Abstract
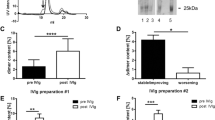
Intravenous immunoglobulins (IVIg) are standard treatment for Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS). Their exact mechanisms of action are versatile and not fully understood. One possible mechanism is neutralization of circulating autoantibodies via binding to anti- idiotypic antibodies forming idiotype-anti-idiotype dimeric IgG immune complexes. To examine the role of immune complex formation as mechanism of action for IVIg in GBS, 34 C57Bl/6 mice were either treated with anti-ganglioside antibodies and IVIg or IVIg and PBS alone, whereas eight additional mice were treated either with anti-ganglioside autoantibodies and IVIg or anti-ganglioside autoantibodies alone. Subsequently IgG dimer formation was assessed by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and enzyme- linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). In addition, IgG dimer formation was measured in sera of eight GBS patients who were treated with IVIg. In mice, a significant increase of dimeric IgG after administration of anti-ganglioside antibodies and IVIg could be observed. Re-monomerized IgG dimers showed immunoreactivity against gangliosides and serum immunoreactivity was significantly reduced after IVIg infusion. Likewise also in GBS patients, IgG dimer formation could be detected after IVIg treatment. Our data indicate that dimeric IgG immune complexes contain anti-idiotypic antibodies and provide proof of concept that IVIg treatment in GBS results in measurable amounts of IgG dimers. Larger patient cohorts are needed to evaluate serum IgG dimer increase as a possible marker for treatment response in GBS.
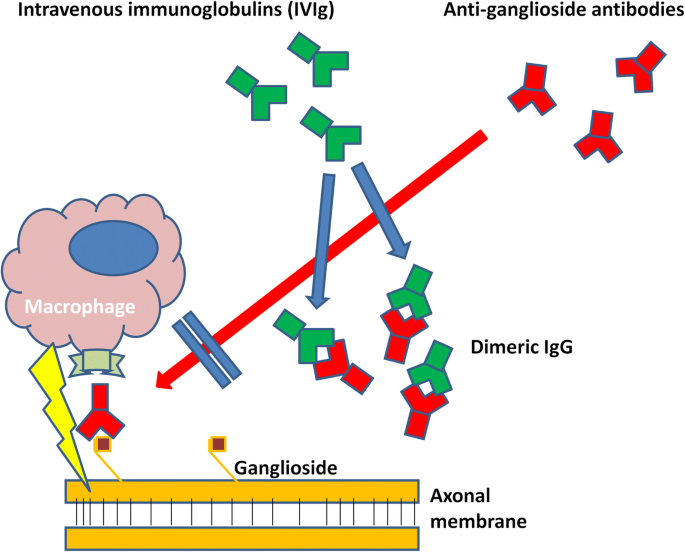
Mechanism of action: Intravenous immunoglobulins (IVIg) and anti-ganglioside antibodies form dimeric IgG immune complexes, preventing axonal damage in Guillain-Barré Syndrome.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersson J, Skansén-Saphir U, Sparrelid E, Andersson U (1996) Intravenous immune globulin affects cytokine production in T lymphocytes and monocytes/macrophages. Clin Exp Immunol 104(Suppl):10–20
Bleeker WK, Teeling JL, Verhoeven AJ, Rigter GM, Agterberg J, Tool AT, Hack CE (2000) Vasoactive side effects of intravenous immunoglobulin preparations in a rat model and their treatment with recombinant platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase. Blood 95(5):1856–1861 Retrieved from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10688848
Bolli R, Woodtli K, Bärtschi M, Höfferer L, Lerch P (2010) L-proline reduces IgG dimer content and enhances the stability of intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) solutions. Biologicals 38(1):150–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biologicals.2009.09.002
Brem MD, Jacobs BC, van Rijs W, Fokkink WJR, Tio-Gillen AP, Walgaard C et al (2019) IVIg-induced plasmablasts in patients with Guillain-Barré syndrome. Ann Clin Trans Neurol 6(1):129–143. https://doi.org/10.1002/acn3.687
Gilardin L, Bayry J, Kaveri SV (2015) Intravenous immunoglobulin as clinical immune-modulating therapy. CMAJ. 187:257–264. https://doi.org/10.1503/cmaj.130375
Hillion, S., Seité, J.-F., Goutsmedt C., Yoinou, P., Pers, J.-O. (2013). Intravenous immunoglobulin induces functionnal silencing in human B lymphocytes. Ann. Rheum. Dis, 72, A37–A38. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-203219.20LK
Hughes RAC, Newsom-Davis JM, Perkin GD, Pierce JM (1978) Controlled trial of prednisolone in acute polyneuropathy. Lancet 312:750–753. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(78)92644-2
Jungi TW, Brcic M, Kuhnert P, Spycher MO, Li F, Nydegger UE (1990) Effect of IgG for intravenous use on fc receptor-mediated phagocytosis by human monocytes. Clin Exp Immunol 82(1):163–169.
