Abstract
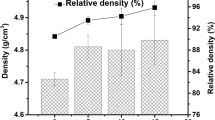
The 50 vol% SrTiO3/yttria-stabilized zirconia (YSZ) composite ceramic was prepared through powder sintering route in 1400∼1500 °C. Only the cubic YSZ and SrTiO3 phases are detected in all the sintered ceramics, and the typical XRD peak positions of both phases have varied dramatically. The grain sizes and relative densities of all specimens increase evidently with the sintering temperature. The width of the SrTiO3/YSZ interfacial region increases from 100.4 to 468.8 nm as the sintering temperature rises from 1400 to 1500 °C. The total electrical conductivities of the sample sintered at 1500 °C are remarkably higher than those at 1400 and 1450 °C, while the ion transference numbers drop from 0.837 to 0.731 with sintering temperature from 1400 to 1500 °C. The variations in the electrical properties above can be interpreted based on the effects of sintering temperature on the elemental diffusions during the sintering process.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ma QL, Iwanschitz B, Dashjav E, Mai A, Tietz F, Buchkremer HP (2014) Electrochemical performance and stability of electrolyte-supported solid oxide fuel cells based on Y-substituted SrTiO3 ceramic anodes. Solid State Ionics 262:465–468
Fu QX, Tietz F, Sebold D, Tao SW, Irvine JTS (2007) An efficient ceramic-based anode for solid oxide fuel cells. J Power Sources 171:663–669
McColm TD, Irvine JTS (2001) B site doped strontium titanate as a potential SOFC substrate. Ionics 7:116–212
Kolodiazhnyi T, Petric A (2005) The applicability of Sr-deficient n-type SrTiO3 for SOFC anodes. J Electroceram 15:5–11
Sun XF, Guo RS, Li J (2008) Preparation and properties of yttrium-doped SrTiO3 anode materials. Ceram Int 34:219–223
Abrantes JCC, Labrincha JA, Frade JR (1997) Combined effects of A-site deficiency and dopant content on the transport properties of Nb-doped strontium titanate. Ionics 3:16–22
Hussain AM, Hogh JVT, Jacobsen T, Bonanos N (2012) Nickel-ceria infiltrated Nb-doped SrTiO3 for low temperature SOFC anodes and analysis on gas diffusion impedance. Int J Hydrog Energy 37:4309–4318
Sudireddy BR, Blennow P, Nielsen KA (2012) Microstructural and electrical characterization of Nb-doped SrTiO3-YSZ composites for solid oxide cell electrodes. Solid State Ionics 216:44–49
He HP, Huang YY, Vohs JM, Gorte RJ (2004) Characterization of YSZ-YST composites for SOFC anodes. Solid State Ionics 175:171–176
Bochentyn B, Karczewski J, Molin S, Klimczuk T, Gazda M, Jasinski P, Safarik DJ, Kusz B (2012) The comparison of SrTi0.98Nb0.02O3-δ-CeO2 and SrTi0.98Nb0.02O3-δ -YSZ composites for use in SOFC anodes. J Electroceram 28:132–138
Ma Q, Tietz F, Sebold D, Stöer D (2010) Y-substituted SrTiO3-YSZ composites as anode materials for solid oxide fuel cells: interaction between SYT and YSZ. J Power Sources 195:1920–1925
Ma Q, Iwanschitz B, Dashjav E, Baumann S, Sebold D, Raj IA, Mai A, Tietz F (2015) Microstructural variations and their influence on the performance of solid oxide fuel cells based on yttrium-substituted strontium titanate ceramic anodes. J Power Sources 279:678–685
Bochentyn B, Karczewski J, Gazda M, Jasinski P, Kusz B (2013) Interactions between components of SrTi0.98Nb0.02O3-δ-YSZ and SrTi0.98Nb0.02O3-δ-CeO2 composites. Phys Status Solidi A 210:538–545
Cho S, Fowler DE, Miller EC, Cronin JS, Poeppelmeier KR, Barnett SA (2013) Fe-substituted SrTiO3-δ-Ce0.9Gd0.1O2 composite anodes for solid oxide fuel cells. Energy Environ Sci 6:1850–1857
