Abstract
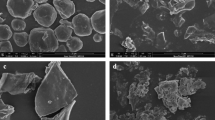
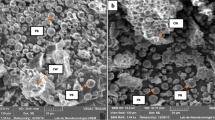
This study investigated the impact of heating and microwave treatment on the in vitro digestibility (using the INFOGEST method) of buckwheat protein isolates (BPIs) and explored the mechanism. The microwave treatment at level 4 (480 W) for 3 min (ML4T3) increased the BPI digestibility by 67.1% over that of the control, while heating for 20—40 min decreased the digestibility by 26.7% on average. Structural analysis showed that microwave treatment decreased the disulfide content, increased the sulfhydryl content, and distorted both the protein microstructure and surface morphology. Meanwhile, microwave treatment decreased the β-turn content and increased both the contents of the β-sheet structure by 35.6% and the random coil structure by 6.9%. In contrast, conventional heating increased the disulfide content and formation of aggregates, and decreased the contents of the random coil, α-helix and β-turn with concomitant increase in the β-sheet content. In conclusion, microwave treatment could be an effective approach to improve the digestibility of BPIs because of its multi-effects on the structure of proteins.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ATR/FT-IR:
-
Attenuated total reflectance Fourier transform infrared
- BPIs:
-
Buckwheat protein isolates
- DSC:
-
Differential scanning calorimetry
- DTNB:
-
5,5'-Dithiobis-(2-nitrobenzoic acid)
- H20:
-
Heating at 100 °C for 20 min
- H30:
-
Heating at 100 °C for 30 min
- H40:
-
Heating at 100 °C for 40 min
- IVD:
-
In vitro Digestibility
- ML4T1:
-
Microwave treatment at level 4 for 1 min
- ML4T2:
-
Microwave treatment at level 4 for 2 min
- ML4T3:
-
Microwave treatment at level 4 for 3 min
- ML4T4:
-
Microwave treatment at level 4 for 4 min
- ML4T5:
-
Microwave treatment at level 4 for 5 min
- ML6T3:
-
Microwave treatment at level 6 for 3 min
- ML8T3:
-
Microwave treatment at level 8 for 3 min
- PAGE:
-
Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
- RSH:
-
Reactive sulfhydryl
- SDS:
-
Sodium dodecyl sulfate
- SS:
-
Disulfide bond
- Tris:
-
(Hydroxymethyl)methyl aminomethane
- TSH:
-
Total sulfhydryl
References
J. Jin, I.C. Ohanenye, C.C. Udenigwe, Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 1–13, (2020).
Y. Deng, O. Padilla-Zakour, Y. Zhao, S. Tao, Food Bioprocess Tech. 8, 2235 (2015)
Y. Ma, Y.L. Xiong, J. Agri. Food Chem. 57, 4372 (2009)
T.D. Cirkovic Velickovic, D.J. Stanic Vucinic, Compre. Rev. Food Sci. 17, 82 (2018).
S. Rohn, H.M. Rawel, J. Kroll, J. Agri. Food Chem. 50, 3566 (2002)
D.J. McClements, L. Grossmann, Compr. Rev. Food Sci., (2021).
F.M. Chian, L. Kaur, I. Oey, T. Astruc, S. Hodgkinson, M. Boland, LWT - Food Sci. Technol. 103, 253 (2019)
M.A.B. Siddique, P. Maresca, G. Pataro, G. Ferrari, Food Res. Int. 87, 189 (2016)
