Abstract
Objective
The ATP responsive P2 purinergic receptors can be subdivided into metabotropic P2X family and ionotropic P2Y family. Among these, P2X3 is a type of P2X receptor which is specifically expressed on nerves, especially on pre-ganglionic sensory fibers. This study investigates whether gefapixant possesses the potential of inhibiting cardiac sympathetic hypersensitivity to protect against cardiac remodeling in the context of myocardial infarction.
Methods
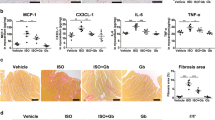
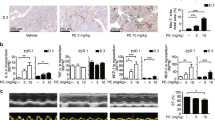
The Sprague-Dawley rats were divided randomly into three groups: sham group-myocardial infarction group, and myocardial infarction with gefapixant treatment group. Myocardial infarction was induced by left anterior descending branch ligation. The gefapixant solution was intraperitoneally injected each time per day for 7 days and the appropriate dosage of gefapixant was determined according to the results of hematoxylin-eosin (HE) staining and myocardial injury biomarkers. Conditions of cardiac function were assessed by echocardiograph and cardiac fibrosis was evaluated by Western blotting and immunofluorescence staining of collagen I and collagen III. The sympathetic innervation was detected by norepinephrine concentration (pg/mL), in-vivo electrophysiology, and typical sympathetic biomarkers. Inflammatory cell infiltration was shown from immunofluorescence staining and pro-inflammatory signaling pathway activation was checked by immunohistology, quantitative realtime PCR (qPCR) and Western blotting.
Results
It was found that gefapixant injection of 10 mg/kg per day had the highest dosage-efficacy ratio. Furthermore, gefapixant treatment improved cardiac pump function as shown by increased LVEF and LVFS, and decreased LVIDd and LVIDs. The expression levels of collagen I and collagen III, and TNF-α were all decreased by P2X3 inhibition. Mechanistically, the decreased activation of nucleotide-binding and oligomerization domain-like receptors family pyrin-domain-containing 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome and subsequent cleavage of caspase-1 which modulated interleukin-1β (IL-1β) and IL-18 level in heart after gefapixant treatment were associated with the suppressed cardiac inflammation.
Conclusion
It is suggested that P2X3 inhibition by gefapixant ameliorates post-infarct autonomic nervous imbalance, cardiac dysfunction, and remodeling possibly via inactivating NLRP3 inflammasome.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Salah HM, Minhas AMK, Khan MS, et al. Trends in Hospitalizations for Heart Failure, Acute Myocardial Infarction, and Stroke in the United States from 2004–2018. ESC Heart Fail, 2022,9(2):947–952
Fujiu K, Manabe I. Nerve-macrophage interactions in cardiovascular disease. Int Immunol, 2022,34(2):81–95
Zhao S, Dai Y, Ning X, et al. Vagus nerve stimulation in early stage of acute myocardial infarction prevent ventricular arrhythmias and cardiac remodeling. Front Cardiovasc Med, 2021,8:648910
Sun X, Wei Z, Li Y, et al. Renal denervation restrains the inflammatory response in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Basic Res Cardiol, 2020,115(2):15
Wang Y, Hu H, Yin J, et al. TLR4 participates in sympathetic hyperactivity Post-MI in the PVN by regulating NF-κB pathway and ROS production. Redox Biol, 2019,24:101186
Merz J, Nettesheim A, von Garlen S, et al. Pro- and anti-inflammatory macrophages express a sub-type specific purinergic receptor profile. Purinergic Signal, 2021,17(3):481–492
Xu X, Liu B, Yang J, et al. Glucokinase in stellate ganglia cooperates with P2X3 receptor to develop cardiac sympathetic neuropathy in type 2 diabetes rats. Brain Res Bull, 2020,165:290–297
Xia LP, Luo H, Ma Q, et al. GPR151 in nociceptors modulates neuropathic pain via regulating P2X3 function and microglial activation. Brain, 2021,144(11):3405–3420
Li M, Wang Y, Banerjee R, et al. Molecular mechanisms of human P2X3 receptor channel activation and modulation by divalent cation bound ATP. Elife, 2019,8:e47060
Cheung KK, Marques-Da-Silva C, Vairo L, et al. Pharmacological and molecular characterization of functional P2 receptors in rat embryonic cardiomyocytes. Purinergic Signal, 2015,11:127–138
