Abstract
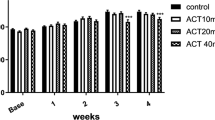
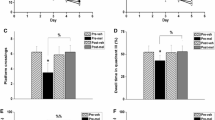
Clothianidin (CLO) is one of the pesticides used to protect against insects, and its potential toxic effects on cognitive functions are not clearly known. This study aims to evaluate the possible effects of dose-dependent CLO on learning and memory in infant and adult male rats and the expression of related genes in the hippocampus. Doses of 2, 8 and 24 mg/kg of CLO were administered to newborn infant and adult albino Winstar rats in the form of gavage and dissolved in vehicle matter. Their cognitive and learning functions were evaluated by the Morris water maze and probe tests. Expression levels of N-methyl D-aspartate 1 (GRIN1), muscuranic receptor M1, synoptophysin (SYP) and growth-associated protein 43 (GAP-43) of tissues isolated from the hippocampus were determined using the real-time PCR method. In the Morris water maze test, no change (p > 0.05) was exhibited in the adult and infant rats after CLO was applied, although there was a significant difference (p < 0.05) in performance between infants and the control group after 24 mg/kg was applied in the probe test. Also, expression levels GRIN1, M1, SYP, GAP-43 did not change when compared to the control (p > 0.05). Our study shows that exposure to high doses of CLO causes deterioration of cognitive functions in infant rats.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abou-Donia MB, Goldstein LB, Bulman S et al (2008) Imidacloprid induces neurobehavioral deficits and increases expression of glial fibrillary acidic protein in the motor cortex and hippocampus in offspring rats following in utero exposure. J Toxicol Environ Heal 71:119–130
Baydas G, Koz ST, Tuzcu M, Nedzvetsky VS, Etem E (2007) Effects of maternal hyperhomocysteinemia induced by high methionine diet on the learning and memory performance in offspring. Int J Devl Neurosci 25:133–139
Calderón-Segura ME, Gómez-Arroyo S, Villalobos-Pietrini R et al (2012) Evaluation of genotoxic and cytotoxic effects in human peripheral blood lymphocytes exposed in vitro to neonicotinoid insecticides news. J Toxicol 2012:612647. doi:10.1155/2012/612647
Casida JE (2011) Neonicotinoid metabolism: compounds, substituents, pathways, enzymes, organisms, and relevance. J Agric Food Chem 59:2923–2931
Courjaret R, Lapied B (2001) Complex intracellular messenger pathways regulate one type of neuronal-bungarotoxin resistant nicotinic acetylcholine receptors expressed in insect neurosecrotory cells (dorsal unpaired median neurons). Mol Pharmacol 60:80–91
Faro LR, Oliveira IM, Durán R, Alfonso M (2012) In vivo neurochemical characterization of clothianidin induced striatal dopamine release. Toxicology 16; 302 (2–3):197–202
Feng S, Kong Z, Wang X, Peng P, Zeng EY (2005) Assessing the genotoxicity of imidacloprid and RH-5849 in human peripheral blood lymphocytes in vitro with comet assay and cytogenetic tests. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 61:239–246
Fishel FM (2005) Pesticide toxicity profile: Neonicotinoid Pesticides. This document is PI 80, one of a series of the pesticide information office, Florida cooperative extension service. Institute of Food and Agricultural Sciences, University of Florida 2005. http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu
Ford KA, Casida JE (2006) Unique and common metabolites of thiamethoxam, clothianidin, and dinotefuran in mice Chem Res Toxicol 19:1549–1556
Gahring LC, Rogers SW (2006) Neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor expression and function on nonneuronal cells. AAPS J 7(4):885–894
Matsuda K, Buckingham SD, Kleier D et al (2001) Neonicotinoids: insecticides acting on insect nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Trends Pharmacol Sci 22:573–580
Muñoz-Quezada MT, Lucero BA, Barr DB et al (2013) Neurodevelopmental effects in children associated with exposure to organophosphate pesticides: a systematic review. Neuro Toxicol 39:158–168
Oliveira IM, Nunes BV, Barbosa DR, Pallares AM, Faro LR (2010) Effects of the neonicotinoids thiametoxam and clothianidin on in vivo dopamine release in rat striatum. Toxicol Lett 15; 192(3):294–297
Pimentel D, Greiner A, Bashore T (1998) Economic and environmental costs of pesticide use. In: Rose J (ed) Environmental toxicology: Current developments. Gordon and Breach Science Publisher, UK, pp 121–187
Romanelli MN, Gualtieri F (2003) Cholinergic nAChRs: competitive ligands, allosteric modulators, and their potential applications. Med Res Rev 23:393–426
Tomizawa M, Casida JE (2003) Selective toxicity of neonicotinoids attributable to specificity of insect and mammalian nicotinic receptors. Ann Rev Entomol 48:339–364
Tomizawa M, Casida JE (2005) Neonicotinoid insecticide toxicology: mechanisms of selective action. Ann Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 45:247–268
Tuzcu M, Baydas G (2006) Effect of melatonin and vitamin E on diabetes-induced learning and memory impairment in rats. Euro J Pharma 537:106–110
Vural N (2005) Toksikoloji. Ankara Üniversitesi Basımevi, Ankara
Waller MB, Waller PF, Brewster LA (1960) A water maze for use in studies of drive and learning. Psychol Rep 7:99–102
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Özdemir, H.H., Kara, M., Yumrutas, O. et al. Determination of the effects on learning and memory performance and related gene expressions of clothianidin in rat models. Cogn Neurodyn 8, 411–416 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11571-014-9293-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11571-014-9293-1