Z. Zhang, X. Zhang, W. Chen, P. Zhou, Food Chem. 245, 997 (2018)
J. Jin, O.D. Okagu, A.E.A. Yagoub, C.C. Udenigwe, Ultrason. Sonochem. 70, (2021).
X. Guo, H. Yao, Z. Chen, Food Chem. 102, 118 (2007)
M.G. Nosworthy, A. Franczyk, A. Zimoch-Korzycka, P. Appah, A. Utioh, J. Neufeld, J.D. House, J. Agri. Food Chem. 65, 3919 (2017)
P. Gulati, A. Li, D. Holding, D. Santra, Y. Zhang, D.J. Rose, J. Agri. Food Chem. 65, 1952 (2017)
S. Chandrasekaran, S. Ramanathan, T. Basak, Food Res. Int. 52, 243 (2013)
L. Cai, J. Feng, A. Cao, Y. Zhang, Y. Lv, J. Li, Food Bioprocess Tech. 11, 417 (2018)
K. Iris, J. Fan, V.L. Budarin, F.P. Bouxin, J.H. Clark, D.C. Tsang, Green Chem. 22, 7109 (2020)
X. Sun, I.C. Ohanenye, T. Ahmed, C.C. Udenigwe, Food Chem., (2020).
D.B. Kamble, R. Singh, B.P. Kaur, S. Rani, A. Upadhyay, J. Food Meas. Charact. 14, 761 (2020)
S. Xiang, H. Zou, Y. Liu, R. Ruan, J. Food Sci.Technol., (2020).
J.H. Waterborg, The protein protocols handbook, 2009.
S.M. Choi, C.Y. Ma, J. Agri. Food Chem. 53, 8046 (2005)
F. Secundo, N. Guerrieri, J. Agri. Food Chem. 53, 1757 (2005)
K. Ikeda, M. Kishida, Fagopyrum 13, 21 (1993)
S.M. Choi, Y. Mine, C.Y. Ma, Int. J. Bio. Macro. 39, 201 (2006)
M. Zhang, D. Zhao, S. Zhu, Y. Nian, X. Xu, G. Zhou, C. Li, Food Res. Int., (2020)
H. Chang, X. Xu, C. Li, M. Huang, D. Liu, G. Zhou, J. Food Process Eng. 34, 2233 (2011)
H. Cao, D. Fan, X. Jiao, J. Huang, J. Zhao, B. Yan, W. Zhou, W. Zhang, H. Zhang, J. Food Eng. 228, 1 (2018)
I. Van der Plancken, A. Van Loey, M.E. Hendrickx, J. Agri. Food Chem. 53, 5726 (2005)
X. Guo, H. Yao, Food Chem. 98, 90 (2006)
S.M. Choi, C.Y. Ma, Food Res. Int. 39, 974 (2006)
J. Jin, H. Ma, K. Wang, A.E.G.A. Yagoub, J. Owusu, W. Qu, R. He, C. Zhou, X. Ye, Ultrason Sonochem. 24, 55 (2015)
H. Ramaswamy, J. Tang, Food Sci. Tech. Int. 14, 423 (2008)
H.X. Zhou, X. Pang, Chem. Rev. 118, 1691 (2018)
Y. Li, Y. Cheng, Z. Zhang, Y. Wang, B.K. Mintah, M. Dabbour, H. Jiang, R. He, H. Ma, Ultrason Sonochem. 69, (2020)
B. Zhang, K. Wang, J. Hasjim, E. Li, B.M. Flanagan, M.J. Gidley, S. Dhital, J. Agri. Food Chem. 62, 1482 (2014)
L. Mehryar, M. Esmaiili, F. Zeynali, R. Sadeghi, M. Imani, Food Sci. Biotech 26, 653 (2017)
Acknowledgements
Jian Jin was supported by the China Scholarship Council (No. 201908510042), National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 32001462), and Key Laboratory of Coarse Cereals Processing, Ministry of Agriculture, Chengdu University (2018CC14), and Longshan Talents program of Southwest University of Science and Technology (17LZX549). This project was supported by Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC) through the Discovery Grant Program (RGPIN-2018-06839), and by the University of Ottawa through the University Research Chair Program (C.C. Udenigwe).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Jian Jin: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Validation, Visualization, Funding acquisition, Writing—original draft, Writing—review & editing. Ogadimma Okagu: Formal analysis, Validation, Writing—original draft, Writing—review & editing. Chibuike C. Udenigwe: Conceptualization, Validation, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing—review & editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, J., Okagu, O.D. & Udenigwe, C.C. Differential Influence of Microwave and Conventional Thermal Treatments on Digestibility and Molecular Structure of Buckwheat Protein Isolates. Food Biophysics 17, 198–208 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11483-021-09709-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11483-021-09709-4