Abstract
The objectives of this study were to describe the different modalities of physical activity programs designed for moderate to severe dementia and to identify their impact on functional independence in activities of daily living (ADL). A critical review of randomized controlled trials related to the impact of physical activity programs in moderately to severely demented persons on ADL performance and meta-analysis of the identified studies were performed. Among the 303 identified articles, five responded to the selection criteria. Four out of the five studies demonstrated limited methodological quality. In one high-quality study, physical activity programs significantly delayed deterioration of ADL performance. The program components and ADL assessment tools vary widely across studies. Although the proposed treatments have not proven their efficiency in improving the ADL status of the patients, they were able to limit the decline in ADL functioning. Future research is warranted in order to identify clinically relevant modalities for physical activity programs for people with moderate to severe dementia.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Dementia, a syndrome usually resulting from a chronic or progressive brain disorder such as Alzheimer’s disease, currently affects 18 million people worldwide. Dementia is characterized by a decline of cognitive functions such as memory, language, recognition, reasoning, and judgment [1]. The risk of developing dementia increases with age; thus, the number of patients with dementia will increase worldwide over the coming decades along with the demographic aging of the population.
A considerable number of patients suffering from dementia at moderate to advanced stages are institutionalized. Factors contributing to institutionalization vary and can include behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia [2, 3] as well as physical performance or level of independence in activities of daily living (ADL). Indeed, dependence in ADL is a critical risk factor for institutionalization [4, 5]. Furthermore, dependence for ADL causes direct and indirect costs related to the care of this population to increase in parallel [6].
Recent data about the relationship between cognitive functioning and physical performance suggest that regular physical activity could provide cognitive benefits for patients with Alzheimer’s disease [7, 8]. A high-intensity physical activity program may delay ADL decline in older nursing home residents with severe cognitive impairment [9]. However, sound evidence on which form of physical activity has the highest impact is still lacking. Knowing what can be done, in which form, at what time, how long, and at what stage of the illness is of crucial importance to caregivers, to healthcare professionals, and to public health decision makers. This is especially important at moderate to severe stages of the illness when ADL ability decreases.
The objectives of this review are (1) to describe the different types of physical activity programs designed for patients with moderate to severe dementia and (2) to identify the impact of these activities on functional independence in ADL. These findings will provide guidance for clinical practice and future research.
Methods
A computerized search strategy was applied using the following MESH terms: (“Motor Activity” [Mesh] OR “Exercise” [Mesh] OR physical activity) AND “Dementia” [Mesh] AND (“Activities of Daily Living” [Mesh] OR functional independence). The consulted databases were Medline via PubMed, CINAHL, Cochrane Library, ISI Social Sciences Citation Index, OTseeker, and PEDro. The search stop date was December 12th 2009. We completed our computerized search by checking the reference lists of the included articles, of five systematic reviews [7, 10–13], and one meta-analysis [14].
Studies were included if they investigated physical activity interventions applied to moderately to severely demented persons (defined as an Mini-mental State Examination (MMSE) score of 17 or less) [15, 16]. Additional inclusion criteria were the presence of outcome measures for ADL, the randomized controlled trial design, and the language of the article; only articles written in English, French, German, or Italian were considered.
Quality assessment was carried out using the scale developed by Downs and Black which is appropriate for assessing randomized and non-randomized studies [17]. This scale has good reliability and validity [17]. We adapted the last criterion of this scale, i.e., the power of the study, and attributed one point if the authors did a prior sample size calculation. Two authors (EB, NK) independently assessed the quality of the included papers after having completed the training of the scale application on one study which had not been included in the review. Disagreement was resolved through discussion, and if necessary, the judgment of a third person (AvG) was retained.
Data extraction and analysis
We summarized the characteristics of each study sample, the physical activity interventions and their modalities of application, the measured ADL outcomes, the assessment tools used to measure ADL capacities, and the effect on the patients’ capacities to perform ADL. For missing data, the original author of the trial was contacted in order to receive the required information.
Three meta-analyses were conducted in order to combine the results of the different studies included in our review. The first analysis compared the pre- and post-treatment values of the experimental group, the second analysis compared the pre- and post-treatment values of the control group, and the last analysis compared the post-treatment difference of both groups. Since the number of included studies was small and since different exercise programs were proposed across these studies, the use of additional meta-analyses for the comparison of the different intervention modes was not feasible.
