Abstract
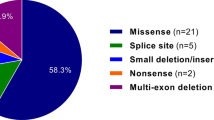
Marfan syndrome (MFS) is a systemic connective tissue disease principally affecting the ocular, skeletal and cardiovascular systems. This autosomal dominant disorder carries a prevalence of 1:3,000 to 1:5,000. This study aims to define the mutational spectrum of MFS related genes in Chinese patients and to establish genotype-phenotype correlations in MFS. Panel-based targeted next-generation sequencing was used to analyze the FBN1, TGFBR1 and TGFBR2 genes in 123 unrelated Chinese individuals with MFS or a related disease. Genotype-phenotype correlation analyses were performed in mutation-positive patients. The results showed that 97 cases/families (78.9%; 97/123) harbor at least one (likely) pathogenic mutation, most of which were in FBN1; four patients had TGFBR1/2 mutations; and one patient harbored a SMAD3 mutation. Three patients had two FBN1 mutations, and all patients showed classical MFS phenotypes. Patients with a dominant negative-FBN1 mutation had a higher prevalence of ectopia lentis (EL). Patients carrying a haploinsufficiency-FBN1 mutation tended to have aortic dissection without EL. This study extends the spectrum of genetic backgrounds of MFS and enriches our knowledge of genotype-phenotype correlations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnaud, P., Hanna, N., Aubart, M., Leheup, B., Dupuis-Girod, S., Naudion, S., Lacombe, D., Milleron, O., Odent, S., Faivre, L., et al. (2017). Homozygous and compound heterozygous mutations in the FBN1 gene: unexpected findings in molecular diagnosis of Marfan syndrome. J Med Genet 54, 100–103.
Aubart, M., Gross, M.S., Hanna, N., Zabot, M.T., Sznajder, M., Detaint, D., Gouya, L., Jondeau, G., Boileau, C., and Stheneur, C. (2015). The clinical presentation of Marfan syndrome is modulated by expression of wild-type FBN1 allele. Hum Mol Genet 24, 2764–2770.
Baetens, M., Van Laer, L., De Leeneer, K., Hellemans, J., De Schrijver, J., Van De Voorde, H., Renard, M., Dietz, H., Lacro, R.V., Menten, B., et al. (2011). Applying massive parallel sequencing to molecular diagnosis of Marfan and Loeys-Dietz syndromes. Hum Mutat 32, 1053–1062.
Blinc, A., Maver, A., Rudolf, G., Tasič, J., Pretnar Oblak, J., Berden, P., and Peterlin, B. (2015). Clinical exome sequencing as a novel tool for diagnosing Loeys-Dietz syndrome type 3. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 50, 816–821.
Brennan, P. (2011). Revised diagnostic criteria for Marfan syndrome. J R Coll Phys Edinb 41, 223.
Chaudhry, S.S., Cain, S.A., Morgan, A., Dallas, S.L., Shuttleworth, C.A., and Kielty, C.M. (2007). Fibrillin-1 regulates the bioavailability of TGFβ1. J Cell Biol 176, 355–367.
Collod-Béroud, G., Le Bourdelles, S., Ades, L., Ala-Kokko, L., Booms, P., Boxer, M., Child, A., Comeglio, P., De Paepe, A., Hyland, J.C., et al. (2003). Update of the UMD-FBN1 mutation database and creation of an FBN1 polymorphism database. Hum Mutat 22, 199–208.
Dietz, H.C., Loeys, B., Carta, L., and Ramirez, F. (2005). Recent progress towards a molecular understanding of Marfan syndrome. Am J Med Genet 139C, 4–9.
Faivre, L., Collod-Beroud, G., Callewaert, B., Child, A., Loeys, B.L., Binquet, C., Gautier, E., Arbustini, E., Mayer, K., Arslan-Kirchner, M., et al. (2009). Pathogenic FBN1 mutations in 146 adults not meeting clinical diagnostic criteria for Marfan syndrome: further delineation of type 1 fibrillinopathies and focus on patients with an isolated major criterion. Am J Med Genet 149A, 854–860.
Franken, R., den Hartog, A.W., Radonic, T., Micha, D., Maugeri, A., van Dijk, F.S., Meijers-Heijboer, H.E., Timmermans, J., Scholte, A.J., van den Berg, M.P., et al. (2015). Beneficial outcome of Losartan therapy depends on type of FBN1 mutation in Marfan syndrome. Circ Cardiovasc Genet 8, 383–388.
Franken, R., Groenink, M., de Waard, V., Feenstra, H.M., Scholte, A.J., van den Berg, M.P., Pals, G., Zwinderman, A.H., Timmermans, J., Mulder, B.J. (2016) Genotype impacts survival in Marfan syndrome. Eur Heart J 37, 3285–3290.
