Abstract
Purpose
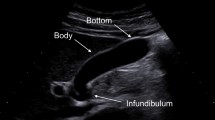
As gallbladder diseases including gallstone and cholecystitis are mainly diagnosed by using ultra-sonographic examinations, we propose a novel method to segment the gallbladder and gallstones in ultrasound images.
Methods
The method is divided into five steps. Firstly, a modified Otsu algorithm is combined with the anisotropic diffusion to reduce speckle noise and enhance image contrast. The Otsu algorithm separates distinctly the weak edge regions from the central region of the gallbladder. Secondly, a global morphology filtering algorithm is adopted for acquiring the fine gallbladder region. Thirdly, a parameter-adaptive pulse-coupled neural network (PA-PCNN) is employed to obtain the high-intensity regions including gallstones. Fourthly, a modified region-growing algorithm is used to eliminate physicians’ labeled regions and avoid over-segmentation of gallstones. It also has good self-adaptability within the growth cycle in light of the specified growing and terminating conditions. Fifthly, the smoothing contours of the detected gallbladder and gallstones are obtained by the locally weighted regression smoothing (LOESS).
Results
We test the proposed method on the clinical data from Gansu Provincial Hospital of China and obtain encouraging results. For the gallbladder and gallstones, average similarity percent of contours (EVA) containing metrics dice’s similarity , overlap fraction and overlap value is 86.01 and 79.81%, respectively; position error is 1.7675 and 0.5414 mm, respectively; runtime is 4.2211 and 0.6603 s, respectively. Our method then achieves competitive performance compared with the state-of-the-art methods.
Conclusions
The proposed method is potential to assist physicians for diagnosing the gallbladder disease rapidly and effectively.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hareendranathan AR, Mabee M, Punithakumar K, Noga M, Jaremko JL (2016) A technique for semiautomatic segmentation of echogenic structures in 3D ultrasound, applied to infant hip dysplasia. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 11(1):31–42. doi:10.1007/s11548-015-1239-5
Nobel JA, Boukerroui D (2006) Ultrasound image segmentation: a survey. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 25(8):987–1010. doi:10.1109/TMI.2006.877092
Gupta A, Gosain B, Kaushal S (2010) A comparison of two algorithms for automated stone detection in clinical B-mode ultrasound images of the abdomen. Int J Clin Monit Comput 24(5):341–362. doi:10.1007/s10877-010-9254-0
Yang X, Ye X, Slabaugh G (2015) Multilabel region classification and semantic linking for colon segmentation in CT colonography. IEEE Trans B Biomed Eng 62(3):948–959. doi:10.1109/TBME.2014.2374355
Hu S, Hoffman E, Reinhardt JM (2001) Automatic lung segmentation for accurate quantitation of volumetric X-RAY CT images. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 20(6):490–498. doi:10.1109/42.929615
Dandin O, Teomete U, Osman O, Tulum G, Ergin T, Sabuncuoglu M (2016) Automated segmentation of the injured spleen. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 11(3):351–368. doi:10.1007/s11548-015-1288-9
Grau V, Mewes A, Alcaniz M, Kikinis R, Warfield SK (2004) Improved watershed transform for medical image segmentation using prior information. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 23(4):447–458. doi:10.1109/TMI.2004.824224
Ma Y, Wang L, Ma Y, Dong M, Du S, Sun X (2016) Novel automatic segmentation of left ventricle in cardiac cine MR images. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 11(11):1951–1964. doi:10.1007/s11548-016-1429-9
Faghih Roohi S, Aghaeizadeh Zoroofi R (2013) 4D statistical shape modeling of the left ventricle in cardiac MR images. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 8(3):335–351. doi:10.1007/s11548-012-0787-1
Ciecholewski M (2010) Gallbladder boundary segmentation from ultrasound images using active contour model. In: Lecture notes in computer science-LNCS. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-15381-5_8
Ciecholewski M, Chochołowicz J (2013) Gallbladder shape extraction from ultrasound images using active contour models. Comput Biol Med 43(12):2238–2255. doi:10.1016/j.compbiomed.2013.10.009
Xie W, Ma Y, Shi B, Wang Z (2013) Gallstone segmentation and extraction from ultrasound images using level set model. In: IEEE biosignals and biorobotics conference, Rio de Janeiro. doi:10.1109/BRC.2013.6487452
Jain A, Agrawal M, Gupta A, Khandelwal V (2008) A novel approach to video matting using automated scribbling by motion analysis. In: Proceedings annual international IEEE virtual environment human–computer. Interfaces measurement systems VECIMS, pp 25–30. doi:10.1109/VECIMS.2008.4592747
