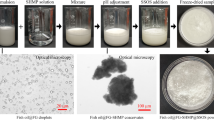
Abstract
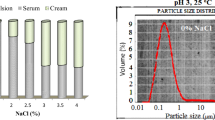
This study investigated the influence of thermal treatment (30 °C to 110 °C, 30 min) on the physicochemical and rheological properties of an emulsion stabilized by black tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus) skin at pH 4. The protein pattern of tilapia gelatin did not have any significant difference after the gelatin was heated within a temperature range of 30 °C to 70 °C. However, at 90 °C and 110 °C, denaturation occurred where α-, β- and γ-chains of the gelatin were degraded, leading to a concomitant increase in low molecular peptides. The emulsion stability was investigated through a particle size analyzer, zeta potential, microscopic observation and creaming index. The gelatin emulsion was physically stable at 30 °C to 70 °C with a mean droplet size of less than 13 μm. When the heating temperature was increased to 90 °C and 110 °C, the emulsion showed a pronounced increase in droplet size due to coalescence. The gelatin emulsion heated at 90 °C and 110 °C also displayed instability against creaming after storage at room temperature for 7 days. As the heating temperature increased, the gelatin emulsion exhibited a decrease in apparent viscosity and the flow behavior changed from shear thinning to Newtonian. The rheological data also showed that the storage modulus (G′) of emulsion became more frequency dependent as the heating temperature increased, indicating weak droplet interactions. The tilapia gelatin emulsion was physically unstable when subjected to thermal treatment above 70 °C. The data reported in this study provides useful insight into the formulation of acidic food emulsions that require thermal treatment.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Not applicable.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
References
D.J. McClements, C.E. Gumus, Adv. Colloid Interf. Sci. 234, 3 (2016)
R.S.H. Lam, M.T. Nickerson, Food Chem. 141, 975 (2013)
D.J. McClements, Food Emulsions: Principles, Practices and Techniques, 3rd edn. (CRC Press, Boca Raton, 2016)
P. Fustier, A. Achouri, A.R. Taherian, M. Britten, M. Pelletier, H. Sabik, S. Villeneuve, M. Mondor, J. Agric. Food Chem. 63, 9239 (2015)
M.L.F. Freitas, K.M. Albano, V.R.N. Telis, Polimeros 27, 62 (2017)
T. Strixner and U. Kulozik, in Handb. Food Proteins, edited by G. O. Phillips and P. A. Williams (Elsevier, Cambridge, 2011), pp. 150–209
A.A. Karim, R. Bhat, Food Hydrocoll. 23, 563 (2009)
C.-C. Tan, A.A. Karim, U. Uthumporn, F.C. Ghazali, J. Phys. Sci. 30, 1 (2019)
L. Niu, X. Zhou, C. Yuan, Y. Bai, K. Lai, F. Yang, Y. Huang, Food Hydrocoll. 33, 336 (2013)
FAO, The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2018 - Meeting the Sustainable Development Goals (Rome, 2018)
A. Sarkar, H. Kamaruddin, A. Bentley, S. Wang, Food Hydrocoll. 57, 160 (2016)
J. Surh, E.A. Decker, D.J. McClements, Food Hydrocoll. 20, 596 (2006)
P. Kittiphattanabawon, S. Benjakul, W. Visessanguan, F. Shahidi, Food Bioprocess Technol. 5, 2646 (2012)
M.A. Amiza, W.M.W.M. Shima, I.N. Hayati, M.N. Juhaida, Int. Food Res. J. 22, 213 (2015)
P. Kaewruang, S. Benjakul, T. Prodpran, S. Nalinanon, Food Biosci. 2, 1 (2013)
T. Aewsiri, S. Benjakul, W. Visessanguan, A.B. Encarnacion, P.A. Wierenga, H. Gruppen, Food Bioprocess Technol. 6, 671 (2013)
F. Niu, D. Niu, H. Zhang, C. Chang, L. Gu, Y. Su, Y. Yang, Food Hydrocoll. 52, 607 (2016)
S. Sinthusamran, S. Benjakul, H. Kishimura, Food Chem. 152, 276 (2014)
B. Jamilah, K.W. Tan, M.R. Umi Hartina, A. Azizah, Food Hydrocoll. 25, 1256 (2011)
M. Gudmundsson, H. Hafsteinsson, J. Food Sci. 62, 37 (1997)
H. Liu, B. Wang, C.J. Barrow, B. Adhikari, Food Chem. 143, 484 (2014)
N. Alizadeh-Pasdar, E. Li-Chan, J. Agric. Food Chem. 48, 328 (2000)
X. Duan, M. Li, J. Shao, H. Chen, X. Xu, Z. Jin, X. Liu, Food Hydrocoll. 75, 223 (2018)
N.N. Wu, X. Huang, X.Q. Yang, J. Guo, E.L. Zheng, S.W. Yin, J.H. Zhu, J.R. Qi, X.T. He, J.B. Zhang, Food Hydrocoll. 28, 110 (2012)
A. Schröder, C. Berton-Carabin, P. Venema, L. Cornacchia, Food Hydrocoll. 73, 129 (2017)
A. Kulmyrzaev, M.P.C. Sivestre, D.J. McClements, Food Res. Int. 33, 21 (2000)
M.I. Capitani, S.M. Nolasco, M.C. Tomás, Food Hydrocoll. 61, 537 (2016)
R. E. Hudson, A. J. Holder, K. M. Hawkins, P. R. Williams, and D. J. Curtis, Phys. Fluids 29, (2017)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Malaysia Ministry of Higher Education through the High Rising Star Award (Grant no: 203.PTEKIND.6711530). The author would also like to thank the MyBrain program under the Malaysia Ministry of Higher Education for the financial support backing his PhD study.
Funding
This work was supported by the Malaysia Ministry of Higher Education through the High Rising Star Award (Grant no: 203.PTEKIND.6711530). The author would also like to thank the MyBrain program under the Malaysia Ministry of Higher Education for the financial support backing his PhD study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Chek-Chuan Tan. Supervision: Alias A. Karim, U. Uthumporn and Farid. C. Ghazali. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Chek-Chuan Tan and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tan, CC., Karim, A.A., Uthumporn, U. et al. Effect of Thermal Treatment on the Physicochemical Properties of Emulsion Stabilized by Gelatin from Black Tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus) Skin. Food Biophysics 15, 423–432 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11483-020-09638-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11483-020-09638-8