Kaida K, Morita D, Kanzaki M, Kamakura K, Motoyoshi K, Hirakawa M, Kusunoki S (2007) Anti-ganglioside complex antibodies associated with severe disability in GBS. J Neuroimmunol 182(1–2):212–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneuroim.2006.09.013
Kaida K, Sonoo M, Ogawa G, Kamakura K, Ueda-Sada M, Arita M, Kusunoki S (2008) GM1/GalNAc-GD1a complex: a target for pure motor Guillain-Barré syndrome. Neurology 71(21):1683–1690. https://doi.org/10.1212/01.wnl.0000335160.72184.7d
Kaveri SV (2012) Intravenous immunoglobulin: exploiting the potential of natural antibodies. Autoimmun Rev 11:792–794. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autrev.2012.02.006
Lehmann HC, Hartung H-P (2011) Plasma exchange and intravenous immunoglobulins: mechanism of action in immune-mediated neuropathies. J Neuroimmunol 231(1–2):61–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneuroim.2010.09.015
Lunn MPT, Johnson LA, Fromholt SE, Itonori S, Huang J, Vyas AA, Sheikh KA (2000) High-affinity anti-ganglioside IgG antibodies raised in complex ganglioside knockout mice: reexamination of GD1a immunolocalization. J Neurochem 75(1):404–412. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1471-4159.2000.0750404.x
Ritter C, Bobylev I, Lehmann HC (2015) Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (CIDP): change of serum IgG dimer levels during treatment with intravenous immunoglobulins. J Neuroinflammation 12(148):148. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-015-0361-1
Roux KH, Tankersley DL (1990) A view of the human idiotypic repertoire. Electron microscopic and immunologic analyses of spontaneous idiotype-anti-idiotype dimers in pooled human IgG. J Immunol 144(4):1387–1395 Retrieved from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=PubMed&dopt=Citation&list_uids=2303712
Teeling JL, Jansen-Hendriks T, Kuijpers TW, De Haas M, Van De Winkel JGJ, Erik Hack C, Bleeker WK (2001) Therapeutic efficacy of intravenous immunoglobulin preparations depends on the immunoglobulin G dimers: studies in experimental immune thrombocytopenia. Blood 98(4):1095–1099. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood.V98.4.1095
Tremblay T, Paré I, Bazin R (2013) Immunoglobulin G dimers and immune complexes are dispensable for the therapeutic efficacy of intravenous immune globulin in murine immune thrombocytopenia. Transfusion 53(2):261–269. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1537-2995.2012.03725.x
van Koningsveld R, Steyerberg EW, Hughes RA, Swan AV, van Doorn PA, Jacobs BC (2007) A clinical prognostic scoring system for Guillain-Barré syndrome. Lancet Neurol 6:589–594. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(07)70130-8
van Doorn PA, Kuitwaard K, Walgaard C, van Koningsveld R, Ruts L, Jacobs BC (2010) IVIG treatment and prognosis in Guillain-Barre syndrome. J Clin Immunol 30(Suppl 1):S74–S78. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-010-9407-4
Zhang G, Lopez PHH, Li CY, Mehta NR, Griffin JW, Schnaar RL, Sheikh KA (2004) Anti-ganglioside antibody-mediated neuronal cytotoxicity and its protection by intravenous immunoglobulin: implications for immune neuropathies. Brain J. Neurol 127(Pt 5):1085–1100. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awh127
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. For animal experiments, all applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Informed Consent
Written informed consent was obtained from all subjects participating in this study.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Svačina, M.K.R., Röth, P., Bobylev, I. et al. Changes of Serum IgG Dimer Levels after Treatment with IVIg in Guillain-Barré Syndrome. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 14, 642–648 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-019-09871-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-019-09871-0