Published results were first converted into a common effect size measure: the standardized mean difference which is defined as the mean difference divided by the corresponding standard deviation [18]. Bias was removed using Hedges’ g method [19], and the homogeneity between studies was evaluated by the Q test [20]. Here, the homogeneity was rejected for all analyses, meaning that the true effect size in each study can be considered as similar, but not as identical. The solution was then to compute the overall effect size under the assumption of a random effect model. In practice, each study was weighted by the inverse of a variance composed of two terms: the variance of the study and a constant computed from Q and representing the variability of the effect size across studies [21, 22].
The study by Steinberg et al. [23] could not be included in the meta-analyses because the results were in a form incompatible with the computation of standardized mean differences. For similar reasons, the study by Stevens and Killeen [24] could not be included in the third meta-analysis. So, to be coherent between the analyses, we decided to perform twice each of the first two analyses: with and without the Stevens and Killeen’s study [24]. Since the results with only three studies included did not significantly differ from those with the four studies included, we reported results for the latter case only. Results were reported as forest plots including the effect sizes and the 95% confidence intervals.
Results
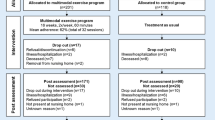
Out of the 303 identified articles, 43 were duplicates. Further reasons for exclusion comprised other or missing interventions (125), other outcomes (49), other languages (12), other populations (51), and other designs (16). After reading the full text, we excluded two additional studies with samples whose MMSE score was higher than 17 (Fig. 1). Overall, five articles met the selection criteria and will be further discussed below. The results of the quality assessment (Table 1) showed that only one of the five randomized clinical trials included demonstrated a high-quality score (25 of 27) [25].
Flowchart of identified and included studies. The first column represents the number of articles identified on the consulted databases (Medline, CINAHL, PEDro, ISI Social Sciences Citation Index, Cochrane, OTseeker) and those found by hand search. The second column refers both to the articles excluded after reading the title or the abstract and to the reason of exclusion. The last column contains the number of the articles that were assessed
The main weaknesses of the included articles were the lack of information concerning the following three criteria: external validity, description of randomization, and description of the patients lost to follow-up. Blinding of therapists and participants is not feasible when applying physical activity interventions, and hence, item 14 was not retained as a quality criterion. The agreement between the two raters when applying the Downs and Black scale was good with a chance corrected kappa coefficient of 0.67. We checked the internal validity of the included studies by applying the Cochrane criteria that are specific for randomized trials.
The results confirmed that none of the studies was free of bias. According to the Cochrane criteria, the main weaknesses consisted of (1) the unclear process of randomization for four [23, 24, 26, 27] out of the five included studies, (2) the unequal treatment time in two studies [25, 26], (3) the lack of blinding of the outcome assessors in three studies [24, 26, 27], and (4) the missing report of withdrawals in three studies [24, 26, 27].
The extracted information is summarized in Tables 2 and 3.
The included studies were conducted between 2006 and 2009, except for one publication dating back to 1997 [27]. Three studies [24, 25, 27] included nursing home residents and two studies [23, 26] community-dwelling people. The participants were 75 years or older and, according to the MMSE scores or population description, moderately to severely demented.
The physical activity programs differed in each study, and in one study [26], references for the activity programs were missing. The intervention modalities varied widely. The most frequently mentioned interventions were strengthening exercises, balance, and gait training [23, 25, 26] as well as endurance training [23–25].
The duration of the programs varied from 7 weeks to 12 months. The frequency varied between biweekly and daily and the duration of each session between 20 and 75 min. The intensity of exercises was inconsistently reported with few information: oxygen consumption [26], aerobic exertion [24, 25, 27], and compliance measures [23, 25].
Each study used a different assessment tool. Among them, the Katz Index was the most common ADL assessment tool [25]. One article indicated the applied assessment method and the considered ADL items [26].
In three studies [23, 24, 26], the physical activity program significantly improved ADL performance in the experimental group by the end of the intervention. One study reported a significant delay of decline in ADL. It was a small but clinically meaningful difference in the experimental group compared to the control group after 12 months of intervention; the intermediate result after 6 months was not significant [25]. Physical activity practice showed a significant effect already after 6 months [26], although modalities of the physical activity program were quite similar between these two studies. One very small study—including only six participants in the experimental group—did not show any significant effect on ADL performance [27]. Among the controls, ADL performance deteriorated over the short observational period (Table 4).