Gross MD, Carver KM, Deighan MA, Schenkel A, Smith BM, Yee AZ (2009) Redox stability of SrNb x Ti1−x O3-YSZ for use in SOFC anodes. J Electrochem Soc 156:B540–B545
Meng B, Miao ZY, Kong M, Liu XX, Yu J, Yang QQ (2014) Microstructure and ionic conductivity of SrTiO3 heterogeneously doped YSZ composite ceramics. Solid State Ionics 258:61–66
Li X, Zhao HL, Xu NS, Zhou X, Zhang CJ, Chen N (2009) Electrical conduction behavior of La, Co co-doped SrTiO3 perovskite as anode material for solid oxide fuel cells. Int J Hydrog Energy 34:6407–6414
Roddatis VV, Vasiliev AL, Stepantsov EA, Kiselev NA, Olsson E, Ivanov ZG, Claeson T (1998) Microstructure of yttrium stabilized ZrO2 crystals with CeO2 and SrTiO3 intermediate layers. Thin Solid Films 333:207–212
Cavallaro A, Burriel M, Roqueta J, Apostolidis A, Bernardi A, Tarancón A, Srinivasan R, Cook SN, Fraser HL, Kilner JA, McComb DW, Santiso J (2010) Electronic nature of the enhanced conductivity in YSZ-STO multilayers deposited by PLD. Solid State Ionics 181:592–601
Savaniu CD, Irvine JTS (2011) La-doped SrTiO3 as anode material for IT-SOFC. Solid State Ionics 192:491–493
Li X, Zhao H, Shen W, Gao F, Huang X, Li Y, Zhu Z (2007) Synthesis and properties of Y-doped SrTiO3 as an anode material for SOFCs. J Power Sources 166:47–52
Varanasi C, Juneja C, Chen C, Kumar B (2005) Electrical conductivity enhancement in heterogeneously doped Scandia-stabilized zirconia. J Power Sources 147:128–135
Avila-Paredes HJ, Kim S (2006) The effect of segregated transition metal ions on the grain boundary resistivity of gadolinium doped ceria. Solid State Ionics 177:3075–3080
Ito M, Ohira N (2008) Synthesis of Y-doped n-type SrTiO3 thermoelectric oxides by polymerized complex process. Mater Trans 49(8):1844–1847
Obara H, Yamamoto A, Lee C-H, Kobayashi K, Matsumoto A, Funahashi R (2004) Thermoelectric properties of Y-doped polycrystalline SrTiO3. Jpn J Appl Phys 43(4B):L540–L542
Skarmoutsos D, Nikolopoulos P, Tsoga A (1999) Titania doped YSZ for SOFC anode Ni-cermet. Ionics 5:455–459
Colomer MT, Dìaz-Moreno S, Boada R, Maczka M, Chaboy J (2014) Relationships between structural and electrical properties in mixed conductors duplex materials in the ZrO2-Y2O3-TiO2 ternary system. Phys Rev B 89:094–101
Torquato S (2000) Modeling of physical properties of composite materials. Int J Solids and Struct 37:411–422
Zulfequar M, Kumar A (1986) Effect of porosity on electrical conductivity of hot pressed AlN ceramic. Revue Phys Appl 21:525–529
Yu Y, Wu XP (2010) Study of the generalized mixture rule for determining effective conductivity of two-phase stochastic models. Appl Geophys 7(3):210–216
Kaiser A, Feighery AJ, Fagg DP, Irvine JTS (1998) Electrical characterization of highly titania doped YSZ. Ionics 4:215–219
Acknowledgments
We, all the authors, gratefully acknowledge the financial supports from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51462018), the China Scholarship Council (No. 201508535036), and the Academic Team Research Project on Membrane and Electrode Materials of Advanced Batteries in Kunming University of Science and Technology (No. 14078311).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Q.Q., Meng, B., Lin, Z.L. et al. Effect of sintering temperature on the elemental diffusion and electrical conductivity of SrTiO3/YSZ composite ceramic. Ionics 23, 967–975 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-016-1866-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-016-1866-z