Abstract
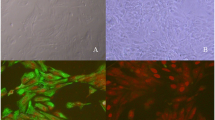
Guangxi Huanjiang Xiang pig is a unique miniature pig strain that is originally from Huanjiang Maonan Autonomous County of Guangxi province, China, and shows great potential in agricultural and biomedical research. Although cloning and genetic modification of this pig would enhance its application value, cloning of this strain has not yet been reported. We sought to establish appropriate cloning procedures and produce transgenic embryos in Huanjiang Xiang pigs through the following methods. We isolated fibroblasts from tails of Huanjiang Xiang pig and genetically modified them using Xfect transfection. Fibroblasts, either in non-transgenic or transgenic forms, were used as donor cells for reconstructed embryos by somatic cell nuclear transfer (SCNT), and in vitro development was monitored after the reconstruction. We found no difference in blastocyst formation rate between non-transgenic and transgenic embryos (10.8% vs. 10.3%; P ≥ 0.05). In addition, we tested whether Scriptaid, a widely used histone deacetylase inhibitor, could enhance the in vitro development of Huanjiang Xiang pig cloned embryos. Treatment with 500 nM Scriptaid for 16 h post-activation significantly increased the blastocyst formation rate (26.1% vs. 10.8% for non-transgenic nuclear transfer groups with vs. without the Scriptaid treatment and 28.5% vs. 10.3% for transgenic nuclear transfer groups with vs. without the Scriptaid treatment; P < 0.05). This study provided a basis for further generation of cloned and transgenically cloned Huanjiang Xiang pigs used in agricultural and biomedical research.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bähr A, Wolf E (2012) Domestic animal models for biomedical research. Reprod Domest Anim 47:59–71
Cao JZ, Zhang XM (2012) Comparative in vivo analysis of the nsp15 endoribonuclease of murine, porcine and severe acute respiratory syndrome coronaviruses. Virus Res 167:247–258
Fan NN, Chen JJ, Shang ZC, Dou HW, Ji GZ, Zou QJ, Wu L, He LXZ, Wang F, Liu K, Liu N, Han JY, Zhou Q, Pan DK, Yang DS, Zhao BT, Ouyang Z, Liu ZM, Zhao Y, Lin L, Zhong CM, Wang QL, Wang SQ, Xu Y, Luan J, Liang Y, Yang ZZ, Li J, Lu CX, Vajta G, Li ZY, Ouyang HS, Wang HY, Wang Y, Yang Y, Liu ZH, Wei H, Luan ZD, Esteban MA, Deng HK, Yang HM, Pei DQ, Li N, Pei G, Liu L, Du YT, Xiao L, Lai LX (2013) Piglets cloned from induced pluripotent stem cells. Cell Res 23:162–166
Godin LM, Vergen J, Prakash YS, Pagano RE, Hubmayr RD (2011) Spatiotemporal dynamics of actin remodeling and endomembrane trafficking in alveolar epithelial type I cell wound healing. Am J Physiology-Lung Cell Mol Physiol 300:615–623
Hao CL, Zhu XX, Zeng YL, Quan SN, Lu SS (2014) Construction of Guangxi Bama minipig transgenic somatic cells via liposome transfection method and production of transgenic cloned embryos. Jiyinzuxue Yu Yingyong Shengwuxue (Genom Appl Biol) 33:285–290 (In Chinese)
Huang Y, Zhu XX, Quan SN, Lu SS (2014) Optimization of the voltage of electrotransfection and production of Bama minipig transgenic cloned embryos. Jiyinzuxue Yu Yingyong Shengwuxue (Genom Appl Biol) 33:348–336 (In Chinese)
Huang YY, Ouyang HS, Yu H, Lai LX, Pang DX, Li ZJ (2013) Efficiency of porcine somatic cell nuclear transfer—a retrospective study of factors related to embryo recipient and embryos transferred. Biol Open 2:1223–1228
Kurome M, Geistlinger L, Kessler B, Zakhartchenko V, Klymiuk N, Wuensch A, Richter A, Baehr A, Kraehe K, Burkhardt K, Flisikowski K, Flisikowska T, Merkl C, Landmann M, Durkovic M, Tschukes A, Kraner S, Schindelhauer D, Petri T, Kind A, Nagashima H, Schnieke A, Zimmer R, Wolf E (2013) Factors influencing the efficiency of generating genetically engineered pigs by nuclear transfer: multi-factorial analysis of a large data set. BMC Biotechnol 13:43
Lee K, Prather RS (2014) Cloning pigs by somatic cell nuclear transfer. In: Cibelli J, Gurdon J, Wilmut I, Jaenisch R, Lanza R, West MD, Campbell KHS (eds) Principles of cloning, 2nd edn. Elsevier, San Diego, pp 245–254
Liu HB, Lv PR, He RG, Yang XG, Pan TB, Huang GY, Huang MR, Lu YQ, Lu SS, Li DS, Lu KH (2010) Cloned Guangxi Bama minipig (Sus scrofa) and its offspring have normal reproductive performance. Cell Reprogram 12:543–550
Liu HB, Lv PR, Yang XG, Qin XE, Pi DY, Lu YQ, Lu KH, Lu SS, Li DS (2009) Fibroblasts from the new-born male testicle of Guangxi Bama mini-pig (Sus scrofa) can support nuclear transferred embryo development in vitro. Zygote 17:147–156
Liu HB, Lv PR, Zhu XX, Wang XW, Yang XG, Zuo EW, Lu YQ, Lu SS, Lu KH (2014) In vitro development of porcine transgenic nuclear-transferred embryos derived from new-born Guangxi Bama mini-pig kidney fibroblasts. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 50:811–821