Figures 2, 3, and 4 summarized the main results of each meta-analysis. Figure 2 showed that the ADL status did not significantly change between the pre- and post-measurements among treated patients (aggregate effect size 0.30, 95% confidence interval [−0.49; 1.09]). We examined the effect of including or not including Stevens and Killeen’s study [24] in the meta-analysis, and it did not change our conclusion. When performed on the control group (Fig. 3), the same analysis indicated a significant decline of the ADL functioning between the pre- and post-measurements (−0.63 [−1.02; −0.23]). Finally, the third analysis (Fig. 4) did not show any real difference in post-treatment values of both groups (0.43 [−0.63; 1.50]).
Discussion
Physical activity programs tended to influence ADL performance positively. Thus, the decline in ADL performance in demented subjects may be due not only to disease progression but also to physical inactivity [28]. One study showed that the effect on ADL performance disappeared after cessation of the physical activity programs [28]. This observation may explain why three [23, 24, 26] out of five trials showed a significant effect on ADL performance, but only one reported clinically meaningful results despite differences in their physical activity programs [25]. The negative evolution of ADL performance in all control groups except one [27] tends to support the relationship between physical activity and functional abilities [29]. The most severe ADL degradation was observed in the study which included the patients with the lowest MMSE scores [25]. Delaying ADL deterioration in nursing home residents with moderate or severe cognitive impairment through a physical activity program may be both clinically and economically relevant as ADL care in this patient group accounts for two thirds of the total care time [30].
The descriptive results were supported by our meta-analyses and allowed us to conclude—as Forbes et al. [7] did—that even if the proposed treatments have not proven their efficiency in improving the ADL status of the patients, they could nevertheless limit the decline in ADL functioning.
However, the physical activity programs varied among the included studies. In line with Yu and Kolanowski [31] as well as Taylor et al. [11], we confirm that there are no clinical practice guidelines for aerobic exercises for persons with dementia. Reasons for the lack of both studies on the matter and practice guidelines may include the individual variability of the aging process and the limitation of physical activity practice due to the disabilities of the very old [11]. Nonetheless, endurance can positively influence the physiological aging process of the cardiovascular system at a central and peripheral level [14]. Aging per se causes loss of muscle strength, and regular strengthening exercises can counteract to some degree this loss in the very old [11]. Based on this knowledge, the content of the physical activity programs covering endurance, gait, and strength training proposed in the included studies seemed to be appropriate.
Questions related to the duration and intensity of the physical activity program, the duration of each session, or their frequency remain unanswered. One high-quality study applied a physical activity program with moderate to high intensity and showed a significant delay of ADL decline only after 12 months duration, but not after 6 months [25]. A high intensity strengthening program during 3 months achieved a similar result in dementia nursing home residents [28]. Paterson and Warburton [32] suggest that the intensity of physical activity should be at least moderate in order to improve ADL performance in the elderly. The literature on the topic does not either give clear indications on how long an ideal activity program should last. Our review lists programs lasting from 7 weeks to 12 months. Yu and Kolanowski [31], based on their summary of current knowledge concerning the prevention of Alzheimer’s disease, suggest an ideal program duration of 2 months and the ideal session frequency of three times per week for an aerobic exercise program designed for a medically stable population with dementia and aimed at improving their ADL performance. The most important parameter was regularity of exercising [25] with high exercise adherence significantly preventing ADL decrease. However, none of the studies investigated long-term effects on ADL performances. The result of the study of Littbrand et al. including residents with less severe dementia showed no lasting effect of physical activity training on ADL [28]. Demented people are likely to need some encouragement to stay physically active and to slow the decrease of their ADL performance [28] especially in those with moderate to severe dementia. Overall, the optimal frequency and intensity of physical activities which provide a satisfactory long-term effect are still unknown and their determination highly relevant.
Physical activity programs were accompanied by music in only three studies [24, 25, 27], although there is a growing body of evidence that music in advanced stages of dementia could help improve the performance of patients [33, 34]. According to a qualitative study, demented patients claimed that programs should respond to their psychological and social needs, whereas their caregivers considered maintenance of functional independence as the most important goal [35]. Thus, physical activity in groups accompanied by music could more easily respond to the expectations of demented patients and increase their adherence to a physical activity program. In addition, a further criterion to respect is the meaningfulness of the proposed activities. These activities increase adherence in physical activity programs among the elderly [11].