Song X, Gao X, Guo D, et al. Expression of P2X(2) and P2X (3) receptors in the rat carotid sinus, aortic arch, vena cava, and heart, as well as petrosal and nodose ganglia. Purinergic Signal, 2012,8(1):15–22
Zhang J, Liu S, Xu B, et al. Study of baicalin on sympathoexcitation induced by myocardial ischemia via P2X3 receptor in superior cervical ganglia. Auton Neurosci, 2015,189:8–15
Fu LW, Tjen-A-Looi SC, Barvarz S, et al. Role of opioid receptors in modulation of P2X receptor-mediated cardiac sympathoexcitatory reflex response. Sci Rep, 2019,9(1):17224
Ford AP, Dillon MP, Kitt MM, et al. The discovery and development of gefapixant. Auton Neurosci, 2021,235:102859
Wang J, Wang Y, Cui WW, et al. Druggable negative allosteric site of P2X3 receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2018,115(19):4939–4944
Richards D, Gever JR, Ford AP, et al. Action of MK-7264 (gefapixant) at human P2X3 and P2X2/3 receptors and in vivo efficacy in models of sensitisation. Br J Pharmacol, 2019,176(13):2279–2291
Sheng X, Dan Y, Dai B, et al. Knockdown the P2X3 receptor in the stellate ganglia of rats relieved the diabetic cardiac autonomic neuropathy. Neurochem Int, 2018,120:206–212
Pijacka W, Moraes DJ, Ratcliffe LE, et al. Purinergic receptors in the carotid body as a new drug target for controlling hypertension. Nat Med, 2016,22:1151–1159
Moraes D, Da SM, Spiller PF, et al. Purinergic plasticity within petrosal neurons in hypertension. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol, 2018,315:R963–R971
Xin J, Wu J, Hu G, et al. Alpha(1)-AR overactivation induces cardiac inflammation through NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Acta Pharmacol Sin, 2020,41:311–318
Pan XC, Liu Y, Cen YY, et al. Dual Role of Triptolide in Interrupting the NLRP3 Inflammasome Pathway to Attenuate Cardiac Fibrosis. Int J Mol Sci, 2019,20(2):360
Camell CD, Sander J, Spadaro O, et al. Inflammasome-driven catecholamine catabolism in macrophages blunts lipolysis during ageing. Nature, 2017,550(7674):119–123
Tong Y, Wang Z, Cai L, et al. NLRP3 Inflammasome and Its Central Role in the Cardiovascular Diseases. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2020,2020:4293206
Liu D, Zeng X, Li X, et al. Role of NLRP3 inflammasome in the pathogenesis of cardiovascular diseases. Basic Res Cardiol, 2017,113(1):5
Teixeira JM, Bobinski F, Parada CA, et al. P2X3 and P2X2/3 receptors play a crucial role in articular hyperalgesia development through inflammatory mechanisms in the knee joint experimental synovitis. Mol Neurobiol, 2017,54:6174–6186
Chakrabarti S, Ai M, Wong K, et al. Functional Characterization of Ovine Dorsal Root Ganglion Neurons Reveal Peripheral Sensitization after Osteochondral Defect. ENeuro, 2021,8(5):ENEURO.0237–21.2021
Kwon J, Lee EJ, Cho HJ, et al. Antifibrosis treatment by inhibition of VEGF, FGF, and PDGF receptors improves bladder wall remodeling and detrusor overactivity in association with modulation of C-fiber afferent activity in mice with spinal cord injury. Neurourol Urodyn, 2021,40(6):1460–1469
Jin Y, Wei S, Liu TT, et al. Acute P38-Mediated enhancement of P2X3 receptor currents by TNF-alpha in rat dorsal root ganglion neurons. J Inflamm Res, 2021,14:2841–2850
Schiavuzzo JG, Teixeira JM, Melo B, et al. Muscle hyperalgesia induced by peripheral P2X3 receptors is modulated by inflammatory mediators. Neuroscience, 2015,285:24–33
Morice A, Smith JA, McGarvey L, et al. Eliapixant (BAY 1817080), a P2X3 receptor antagonist, in refractory chronic cough: a randomised, placebo-controlled, crossover phase 2a study. Eur Respir J, 2021,58(5):2004240
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
All the authors of the article report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Additional information
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81370282).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, Yz., Yang, S., Li, W. et al. Gefapixant, a Novel P2X3 Antagonist, Protects against Post Myocardial Infarction Cardiac Dysfunction and Remodeling Via Suppressing NLRP3 Inflammasome. CURR MED SCI 43, 58–68 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-022-2658-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-022-2658-5