Abstract
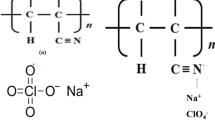
Research and development activities on sodium-ion batteries are becoming prominent in the past few years. Compared to lithium-based batteries, the sodium-based batteries will be cheaper because of the abundancy of sodium raw materials in the earth’s crust and also in seawater. In the current study, we synthesized and characterized poly-acrylonitrile (PAN)-based gel-polymer electrolytes formed with NaClO4 and dissolved in ethylene carbonate (EC) and propylene carbonate (PC). By systematically varying the weight ratios of polymer, salt, and the solvents, we obtained an optimum room temperature ionic conductivity of 4.5 mS cm−1 for the composition 11PAN-12NaClO4-40EC-37PC (wt.%), which is reasonably good for practical applications. This value of conductivity is comparable to a few other Na+ ion conducting gel-polymer electrolyte systems studied in the recent past. Variation of ionic conductivity with inverse temperature showed Arrhenius behavior. Activation energies estimated for all the samples showed only a slight variation suggesting that a single activation process which depends on the EC/PC co-solvent governs the ionic mobility in these gel-polymer electrolytes. Thermo-gravimetric analysis (TGA) revealed that there is no noticeable weight loss of these electrolytes up to 100 °C and hence the electrolytes are thermally stable for operating temperatures up to 100 °C.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aquion manufactures safe and sustainable saltwater batteries. Retrieved on August 31, 2016 from www.aquionenergy.com
The first prototype of a sodium-ion battery. Retrieved on August 31, 2016 from www.energie-rs2e.com/en
Vignarooban K, Kushagra R, Elango A, Badami P, Mellander B-E, Xu X, Tucker TG, Nam C, Kannan AM (2016) Int J Hydrog Energy 41:2829–2846
Stephan AM, Kumar SG, Renganathan NG, Kulandainathan MA (2005) Eur Polym J 41:15–21
Xu W, Angell A (2003) Electrochim Acta 48:2019–2035
Deepa M, Sharma N, Agnihotry SA, Chandra R, Sekhon SS (2002) Solid State Ionics 148:451–455
Deepa M, Sharma N, Agnihotry SA, Singh S, Lal T, Chandra R (2002) Solid State Ionics 152-153:253–258
Kumar D, Hashmi SA (2010) Solid State Ionics 181:416–423
Kumar D, Suleman M, Hashmi SA (2011) Solid State Ionics 202:45–53
Kumar D, Hashmi SA (2010) J Power Sources 195:5101–5108
Yang YQ, Chang Z, Li MX, Wang XW, Wu YP (2015) Solid State Ionics 269:1–7
Gao H, Guo B, Song J, Park K, Goodenough JB (2015) Adv Energy Mater 5:1402235 1-8
Zhang R (2013) Advanced gel-polymer electrolytes for Lithium-Ion polymer batteries, MS thesis. Iowa State University, USA
Stephen AM (2006) Eur Polym J 42:21–42
Vignarooban K, Dissanayake MAKL, Albinsson I, Mellander B-E (2014) Solid State Ionics 266:25–28
Matt P, Roger F (2009) J Phys Chem B 113:5596
Matt P, Roger F (2010) Electrochim Acta 55:1285
Dissanayake MAKL, Thotawatthage CA, Senadeera GKR, Bandara TMWJ, Jayasundara WJMJSR, Mellander B-E (2013) J Appl Electrochem 43(9):891–901
Li M, Wang X, Wang Y, Chen B, Wu Y, Holze R (2015) RSC Adv 5:52382–52387
Song MK, Kim YT, Cho JY, Cho BW, Popov BN, Rhee HW (2004) J Power Sources 125:10–16
Zhu Y, Wang F, Liu L, Xiao S, Yang Y, Wu Y (2013) Scientific Reports 3(3187):1–6
Acknowledgement
KV acknowledges National Science Foundation (NSF), Sri Lanka, for offering an Overseas Special Training Fellowship (No. OSTP/2016/02) to visit the Arizona State University during March-April, 2016. KV and PR acknowledge National Research Council (NRC), Sri Lanka, for the financial assistance (Grant No. NRC 15-078) to the project. KV also acknowledges University Research Grant (URG-2014) obtained from the University of Jaffna, Sri Lanka.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vignarooban, K., Badami, P., Dissanayake, M.A.K.L. et al. Poly-acrylonitrile-based gel-polymer electrolytes for sodium-ion batteries. Ionics 23, 2817–2822 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-017-2002-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-017-2002-4