Information regarding the group sizes was missing. The reduced communication skills, the frailty of this population, and the increased risk of falling may require limited group sizes. An individual approach, as opposed to group sessions, allows meeting a patient’s needs more specifically as community-dwelling participants may prefer exercising at home [36]. The need for individual adaptation of physical activity programs has been stressed by Yu and Kolanowski [31] as patients with moderate to severe dementia do not express reliably exertion and need guidance to exercise at the targeted level. Variability in content and modalities of physical activity programs (session frequency and duration) impede any precise recommendation for clinical practice.
The variety of applied ADL assessment tools hampered comparison of the program effect on the ADL performance across all studies. Any recommendation to use objective measurement tools for moderately to severely demented subjects was altogether missing from the literature. The Katz Index [37] is a clinically relevant measurement [38]. However, it has little or no sensitivity to small changes [38] and is therefore inappropriate for longitudinal studies. Only one study applied a population specific measure, i.e., the Changes in Advanced Dementia Scale [39], to assess ADL performance in demented persons [27]. The reliability and criterion validity of the Changes in Advanced Dementia Scale are promising [39]. Contrary to other tools, it considers a patient’s mobility. Assessing mobility is crucial as it is a key capacity among elderly with moderate to severe dementia [40]. Mobile patients decrease caregiver burden [41], and their quality of life may be better [7]. The majority of items in the Changes in Advanced Dementia Scale deal with cognitive abilities to perform ADL and not physical abilities [27]. However, while physical activity programs act primarily on motor tasks, they may also have an impact on cognition [10]. Given the preponderance of items related to cognition, physical components of ADL capacities may be underestimated when applying the Changes in Advanced Dementia Scale. The preceding considerations may explain the clinicians’ and researchers’ difficulties in selecting the appropriate ADL assessment tool.
Safety was an explicit issue in only two studies [23, 25]. Higher levels of physical activity were beneficial and decreased the number of falls in a mildly to moderately demented population [42]. No study reported serious adverse events related to physical activity, but Steinberg et al. [23] found trends of poorer quality of life and increased depression in their exercise group and discussed the possibility that physical activity may cause distress. However, the finding of higher depression scores was not corroborated by other studies [43, 44].
Several limitations call for a cautious interpretation of the findings reported in the reviewed studies. The methodological quality of the majority of the included studies is low, and information regarding the reliability, validity, and sensitivity to change (i.e., the clinically minimal important change) of the various assessment tools applied to a moderate or severely demented population is missing.
The scores obtained for external validity were low which limits the generalizability of the results and the formulation of recommendations. Internal validity biases reduce confidence in the results. Biases were due to inappropriate randomization methods in four out of the five included studies [23, 24, 26, 27], to the lack of blinding of the outcome assessors in three studies [24, 26, 27] and two studies [23, 26] used ADL assessment tools which were not validated for the moderately and severely demented. The clinical importance of the results was threatened by the insufficient power of three out of the five included studies [23, 26, 27]. The absence of interventions for the control group in two trials [25, 26] represented a further weakness and prevented interpretation of the impact of physical activity programs on ADL in these studies.
The small number of studies corresponding to the selection criteria of our review represents an important limitation of this paper. Although we tried to identify all significant studies, we do not pretend to have conducted a comprehensive review. Defining dementia severity using mean MMSE scores was a pragmatic decision as MMSE scores are the most frequently reported severity measures. However, although populations were described as being moderately to severely demented in the included studies, not all authors reported dementia severity scores [24, 27]. We are aware of the confounding education levels by interpreting MMSE scores [45] as well as the questionability of the cutoff scores which define moderate and severe dementia [46]. While a uniform definition of severity is still lacking [47, 48], the relevant MMSE scores are still debated [49]. We based our decisions on Tombaugh and McIntyre [15] and Feldman and Woodward [16]. Harrell et al. [50] developed a MMSE version which is adapted to severe dementia. However, none of the studies applied it [50].
