Abstract
Purpose
To assess the efficacy and prognostic factors after superselective intra-arterial chemoradiation (RADPLAT) for maxillary sinus squamous cell carcinoma (MS-SCC).
Materials and methods
Prognostic significance of age, gender, T and N factors, gross tumor volume of the primary-site (GTV), total cisplatin dosage, and total cisplatin dosage per GTV (CDDP/GTV) for primary-site recurrence-free survival rate (PRFS) were analyzed. RADPLAT was administered to 27 patients. The median follow-up period was 42.1 months.
Results
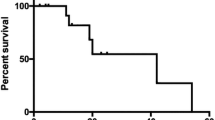
The 3-year rates of overall survival and PRFS were 59.2% and 53.9%, respectively. In univariate analysis, age, male, and total cisplatin dosage were significant factors for PRFS. In multivariate analysis, lymph node metastasis was significant factors for PRFS, and gender and total cisplatin dosage weakly influenced PRFS. In acute phase, no patient showed ≥ grade 3 hematologic toxicity, and grade 3 mucositis developed in 5 patients. Late toxicities were recognized in 3 patients (grade 2 phlegmon of the face, grade 3 maxillofacial osteonecrosis, and retinopathy). Twelve patients (44%) experienced recurrences. Of them, 8 patients showed recurrence at the primarysite.
Conclusion
RADPLAT was effective for MS-SCC, with acceptable toxicity. Total cisplatin dosage is suggested to be important for primary tumor control.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Committee JSfhaNCCR. Report of Head and Neck Cancer Registry of Japan Clinical Statistics of Registered Patients, 2015.
Ogawa K, Toita T, Kakinohana Y, et al. Postoperative radiotherapy for squamous cell carcinoma of the maxillary sinus: analysis of local control and late complications. Oncol Rep. 2001;8:315–9.
Bristol IJ, Ahamad A, Garden AS, et al. Postoperative radiotherapy for maxillary sinus cancer: long-term outcomes and toxicities of treatment. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2007;68:719–30.
Hayashi T, Nonaka S, Bandoh N, Kobayashi Y, Imada M, Harabuchi Y. Treatment outcome of maxillary sinus squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer. 2001;92:1495–503.
Yoshimura R, Shibuya H, Ogura I, et al. Trimodal combination therapy for maxillary sinus carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2002;53:656–63.
Shiga K, Yokoyama J, Hashimoto S, et al. Combined therapy after superselective arterial cisplatin infusion to treat maxillary squamous cell carcinoma. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2007;136:1003–9.
Homma A, Oridate N, Suzuki F, et al. Superselective high-dose cisplatin infusion with concomitant radiotherapy in patients with advanced cancer of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses: a single institution experience. Cancer. 2009;115:4705–14.
Homma A, Sakashita T, Yoshida D, et al. Superselective intra-arterial cisplatin infusion and concomitant radiotherapy for maxillary sinus cancer. Br J Cancer. 2013;109:2980–6.
Robbins KT, Kumar P, Harris J, et al. Supradose intra-arterial cisplatin and concurrent radiation therapy for the treatment of stage IV head and neck squamous cell carcinoma is feasible and efficacious in a multi-institutional setting: results of Radiation Therapy Oncology Group Trial 9615. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:1447–544.
Ethics guideline for medical research concerning humans. Ministry of education, culture, sports, science and technology, Japan. December 22, 2014.
Cancer Therapy Evaluation Program, Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events, Version 3.0, DCTD, NCI, NIH, DHHS. March 31, 2003.
Kanda Y. Investigation of the freely available easy-to-use software 'EZR' for medical statistics. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2013;48:452–8.
Homma A, Onimaru R, Matsuura K, et al. Dose-finding and efficacy confirmation trial of the superselective intra-arterial infusion of cisplatin and concomitant radiotherapy for locally advanced maxillary sinus cancer (Japan Clinical Oncology Group 1212): Dose-finding phase. Head Neck. 2018;40:475–84.
Robbins KT, Hoffman RM. "Decadose" effects of cisplatin on squamous cell carcinoma of the upper aerodigestive tract I. Histoculture experiments. Laryngoscope. 1996;106:32–6.
Robbins KT, Storniolo AM, Hryniuk WM, Howell SB. "Decadose" effects of cisplatin on squamous cell carcinoma of the upper aerodigestive tract II. Clinical studies. Laryngoscope. 1996;106:37–42.
Rasch CR, Hauptmann M, Schornagel J, et al. Intra-arterial versus intravenous chemoradiation for advanced head and neck cancer: results of a randomized phase 3 trial. Cancer. 2010;116:2159–65.
Al-Mamgani A, Monserez D, Rooij P, Verduijn GM, Hardillo JA, Levendag PC. Highly-conformal intensity-modulated radiotherapy reduced toxicity without jeopardizing outcome in patients with paranasal sinus cancer treated by surgery and radiotherapy or (chemo)radiation. Oral Oncol. 2012;48:905–11.
Suh YG, Lee CG, Kim H, et al. Treatment outcomes of intensity-modulated radiotherapy versus 3D conformal radiotherapy for patients with maxillary sinus cancer in the postoperative setting. Head Neck. 2016;38(Suppl 1):E207–E213213.
Paulino A, Fisher S, Marks J. Is prophylactic neck irradiation indicated in patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the maxillary sinus? Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1997;39:283–9.
Le QT, Fu KK, Kaplan MJ, Terris DJ, Fee WE, Goffinet DR. Lymph node metastasis in maxillary sinus carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2000;46:541–9.
Funding
This research was supported by Grand-in-Aid (B-10, 2017) of Gunma Prefectural Cancer Center in Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in the present study were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Ebara, T., Ando, K., Eishima, J. et al. Radiation with concomitant superselective intra-arterial cisplatin infusion for maxillary sinus squamous cell carcinoma. Jpn J Radiol 37, 494–499 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-019-00827-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-019-00827-1