Mao JD, Tessanne K, Whitworth KM, Spate LD, Walters EM, Samuel MS, Murphy CN, Tracy L, Zhao JG, Prather RS (2012) Effects of combined treatment of MG132 and Scriptaid on early and term development of porcine somatic cell nuclear transfer embryos. Cell Reprogram 14:385–389
Nagashima H, Matsunari H, Nakano K, Watanabe M, Umeyama K, Nagaya M (2012) Advancing pig cloning technologies towards application in regenerative medicine. Reprod Domest Anim 47:120–126
Niemann H, Lucas-Hahn A (2012) Somatic cell nuclear transfer cloning: practical applications and current legislation. Reprod Domest Anim 47:2–10
Park SJ, Park HJ, Koo OJ, Choi WJ, Moon JH, Kwon DK, Kang JT, Kim S, Choi JY, Jang G, Lee BC (2012) Oxamflatin improves developmental competence of porcine somatic cell nuclear transfer embryos. Cell Reprogram 14:398–406
Prather RS, Lorson M, Ross JW, Whyte JJ, Walters E (2013) Genetically engineered pig models for human diseases. Annu Rev Anim Biosci 1:203–219
Richter A, Kurome M, Kessler B, Zakhartchenko V, Klymiuk N, Nagashima H, Wolf E, Wuensch A (2012) Potential of primary kidney cells for somatic cell nuclear transfer mediated transgenesis in pig. BMC Biotechnol 12:84
Schook LB, Collares TV, Darfour-Oduro KA, De AK, Rund LA, Schachtschneider KM, Seixas FK (2015) Unraveling the swine genome: implications for human health. Annu Rev Anim Biosci 3:219–244
Shang HT, Wei H (2007) Preliminary analysis of Chinese miniature pig strains and resources. Zhongguo Shiyandongwu Xuebao (Acta Lab Anim Sci Sin) 15:70–75 (In Chinese)
Wang MX, Guo ZY, Wang SL (2013) Regulation of cystathionine c-lyase in mammalian cells by hypoxia. Biochem Genet 52:29–37
Whitworth KM, Zhao JG, Spate LD, Li RF, Prather RS (2011) Scriptaid corrects gene expression of a few aberrantly reprogrammed transcripts in nuclear transfer pig blastocyst stage embryos. Cell Reprogram 13:191–204
Xu WH, Li ZC, Yu B, He XY, Shi JS, Zhou R, Liu DW, Wu ZF (2013) Effects of DNMT1 and HDAC inhibitors on gene-specific methylation reprogramming during porcine somatic cell nuclear transfer. PLoS ONE 8, e64705
Zhao JG, Hao YH, Ross JW, Spate LD, Walters EM, Samuel MS, Rieke A, Murphy CN, Prather RS (2010) Histone deacetylase inhibitors improve in vitro and in vivo developmental competence of somatic cell nuclear transfer porcine embryos. Cell Reprogram 12:75–83
Zhao JG, Ross JW, Hao YH, Spate LD, Walters EM, Samuel MS, Rieke A, Murphy CN, Prather RS (2009) Significant improvement in cloning efficiency of an inbred miniature pig by histone deacetylase inhibitor treatment after somatic cell nuclear transfer. Biol Reprod 81:525–530
Zhou Y, Huang YY, Xie WH, Song Q, Ji Y, Zhang YP, Ouyang HS, Lai LX, Pang DX, Tang XC (2013) Scriptaid affects histone acetylation and the expression of development-related genes at different stages of porcine somatic cell nuclear transfer embryo during early development. Chinese Sci Bull 58:2044–2052
Zhu XX, Quan SN, Huang Y, Lu SS (2013) The application of somatic cell nuclear transfer technology on porcine genetic modification. Jiyinzuxue Yu Yingyong Shengwuxue (Genom Appl Biol) 32:1–8 (In Chinese)
Zhu XX, Quan SN, Huang Y, Lu SS (2015) In vitro production of Guangxi Bama mini-pig transgenic cloned embryos. Jiyinzuxue Yu Yingyong Shengwuxue (Genom Appl Biol) 34:41–46 (In Chinese)
Zhu XX, Quan SN, Zeng YL, Huang Y, Sun RY, Lu KH, Lu SS (2014) Efficient establishment of Guangxi Bama mini-pig transgenic fibroblasts via xfect polymer transfection. Rom Biotech Lett 19:9883–9890
Acknowledgments
The authors are very grateful to Mr. Shili Liang and Pinfang Mo (National Conservation Farm for Huanjiang Xiang pigs, Huanjiang, Guangxi, China) for the donation of a newborn male Huanjiang Xiang piglet for establishment of primary somatic cells. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant No. 31260553), the Guangxi High Education Innovative Research Group and Eminent Scholar Project and the Graduate Programs for Innovational Research founded by the Guangxi Provincial Department of Education (grant No. YCSZ2013003). The manuscript was polished professionally by LetPub.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethics Approval
All animal procedures used in this study were complied with the guidelines of the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) of Guangxi University.
Additional information
T. Okamoto
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, X., Nie, J., Quan, S. et al. In vitro production of cloned and transgenically cloned embryos from Guangxi Huanjiang Xiang pig. In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Animal 52, 137–143 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-015-9957-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-015-9957-0