Conclusion
Evidence for efficacy of physical activity programs on ADL performance in the elderly with moderate to severe dementia remains very limited. One high-quality study showed a small but statistically significant and clinically meaningful effect. Further investigations determining ideal physical activity program content as well as appropriate session duration and frequency are warranted. The variable program content between studies is of concern since it provides little guidance to clinicians as to what protocols may be the most suitable in patient care. Gaining a more complete picture of the impact—and limits—of physical activity programs in this domain is urgent. While the number of people with dementia is growing, reducing ADL dependence contributes to a better control of costs and alleviates family and caregiver burdens [41]. In this context, the issue of the “most effective dose” for physical activity programs (nature, frequency, duration) is of crucial importance to healthcare quality and costs.
References
Cummings JL et al (1998) Alzheimer’s disease: etiologies, pathophysiology, cognitive reserve, and treatment opportunities. Neurology 51(1 Suppl 1):S2–S17, discussion S65-7
Gruber-Baldini AL et al (2004) Behavioral symptoms in residential care/assisted living facilities: prevalence, risk factors, and medication management. J Am Geriatr Soc 52(10):1610–1617
Shin IS et al (2005) Neuropsychiatric symptoms and quality of life in Alzheimer disease. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry 13(6):469–474
Steeman E, Abraham IL, Godderis J (1997) Risk profiles for institutionalization in a cohort of elderly people with dementia or depression. Arch Psychiatr Nurs 11(6):295–303
Astell AJ, Clark SA, Hartley NT (2008) Predictors of discharge destination for 234 patients admitted to a combined geriatric medicine/old age psychiatry unit. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry 23(9):903–908
Kang IO et al (2007) Economic cost of dementia patients according to the limitation of the activities of daily living in Korea. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry 22(7):675–681
Forbes D et al (2008) Physical activity programs for persons with dementia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev (3):CD006489
Lautenschlager NT et al (2008) Effect of physical activity on cognitive function in older adults at risk for Alzheimer disease: a randomized trial. JAMA 300(9):1027–1037
Morris JN et al (1999) Nursing rehabilitation and exercise strategies in the nursing home. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 54(10):M494–M500
Yu F et al (2006) Improving cognition and function through exercise intervention in Alzheimer’s disease. J Nurs Scholarsh 38(4):358–365
Taylor AH et al (2004) Physical activity and older adults: a review of health benefits and the effectiveness of interventions. J Sports Sci 22(8):703–725
Christofoletti G et al (2007) Effects of motor intervention in elderly patients with dementia an analysis of randomized controlled trials. Top Geriatr Rehabil 23(2):149–154
Sherrington C, Lord SR, Finch CF (2004) Physical activity interventions to prevent falls among older people: update of the evidence. J Sci Med Sport 7(1 Suppl):43–51
Heyn PC, Johnson KE, Kramer AF (2008) Endurance and strength training outcomes on cognitively impaired and cognitively intact older adults: a meta-analysis. J Nutr Health Aging 12(6):401–409
Tombaugh TN, McIntyre NJ (1992) The Mini-mental State Examination: a comprehensive review. J Am Geriatr Soc 40(9):922–935
Feldman H, Woodward M (2005) The staging and assessment of moderate to severe Alzheimer disease. Neurology 27(65):10–17
Downs SH, Black N (1998) The feasibility of creating a checklist for the assessment of the methodological quality both of randomised and non-randomised studies of health care interventions. J Epidemiol Community Health 52(6):377–384
Nugent W (2006) The comparability of the standardized mean difference effect size across different measures of the same construct measurement considerations. Educ Psychol Meas 66(4):612–623
Hedges LV (1981) Distribution theory for glass’s estimator of effect size and related estimators. J Educ Stat 6(2):107–128
Cochran WG (1954) The combination of estimates from different experiments. Biometrics 10:101–129
Friedman L (2000) Estimators of random effects variance components in meta-analysis. J Educ Behav Stat 25:1–12
Lipsey M, Wilson D (2000) Practical meta-analysis. Sage, Thousand Oaks
Steinberg M et al (2009) Evaluation of a home-based exercise program in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease: the Maximizing Independence in Dementia (MIND) study. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry 24(7):680–685
Stevens J, Killeen M (2006) A randomised controlled trial testing the impact of exercise on cognitive symptoms and disability of residents with dementia. Contemp Nurse 21(1):32–40
Rolland Y et al (2007) Exercise program for nursing home residents with Alzheimer’s disease: a 1-year randomized, controlled trial. J Am Geriatr Soc 55(2):158–165
