Abstract
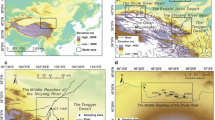
This study aims to understand the particle size distribution and depositional styles of glacier-associated deposits in the Moxi basin in southwest China. Based on field surveys, 28 samples from glacier-associated deposits (including glacial till, fluvioglacial, debris flow, river and lake deposits) were collected and tested in the laboratory. The results showed that the glacier-associated deposits can be differentiated based on particle gradation, particle size distribution and accumulated percentages. We evaluated the evolution of a former dammed lake in the Moxi basin based on glacier-associated deposits. The results of this study also indicated that the Moxi Platform was not formed by a single depositional process but is composed of both fluvioglacial and debris flow deposits. This research shows that the depositional style analysis is useful in identifying different glacier-associated deposits in high mountain regions. Moreover, the evaluation of the differences in particle sizes of the glacierassociated deposits is useful in reconstructing geohazard events in periglacial regions, and this information can help in identifying and reducing the potential risks associated with geo-hazards.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrew JO, Roger DJ, Anthony CM (1999) Measurement of the cumulative particle size distribution of microcrystalline cellulose using near infrared reflectance spectroscopy. Analyst 124: 33–36. DOI: 10.1039/A807134I
Cui ZJ (1958) Preliminary observation of present glaciers in the Mt. Minya Konka. Acta Geographica Sinica 24: 318–338. (In Chinese)
Dave HD, Garry KC, Gwenn EF, et al. (2004) Subglacial erosion and englacial sediment transport modelled for North American ice sheets Quaternary Science Reviews 23: 409–430. DOI:10.1016/j.quascirev.2003.06.005
Ding YJ, Liu SY, Li J (2006) Glacier in response to recent climate warming in west China. Annals of Glaciology 3: 333–338. (In Chinese)
Dyurgerov MB (2001) Mountain glaciers at the end of twentieth century: global analysis in relation to climate and water cycle. Polar Geography 25: 241–336.
Fan WJ (1982) The geological tectonic and its glacial characteristics of Minya Kongka. Journal of Chengdu University of Sciences and Technology 3: 19–33. (In Chinese)
Heim A (1936) The glaciation and solifluction on Minya Gongkar. Geo-Graphical Journal 87: 444–454.
Huggel C, Haeberli W, Kääb A (2004) An assessment procedure for glacial hazards in the Swiss Alps. Canadian Geotechnical Journal 41: 1068–1083. DOI: 10.1139/T04-053
Li CS (1936) Problem on the water conservancy of Moxi Platform, Luding, Xikang province. Geological Review 4: 367–372. (In Chinese)
Liu SZ, Liu XM, Zhao YT, et al. (1983) Geomor-phology and its development in Gongga Mountainous region. In: Chengdu Institute of Geography, CAS. Region Geo-graphic Expediton in the Gongga mountains. Chongqing Branch of Scientific and Technology Docunment Press, Chongqing, China. pp 21–34. (In Chinese)
Lv RR, Zhao HL (1998) Debris Flow Activity And Environment Change On The East Slope Of Mt. Minya Konka In Holocene Epoch, Meteorological Press, Beijing, China. pp 90–101. (In Chinese)
Song GP (1994) Movement features of Hailuogou glacier in the Minya Konka mountain. In: Glaciers And Environment In The Qinghai-Xizang (Tibet) Plateau (1)-The Minya Konka Mountain. Science Press, Beijing, China. pp 21–55. (In Chinese)
Tie YB (2013) Prediction of the run-out distance of the debris flow based on the velocity attenuation coefficient. Natural Hazards 65: 1589–1601.DOI: 10.1007/s11069-012-0430-z
Tie YB, Li ZL (2011) Debris flow characteristics and its environmental response in Moxi basin. Yangzi River 42: 40–43. (In Chinese)
Xie ZC, Liu HC (2010) Introduction to the glaciology. Popular Science Press, Shangha, China. pp 33–67. (In Chinese)
Xu DM, Feng QH (1994) Dangerous glacier lakes and their outburst in the Tibetan Himalayas. Bulletin of Glacier Research 12: 1–8. (In Chinese)
Zhang JY (2006) Early Holocene high magnitude debris flow events and environmental change as illustrated by the Moxi platform, Hengduan mountains, SW China. Journal of Mountain Science 3: 125–130. DOI: 10.1007/s11629-006-0125-6
Zheng BX (2001) Study on the Quaternary glaciation and the formation of the Moxi platform in the east slopes of the Minya Konka mountain. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology 23: 283–291. (In Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
http://orcid.org/0000-0001-7241-2942
http://orcid.org/0000-0003-3110-6169
http://orcid.org/0000-0002-4933-7507
http://orcid.org/0000-0002-3574-3272
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tie, Yb., Feng, Xl., Ran, J. et al. Hydrodynamic processes and depositional styles of glacier-associated deposits in the Moxi basin, Southwest China. J. Mt. Sci. 13, 557–568 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-014-3205-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-014-3205-z