Franken, R., Teixido-Tura, G., Brion, M., Forteza, A., Rodriguez-Palomares, J., Gutierrez, L., Garcia Dorado, D., Pals, G., Mulder, B. J., and Evangelista, A. (2017). Relationship between fibrillin-1 genotype and severity of cardiovascular involvement in Marfan syndrome. Heart 103, 1795–1799.
Frise, C.J., Pitcher, A., and Mackillop, L. (2017). Loeys–Dietz syndrome and pregnancy: The first ten years. Int J Cardiol 226, 21–25.
Gray, J.R., Bridges, A.B., Faed, M.J., Pringle, T., Baines, P., Dean, J., and Boxer, M. (1994). Ascertainment and severity of Marfan syndrome in a Scottish population. J Med Genet 31, 51–54.
Judge, D.P., Rouf, R., Habashi, J., and Dietz, H.C. (2011). Mitral valve disease in Marfan syndrome and related disorders. J Cardiovasc Trans Res 4, 741–747.
Karttunen, L., Raghunath, M., Lonnqvist, L., and Peltonen, L. (1994). A compound-heterozygous Marfan patient: two defective fibrillin alleles result in a lethal phenotype. Am J Hum Genet 55, 1083–1091.
Li, J., Wu, W., Lu, C., Liu, Y., Wang, R., Si, N., Liu, F., Zhou, J., Zhang, S., and Zhang, X. (2017). Gross deletions in FBN1 results in variable phenotypes of Marfan syndrome. Clin Chim Acta 474, 54–59.
Mátyás, G., De Paepe, A., Halliday, D., Boileau, C., Pals, G., and Steinmann, B. (2002). Evaluation and application of denaturing HPLC for mutation detection in Marfan syndrome: Identification of 20 novel mutations and two novel polymorphisms in the FBN1 gene. Hum Mutat 19, 443–456.
Pees, C., Michel-Behnke, I., Hagl, M., and Laccone, F. (2014). Detection of 15 novel mutations in 52 children from 40 families with the Marfan or Loeys-Dietz syndrome and phenotype-genotype correlations. Clin Genet 86, 552–557.
Proost, D., Vandeweyer, G., Meester, J.A.N., Salemink, S., Kempers, M., Ingram, C., Peeters, N., Saenen, J., Vrints, C., Lacro, R.V., et al. (2015). Performant mutation identification using targeted next-generation sequencing of 14 thoracic aortic aneurysm genes. Hum Mutat 36, 808–814.
Rommel, K., Karck, M., Haverich, A., Schmidtke, J., and Arslan-Kirchner, M. (2002). Mutation screening of the fibrillin-1 (FBN1) gene in 76 unrelated patients with Marfan syndrome or Marfanoid features leads to the identification of 11 novel and three previously reported mutations. Hum Mutat 20, 406–407.
Rommel, K., Karck, M., Haverich, A., von Kodolitsch, Y., Rybczynski, M., Müller, G., Singh, K.K., Schmidtke, J., and Arslan-Kirchner, M. (2005). Identification of 29 novel and nine recurrent fibrillin-1 (FBN1) mutations and genotype-phenotype correlations in 76 patients with Marfan syndrome. Hum Mutat 26, 529–539.
Sakai, H., Visser, R., Ikegawa, S., Ito, E., Numabe, H., Watanabe, Y., Mikami, H., Kondoh, T., Kitoh, H., Sugiyama, R., et al. (2006). Comprehensive genetic analysis of relevant four genes in 49 patients with Marfan syndrome or Marfan-related phenotypes. Am J Med Genet 140A, 1719–1725.
Van Dijk, F.S., Hamel, B.C., Hilhorst-Hofstee, Y., Mulder, B.J.M., Timmermans, J., Pals, G., and Cobben, J.M. (2009). Compound-heterozygous Marfan syndrome. Eur J Med Genet 52, 1–5.
Verstraeten, A., Alaerts, M., Van Laer, L., and Loeys, B. (2016). Marfan syndrome and related disorders: 25 years of gene discovery. Hum Mutat 37, 524–531.
Acknowledgements
We thank all patients and their family members who participated in this study. The study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81400187 and 81230015), CAMS Innovation Fund for Medical Sciences (2016-I2M-1-002), the Beijing Municipal Science and Technology Commission (Z151100003915078) and the Special Research Fund for Central Public Scientific Research Institutes, Peking Union Medical College (2016ZX310160).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Compliance and ethics The author(s) declare that they have no conflict of interest. The study was approved by the Peking Union Medical College Institutional Review Board, and all individuals signed written informed consent.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Lu, C., Wu, W. et al. Application of next-generation sequencing to screen for pathogenic mutations in 123 unrelated Chinese patients with Marfan syndrome or a related disease. Sci. China Life Sci. 62, 1630–1637 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-018-9491-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-018-9491-8