YH, Huang JS, et al. (2009) Research progress on the formation mechanism of vegetation distribution pattern in wetlands. Wetl Sin 7:280–288. https://doi.org/10.13248/j.cnki.wetlandsci.2009.03.004
Li XL, George P, Gary B (2013) Restoration Prospects for Heitutan Degraded Grassland in the Sanjiangyuan, China. J Mt Sci 10: 687–698. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-013-2557-0
Li XL, Xue ZB, Gao J (2016) Dynamic Changes of Plateau Wetlands in Madou County, the Yellow River Source Zone of China: 1990–2013. Wetland 36: 299–310. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13157-016-0739-6
Li YN, Zhao L, Xu SY, et al. (2006) Plant community structure and ecological characteristics of Haibei alpine wetland in Qilian Mountains. Glac Frzn Soil 28:76–84. (In Chinese)
Lin CY, Li XL, Li HM, et al. (2019) Distribution characteristics of soil carbon and nitrogen and storage in different degraded alpine wetlands. Acta Agr Sin 27:805–816. (In Chinese). https://doi.org/10.11733/j.issn.1007-0435.2019.04.003
Lin CY, Li XL, Jin HY, et al. (2015) Soil Degradation Characteristics of Floodplain Wetlands in Yellow River Source Zone. Chin Agri Sci Bull 31(33):243–249. (In Chinese)
Liu YH, Wei WD, Wen XC, et al. (2014) Distribution study of soil organic carbon fraction on degradation alpine grassland in the source area of Three Major Rivers of China. Chin J Soil Sci 45(6): 13701376. (In Chinese). https://doi.org/10.19336/j.cnki.trtb.2014.06.013
Liu K, Li XL, Jin LQ, et al. (2017) Characteristics of soil and vegetation in the process of lacustrine wetland degradation in the Yellow River source zone. Ecol Sci 36(3): 23–30. (In Chinese). https://doi.org/10.14108/j.cnki.1008-8873.2017.03.004
Mitschw J, Gosselink J G (2000) Wetlands. New York: Van Nostrand Reinhold Company Inc. pp 89–125.
Niu B, He YT, Zhang XZ, et al. (2017) CO2 exchange in an alpine swamp meadow on the central Tibetan Plateau. Wetlands 37(3):525–543. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13157-017-0888-2
O’Brien SL, Jastrow JD, Grimley DA et al. (2010) Moisture and vegetation controls on decadal scale accrual of soil organic carbon and total nitrogen in restored grasslands. Glob Chang Biol 16(9): 2573–2588. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2486.2009.02114.x
Opdam P, Washington DC (2004) Climate change meets habitat fragmentation: Linking landscape and biogeographical scale levels in research and conservation. Biol Conserv 117: 285–297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocon.2003.12.008
Shi S, Zhang W, Zhang P, et al. (2013) A synthesis of change in deep soil organic carbon stores with afforestation of agricultural soils. For Ecol Manag 296:53–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2013.01.026
Song S (2015) Alpine wetlands in China. Nature 64–65.
Tan XJ, Zhao XS (2006) Spatial distribution and ecological adaptability of wetland vegetation in Yellow River Delta along a water table depth gradient. Chin J Ecol 25: 1460–1464. (In Chinese)
Wang YQ, Shao MA, Zhang CC, et al. (2015) Soil organic carbon in deep profiles under Chinese continental monsoon climate and its relations with land uses. Ecol Eng 82:361–367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2015.05.004
Wang CT, Cao GM, Wang QL, et al. (2007) Changes in species composition and biomass of plant communities along environmental gradients in the alpine meadow on the Tibetan Plateau. Sci China Ser C 37:585–592.
Wang D, Lv YL, Xu L, et al. (2013) The effect of moisture and temperature on soil C mineralization in wetland and steppe of the Zoige region, China. Acta Ecol Sin 20: 6436–6443. (In Chinese)
Wang GP, Liu JS (2002) Overview on Wetlands Biogeochemistry. J Soil Water Conserv 16:144–148. (In Chinese). https://doi.org/10.13870/j.cnki.stbcxb.2002.04.038
Wang R, Li XL, Zhang J, et al. (2019) Effects artificial grass planting on surface matrix substrate on open -pit stag hill in alpine mining area. Acta Agrestic Sin 27: 938–947. https://doi.org/10.11733/j.issn.1007-0435.2019.04.019
Wang Z, Liu GB, Xu MX (2010) Effect revegetation on soil organic carbon concentration in deep soil layers in the hilly Loess Plateau of China. Acta Ecol Sin 30(14): 3947–3952
Wu JG, Xu DY (2004) Impact of Land Use Change on Soil Organic Carbon Storage-Theory, Methodology and Practice. Beijing: China Forestry Press. pp 7–14.
Wu PF, Zhang HZ, Cui LW, et al. (2019) Impacts of alpine wetland degradation on the composition, diversity and trophic structure of soil nematodes on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Nature 422:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1038/S41598-017-00805-5
Xue JY, Zhang HX, He NP, et al. (2015) Responses of SOM decomposition to changing temperature in Zoige alpine wetland, China. Wetl Ecol Manag 23:977–987. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11273-015-9434-2
Yang PG, Byrne JM, Yang M (2016) Spatial variability of soil magnetic susceptibility, organic carbon and total nitrogen from farmland in northern China. Catena 145:92–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2016.05.025
Zhang XH, Li DY, Pan GX, et al. (2008) Conservation of Wetland Soil C Stock and Climate Change of China. Adv Clim Chang Res 4(4): 202–208. (In Chinese)
Zhao W, Wang X, Wang YJ, et al. (2018) Spatial variation and driving factors of carbon and nitrogen density of themeda japoica community in Henan province. Acta Agrestic Sin 26: 846–852. (In Chinese). https://doi.org/10.11733/j.issn.1007-0435.2018.04.008
Acknowledgments
This research was funded by the Qinghai Science and Technology Department (Grant No. 2017-ZJ-799) and the Second Tibetan Plateau Scientific Expedition and Research Program (STEP) (Grant No. 2019QZKK1002). Additional funding was received form Program for the National Natural Sciences Foundation of China (Grant No. 41665008, 31872999, 41565008, 41861049). The authors thank Ma Chen Biao from Qinghai Province geographic situation monitoring Institute for supplying the drainage data. G.J. from University of Auckland provided insightful comments on the original manuscript, and gave constructive guidance and valuable help of the manuscript. Three anonymous reviewers provided helpful comments that helped to improve the quality of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, Cy., Li, Xl., Zhang, J. et al. Effects of degradation succession of alpine wetland on soil organic carbon and total nitrogen in the Yellow River source zone, west China. J. Mt. Sci. 18, 694–705 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-020-6117-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-020-6117-0