Abstract
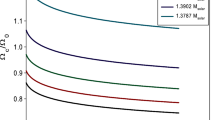
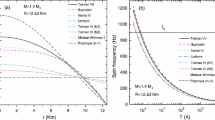
The magnetic damping rate was introduced in the evolution equations of r-modes, which shows that r-modes can generate strong toroidal magnetic fields in the core of accreting millisecond pulsars inducing by differential rotation. With consideration of the coupling evolution of r-modes, spin and thermal evolution, we investigated the influence of the magnetic damping on the differential rotation of nonlinear r-modes of accreting neutron stars. We derived the coupling evolution equations of the star involving the magnetic damping rate in the framework of second-order r-mode theory. The numerical results show that the magnetic damping suppressed the nonlinear evolution of r-modes since the saturation amplitude is reduced to a great extent. In particular, because of the presence of the generated toroidal magnetic field, the spin-down of the stars is terminated and the viscous heating effects are also weakened. Moreover, we could obtain a stronger generated toroidal magnetic field in the second-order r-mode theory. The gravitational radiation may be detected by the advanced laser interferometer detector LIGO if the amount of differential rotation is small when the r-mode instability becomes active and the accretion rate is not very high.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yu Y W, Cheng K S, Cao X F. The role of newly born magnetars in Gamma-ray burst X-ray afterglow emission: Energy injection and internal emission. Astrophys J, 2010, 715: 477–484
Cheng Q, Yu Y W. How can newly born rapidly rotating neutron stars become magnetars. Astrophys J Lett, 2014, 786: L13
Andersson N, Kokkotas K D. The r-mode instability in rotating neutron stars. Int J Mod Phys D, 2001, 10: 381–441
Bildsten L. Gravitational radiation and rotation of accreting neutron stars. Astrophys J, 1998, 501: L89–L93
Andersson N, Kokkotas K D, Stergioulas N. On the relevance of the r-mode instability for accreting neutron stars and white dwarfs. Astrophys J, 1999, 516: 307–314
Ho WC G, Andersson N, Haskell B. Revealing the physics of r-modes in low-mass X-ray binaries. Phys Rev Lett, 2011, 107: 101101
Haskell B, Degenaar N, Ho W C G. Constraining the physics of the r-mode instability in neutron stars with X-ray and ultraviolet observations. Mon Not R Astron Soc, 2012, 424: 93–103
Cuofano C, Drago A. Magnetic fields generated by r-modes in accreting millisecond pulsars. Phys Rev D, 2010, 82: 084027
Bonanno L, Cuofano C, Drago A, et al. Magnetic fields generated by r-modes in accreting quark stars. Astron Astrophys, 2011, 532: A15
Cuofano C, Dall’Osso S, Drago A. Generation of strong magnetic fields by r-modes in millisecond accreting neutron stars: Induced deformations and gravitational wave emission. Phys Rev D, 2012, 86: 044004
Cuofano C, Drago A, Pagliara G. Growth of magnetic fields in accreting millisecond pulsars. Mon Not R Astron Soc, 2013, 428: 1438–1441
Sá P M. Differential rotation of nonlinear r-modes. Phys Rev D, 2004, 69: 084001
Sá P M, Tomé B. Nonlinear evolution of r-modes: The role of differential rotation. Phys Rev D, 2005, 71: 044007
Sá P M, Tomé B. Influence of differential rotation on the detectability of gravitational waves from the r-mode instability. Phys Rev D, 2006, 74: 044011
Owen B J, Lindblom L, Cutler C, et al. Gravitational waves from hot young rapidly rotating neutron stars. Phys Rev D, 1998, 58: 084020
Yu Y W, Cao X F, Zheng X P. Long-term evolution and gravitational wave radiation of neutron stars with differential rotation induced by r-modes. Res Astron Astrophys, 2009, 9: 1024–1034
Andersson N, Jones D I, Kokkotas K D. Strange stars as persistent sources of gravitational waves. Mon Not R Astron Soc, 2002, 337: 1224–1232
Rezzolla L, Lamb F K, Shapiro S L. r-mode oscillations in rotating magnetic neutron stars. Astrophys J, 2000, 531: L139
Rezzolla L, Lamb F K, Marković D, et al. Properties of r-modes in rotating magnetic neutron stars. I. Kinematic secular effects and magnetic evolution equations. Phys Rev D, 2001, 64: 104013
Rezzolla L, Lamb F K, Marković D. et al. Properties of r-modes in rotating magnetic neutron stars. II. Evolution of the r modes and stellar magnetic field. Phys Rev D, 2001, 64: 104014
Watts A L, Andersson N. The spin evolution of nascent neutron stars. Mon Not R Astron Soc, 2002, 333: 943–951
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, G., Zhou, X. & Wang, N. The role of magnetic damping in the r-mode evolution of accreting neutron stars. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 58, 1–6 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-014-5573-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-014-5573-3