Kwak YS et al (2008) Effect of regular exercise on senile dementia patients. Int J Sports Med 29(6):471–474
Francese T, Sorrell J, Butler F (1997) The effects of regular exercise on muscle strength and functional abilities of late stage Alzheimer’s residents. Am J Alzheimers Dis Other Demen 12(3):122–127
Littbrand H et al (2009) The effect of a high-intensity functional exercise program on activities of daily living: a randomized controlled trial in residential care facilities. J Am Geriatr Soc 57(10):1741–1749
Arcoverde C et al (2008) Role of physical activity on the maintenance of cognition and activities of daily living in elderly with Alzheimer’s disease. Arq Neuropsiquiatr 66(2B):323–327
Luttenberger K, Graessel E (2010) Recording care time in nursing homes: development and validation of the “RUD-FOCA” (Resource Utilization in Dementia—Formal Care). Int Psychogeriatr 1–10
Yu F, Kolanowski A (2009) Facilitating aerobic exercise training in older adults with Alzheimer’s disease. Geriatr Nurs 30(4):250–259
Paterson DH, Warburton DE (2010) Physical activity and functional limitations in older adults: a systematic review related to Canada’s Physical Activity Guidelines. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act 7:38
Clair AA, O’Konski M (2006) The effect of rhythmic auditory stimulation (RAS) on gait characteristics of cadence, velocity, and stride length in persons with late stage dementia. J Music Ther 43(2):154–163
Hulme C et al (2009) Non-pharmacological approaches for dementia that informal carers might try or access: a systematic review. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry
Harmer BJ, Orrell M (2008) What is meaningful activity for people with dementia living in care homes? A comparison of the views of older people with dementia, staff and family carers. Aging Ment Health 12(5):548–558
Rolland Y et al (2000) Feasibility of regular physical exercise for patients with moderate to severe Alzheimer disease. J Nutr Health Aging 4(2):109–113
Brorsson B, Asberg KH (1984) Katz index of independence in ADL. Reliability and validity in short-term care. Scand J Rehabil Med 16(3):125–132
Desai AK, Grossberg GT, Sheth DN (2004) Activities of daily living in patients with dementia: clinical relevance, methods of assessment and effects of treatment. CNS Drugs 18(13):853–875
McCracken A et al (1993) Developing a tool to measure functional changes in advanced dementia. Nurs Connect 6(2):55–66
Norman GM, Gibbs JA (1991) Why walk when you can ride? Clinical ambulation incentives for the immobile elderly. J Gerontol Nurs 17(8):28–33
Kim MD et al (2009) Caregiver burden among caregivers of Koreans with dementia. Gerontology 55(1):106–113
Allan LM et al (2009) Incidence and prediction of falls in dementia: a prospective study in older people. PLoS One 4(5):e5521
Regan C et al (2005) Relationship of exercise and other risk factors to depression of Alzheimer’s disease: the LASER-AD study. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry 20(3):261–268
Teri L et al (2003) Exercise plus behavioral management in patients with Alzheimer’s disease: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 290(15):2015–2022
Ganguli M et al (2010) Age and education effects and norms on a cognitive test battery from a population-based cohort: the Monongahela–Youghiogheny Healthy Aging Team. Aging Ment Health 14(1):100–107
Dodge HH et al (2009) Cross-cultural comparisons of the Mini-mental State Examination between Japanese and U.S. cohorts. Int Psychogeriatr 21(1):113–122
Farlow M (2005) Moderate to severe Alzheimer disease: definition and clinical relevance. Neurology 65:S1–S4
Perneczky R et al (2006) Mapping scores onto stages: Mini-mental State Examination and clinical dementia rating. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry 14(2):139–144
Mayor S (2006) NICE recommends drugs for moderate Alzheimer’s disease. BMJ 332(7535):195
Harrell LE et al (2000) The severe Mini-mental State Examination: a new neuropsychologic instrument for the bedside assessment of severely impaired patients with Alzheimer disease. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord 14(3):168–175
Open Access
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial License which permits any noncommercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and source are credited.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Open Access This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/2.0), which permits any noncommercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and source are credited.
About this article
Cite this article
Burge, E., Kuhne, N., Berchtold, A. et al. Impact of physical activity on activity of daily living in moderate to severe dementia: a critical review. Eur Rev Aging Phys Act 9, 27–39 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11556-011-0092-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11556-011-0092-y