Levin A, Lischinski D, Weiss Y (2006) A closed form solution to natural image matting. In: Proceedings Annual International IEEE computer society conference computer vision pattern recognition. CVPR, pp 61–68. doi:10.1109/CVPR.2006.18
Agnihotri S, Loomba H, Gupta A and Khandelwal V (2009) Automated segmentation of gallstones in ultrasound images. In: Proceedings annual international IEEE computer science information technology ICCSIT, pp 56–59. doi:10.1109/ICCSIT.2009.5234996
Otsu N (1979) A threshold selection method from gray-level histograms. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern 9(1):62–66. doi:10.1109/TSMC.1979.4310076
Perona P, Malik J (1990) Scale-space and edge detection using anisotropic diffusion. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Anal 12(7):629–639. doi:10.1109/34.56205
Sarti A, Corsi C, Mazzini E, Lamberti C (2005) Maximum likelihood segmentation of ultrasound images with Rayleigh distribution. IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectr Freq Control 52(6):947–960. doi:10.1109/TUFFC.2005.1504017
Liao PS, Tse-Sheng Ch, Pau-Choo Ch (2001) A fast algorithm for multilevel thresholding. J Inf Sci Eng 17(5):713–727
Musrrat A, Ch W, Pant M (2013) Multi-level image thresholding by synergetic differential evolution. Appl Soft Comput 17(3):1–11. doi:10.1016/j.asoc.2013.11.018
Jan F, Usman I, Agha S (2012) Iris localization in frontal eye images for less constrained iris recognition systems. Digit Signal Process 22(6):971–986. doi:10.1016/j.dsp.2012.06.001
Johnson J, Padgett M (1999) PCNN models and applications. IEEE Trans on Neural Netw 10(3):480–498. doi:10.1109/72.761706
Zhan K, Shi J, Wang H, Xie Y, Li Q (2016) Computational mechanisms of pulse-coupled neural networks: a comprehensive review. Arch Comput Methods Eng 20:1–16. doi:10.1007/s11831-016-9182-3
Chen Y, Park SK, Ma Y, Ala R (2011) A new automatic parameter setting method of a simplified PCNN for image segmentation. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 22(6):880–892. doi:10.1109/TNN.2011.2128880
Zhan K, Zhang H, Ma Y (2009) New spiking cortical model for invariant texture retrieval and image processing. IEEE Trans on Neural Netw 20(12):1980–1986. doi:10.1109/TNN.2009.2030585
Mirghasemi S, Rayudu R, Zhang MJ (2013) A new image segmentation algorithm based on modified seeded region growing and particle swarm optimization. In: 28th international conferences image vision computer New Zealand IVCNZ, pp: 382-387. doi:10.1109/IVCNZ.2013.6727045
Yu P, Qin AK, Clausi DA (2012) Unsupervised polarimetric SAR image segmentation and classification using region growing with edge penalty. IEEE Trans Geosci and Remote Sens 50(4):1302–1317. doi:10.1109/TGRS.2011.2164085
Cleveland W, Devlin S (1988) Locally weighted regression: an approach to regression analysis by local fitting. J Am Stat Assoc 83(403):596–610. doi:10.1080/01621459.1988.10478639
Xu C, Prince JL (1997) Gradient vector flow: a new external force for snakes. CVPR 97:66. doi:10.1109/CVPR.1997.609299
Xu C, Prince JL (1998) Snakes, shapes, and gradient vector flow. IEEE Trans Image Process 7(3):359–369. doi:10.1109/83.661186
Cohen LD (1991) On active contour models and balloons. CVGIP Image Underst 53(2):211–218. doi:10.1016/1049-9660(91)90028-N
Anbeek P, Vincken K, VanOsch M, Bisschops R, VanderGrond J (2004) Probabilistic segmentation of white matter lesions in MR imaging. Neuroimage 21(3):1037–1044. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2003.10.012
Chalana V, Kim Y (1997) A methodology for evaluation of boundary detection algorithms on medical images. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 16(5):642–652. doi:10.1109/42.640755
Khan S, Bennamoun M, Sohel F, Togneri R (2016) Automatic shadow detection and removal from a single image. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 38(3):431–446. doi:10.1109/TPAMI.2015.2462355
Mulleti S, Seelamantula C (2015) Ellipse fitting using the finite rate of innovation sampling principle. IEEE Trans Image Process 25(3):1451–1464. doi:10.1109/TIP.2015.2511580
Acknowledgements
The authors thank all the reviewers for their valuable comments, which further improved the quality of the paper. We also thank Gansu Provincial Hospital for providing the dataset. This study was funded National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant numbers 61175012 & 61201422), Natural Science Foundation of Gansu Province of China (grant number 148RJZA044) and Youth Foundation of Lanzhou Jiaotong University of China (grant number 2014005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lian, J., Ma, Y., Ma, Y. et al. Automatic gallbladder and gallstone regions segmentation in ultrasound image. Int J CARS 12, 553–568 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-016-1515-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-016-1515-z