Summary
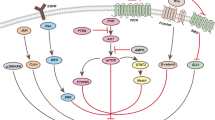
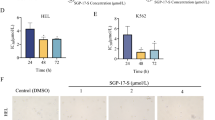
This study examined the mechanism of the inhibitory effect of parthenolide (PTL) on the activity of NF-κB in multiple myeloma (MM). Human multiple myeloma cell line RPMI 8226 cells were treated with or without different concentrations of PTL for various time periods, and then MTT assay was used to detect cell proliferation. Cell cycle and apoptosis were flow cytometrically detected. The level of protein ubiquitination was determined by using immunoprecipitation. Western blotting was employed to measure the level of total protein ubiquitination, the expression of IκB-α in cell plasma and the content of p65 in nucleus. The content of p65 in nucleus before and after PTL treatment was also examined with immunofluorescence. Exposure of RPMI 8226 cells to PTL attenuated the level of ubiquitinated Nemo, increased the expression of IκB-α and reduced the level of p65 in nucleus, finally leading to the decrease of the activity of NF-κB. PTL inhibited cell proliferation, induced apoptosis and blocked cell cycle. Furthermore, the levels of ubiquitinated tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6 (TRAF6) and total proteins were decreased after PTL treatment. By using Autodock software package, we predicted that PTL could bind to TRAF6 directly and tightly. Taken together, our findings suggest that PTL inhibits the activation of NF-κB signaling pathway via directly binding with TRAF6, thereby suppressing MM cell proliferation and inducing apoptosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fuchs O. Targeting of NF-kappaB signaling pathway, other signaling pathways and epigenetics in therapy of multiple myeloma. Cardiovasc Hematol Disord Drug Targets, 2013,13(1):16–34
Karin M, Ben-Neriah Y. Phosphorylation meets ubiquitination: the control of NF-[kappa]B activity. Annu Rev Immunol, 2000,18:621–663
Gasparini C, Celeghini C, Monasta L, et al. NF-kappaB pathways in hematological malignancies. Cell Mol Life Sci, 2014,71(11):2083–2102
Li ZW, Chen H, Campbell RA, et al. NF-kappaB in the pathogenesis and treatment of multiple myeloma. Curr Opin Hematol, 2008,15(4):391–399
Annunziata CM, Davis RE, Demchenko Y, et al. Frequent engagement of the classical and alternative NF-kappaB pathways by diverse genetic abnormalities in multiple myeloma. Cancer Cell, 2007,12(2):115–130
Keats JJ, Fonseca R, Chesi M, et al. Promiscuous mutations activate the noncanonical NF-kappaB pathway in multiple myeloma. Cancer Cell, 2007,12(2):131–144
Smolinski AT, Pestka JJ. Comparative effects of the herbal constituent parthenolide (Feverfew) on lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory gene expression in murine spleen and liver. J Inflamm (Lond), 2005,2:6
Pajak B, Gajkowska B, Orzechowski A. Molecular basis of parthenolide-dependent proapoptotic activity in cancer cells. Folia Histochem Cytobiol, 2008,46(2):129–135
Hewamana S, Lin TT, Jenkins C, et al. The novel nuclear factor-kappaB inhibitor LC-1 is equipotent in poor prognostic subsets of chronic lymphocytic leukemia and shows strong synergy with fludarabine. Clin Cancer Res, 2008,14(24):8102–8111
Guzman ML, Rossi RM, Karnischky L, et al. The sesquiterpene lactone parthenolide induces apoptosis of human acute myelogenous leukemia stem and progenitor cells. Blood, 2005,105(11):4163–4169
Kong F, Chen Z, Li Q, et al. Inhibitory effects of parthenolide on the angiogenesis induced by human multiple myeloma cells and the mechanism. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog [Med Sci], 2008,28(5):525–530
Ghantous A, Sinjab A, Herceg Z et al. Parthenolide: from plant shoots to cancer roots. Drug Discov Today, 2013,18(17–18):894–905
Kwok BH, Koh B, Ndubuisi MI et al. The anti-inflammatory natural product parthenolide from the medicinal herb Feverfew directly binds to and inhibits IkappaB kinase. Chem Biol, 2001,8(8):759–766
Zhang S, Lin ZN, Yang CF et al. Suppressed NF-kappaB and sustained JNK activation contribute to the sensitization effect of parthenolide to TNF-alpha-induced apoptosis in human cancer cells. Carcinogenesis, 2004,25(11):2191–2199
Guzman ML, Rossi RM, Neelakantan S, et al. An orally bioavailable parthenolide analog selectively eradicates acute myelogenous leukemia stem and progenitor cells. Blood, 2007,110(13):4427–4435
Fuchs O. Transcription factor NF-kappaB inhibitors as single therapeutic agents or in combination with classical chemotherapeutic agents for the treatment of hematologic malignancies. Curr Mol Pharmacol, 2010,3(3):98–122
Scheidereit C. IkappaB kinase complexes: gateways to NF-kappaB activation and transcription. Oncogene, 2006,25(51):6685–6705
Gautheron J, Pescatore A, Fusco F, et al. Identification of a new NEMO/TRAF6 interface affected in incontinentia pigmenti pathology. Hum Mol Genet, 2010,19(16):3138–3149
Suvannasankha A, Crean CD, Shanmugam R et al. Antimyeloma effects of a sesquiterpene lactone parthenolide. Clin Cancer Res, 2008,14(6):1814–1822
Gunn EJ, Williams JT, Huynh DT, et al. The natural products parthenolide and andrographolide exhibit anti-cancer stem cell activity in multiple myeloma. Leuk Lymphoma, 2011,52(6):1085–1097
Gopal YN, Chanchorn E, Van Dyke MW. Parthenolide promotes the ubiquitination of MDM2 and activates p53 cellular functions. Mol Cancer Ther, 2009,8(3):552–562
Naito A, Yoshida H, Nishioka E, et al. TRAF6-deficient mice display hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2002,99(13):8766–8771
Yang WL, Wang J, Chan CH, et al. The E3 ligase TRAF6 regulates Akt ubiquitination and activation. Science, 2009,325(5944):1134–1138
Lamothe B, Besse A, Campos AD, et al. Site-specific Lys-63-linked tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6 auto-ubiquitination is a critical determinant of I kappa B kinase activation. J Biol Chem, 2007,282(6):4102–4112
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
These authors contributed equally to this work.
This project was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81272624).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kong, Fc., Zhang, Jq., Zeng, C. et al. Inhibitory effects of parthenolide on the activity of NF-κB in multiple myeloma via targeting TRAF6. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. [Med. Sci.] 35, 343–349 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-015-1435-0
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-015-1435-0