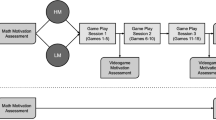
Abstract
In a game-based learning (GBL) environment for seventh-grade students, this study investigated the impact of competition, engagement in games, and the relationship between the two on students’ in-game performance and flow experience, which, in turn, impacted their science learning outcomes. Structural equation modeling was employed to test a hypothesized path model. The findings showed that students’ engagement in games not only predicted their in-game performance, but also had an impact on science learning outcomes via the mediation of in-game performance. While competition alone did not have a direct effect on either in-game performance or flow experience, it was indirectly related to in-game performance via the moderation of students’ engagement in games. The study concludes with implications for future GBL interventions and studies.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Admiraal, W., Huizenga, J., Akkerman, S., & Dam, G. T. (2011). The concept of flow in collaborative game-based learning. Computers in Human Behavior, 27(3), 1185–1194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2010.12.013.
Alessi, S. M., & Trollip, S. R. (2000). Multimedia for learning: Methods and development. Needham Heights: Allyn & Bacon Inc.
Alexander, P. A., Murphy, P. K., Woods, B. S., Duhon, K. E., & Parker, D. (1997). College instruction and concomitant changes in students’ knowledge, interest, and strategy use: A study of domain learning. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 22, 125–146.
Ames, C., & Ames, R. (1984). Goal structures and motivation. Elementary School Journal, 85, 39–50.
Ames, C., & Archer, J. (1988). Achievement goals in the classroom students’ learning strategies and motivation processes. Journal of Educational Psychology, 80, 260–267.
Annetta, L., Minogue, J., Holmes, S. Y., & Cheng, M. (2009). Investigating the impact of video games on high school students’ engagement and learning about genetics. Computers & Education, 53(1), 74–85.
Bandura, A. (2000). Exercise of human agency through collective efficacy. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 9(3), 75–78. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-8721.00064.
Bandura, A., & Locke, E. A. (2003). Negative self-efficacy and goals effects revisited. Journal of Applied Psychology, 88, 87–99.
Barab, S. A., Dodge, T., Thomas, M. K., Jackson, C., & Tuzun, H. (2007). Our designs and the social agendas they carry. The Journal of the Learning Sciences, 16(2), 263–305. https://doi.org/10.1080/10508400701193713.
Barzilai, S., & Blau, I. (2014). Scaffolding game-based learning: Impact on learning achievements, perceived learning, and game experiences. Computers & Education, 70, 65–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2013.08.003.
Cagiltay, N. E., Ozcelik, E., & Ozcelik, N. S. (2015). The effect of competition on learning in games. Computers & Education, 87, 35–41.
Chen, C.-H., & Law, V. (2016). Scaffolding individual and collaborative game-based learning in learning performance and intrinsic motivation. Computers in Human Behavior, 55, 1201–1212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2015.03.010.
Chen, C.-H., Law, V., & Chen, W. Y. (2018a). The effects of peer competition-based science learning game on secondary students’ performance, achievement goals, and perceived ability. Interactive Learning Environments, 26(2), 235–244.
Chen, C.-H., Liu, J.-H., & Shou, W.-C. (2018b). How competition in a game-based science learning environment influences students’ learning achievement, flow experience and learning behavioral patterns. Educational Technology & Society, 21(2), 164–176.
Chen, L.-X., & Sun, C.-T. (2016). Self-regulation influence on game play flow state. Computers in Human Behavior, 54, 341–350.
Cheng, M.-T., Lin, Y.-W., & She, H. C. (2015). Learning through playing virtual age: Exploring the interactions among student concept learning, gaming performance, in-game behaviors, and the use of in-game characters. Computers & Education, 86, 18–29.
Cheng, H. N. H., Wu, W. M. C., Liao, C. C. Y., & Chan, T. W. (2009). Equal opportunity tactic: Redesigning and applying competition games in classrooms. Computers & Education, 53(3), 866–876. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2009.05.006.
Clark, D., Nelson, B. C., Chang, H.-Y., Martinez, M., Slack, K., & D’Angelo, C. M. (2011). Exploring Newtonian mechanics in a conceptually-integrated digital game: Comparison of learning and affective outcomes for students in Taiwan and the United States. Computers & Education, 57, 2178–2195.
Cohen, J., Cohen, P., West, S. G., & Aiken, L. S. (2003). Applied multiple regression/correlation analysis for the behavioral sciences. London: Routledge.
Connell, J. P., & Wellborn, J. G. (1991). Competence, autonomy, and relatedness: A motivational analysis of self-system processes. In M. R. Gunnar & L. A. Sroufe (Eds.), Self processes in development: Minnesota Symposium on Child Psychology (Vol. 23, pp. 43–77). Hillsdale: Erlbaum.
Connolly, T. M., Boyle, E. A., MacArthur, E., Hainey, T., & Boyle, J. M. (2012). A systematic literature review of empirical evidence on computer games and serious games. Computers & Education, 59, 661–686.
Corno, L., & Mandinach, E. B. (1983). The role of cognitive engagement in classroom learning and motivation. Educational Psychologist, 18(2), 88–108. https://doi.org/10.1080/00461528309529266.
Csikszentmihalyi, M. (1975). Beyond boredom and anxiety. San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
Csikszentmihalyi, M. (1990). Flow: The psychology of optimal experience. New York: Harper and Row.
Erhel, S., & Jamet, E. (2013). Digital game-based learning: Impact of instructions and feedback on motivation and learning effectiveness. Computers & Education, 67, 156–167.
Eseryel, D., Law, V., Ifenthaler, D., Ge, X., & Miller, R. (2014). An investigation of the interrelationships between motivation, engagement, and complex problem solving in game-based learning. Journal of Educational Technology & Society, 17(1), 42–53.
Eslinger, E., White, B., Frederiksen, J., & Brobst, J. (2008). Supporting inquiry processes with an interactive learning environment: Inquiry Island. Journal of Science Education and Technology, 17, 610–617.
Fisher, J. E. (1976). Competition and gaming: An experimental study. Simulation & Gaming, 7(3), 321–328.
Foo, J. C., Nagase, K., Naramura-Ohno, S., Yoshiuchi, K., Yamamoto, Y., & Morita, K. (2017). Rank among peers during game competition affects the tendency to make risky choices in adolescent males. Frontiers in Psychology, 8, 16. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2017.00016.
Fredricks, J. A., Blumenfeld, P. C., Friedel, J., & Paris, A. (2005). School engagement. In K. A. Moore & L. Lippman (Eds.), Conceptualizing and measuring indicators of positive development: What do children need to flourish (pp. 305–321). New York: Kluwer Academic/Plenum Press.
Fredricks, J. A., Blumenfeld, P. C., & Paris, A. H. (2004). School engagement: potential of the concept, state of the evidence. Review of Educational Research, 74, 59–109.
Fredricks, J. A., Filsecker, J., & Lawson, M. A. (2016a). Student engagement, context, and adjustment: Addressing definitional, measurement, and methodological issues. Learning and Instruction, 43, 1–4.
Fredricks, J. A., Wang, M. T., Linn, J. S., Hofkens, T. L., Sung, H., Parr, A., et al. (2016b). Using qualitative methods to develop a survey measure of math and science engagement. Learning and Instruction, 43, 5–15.
Gee, J. P. (2005). Why video games are good for your soul: Pleasure and learning. Melbourne: Common Ground.
Gefen, D., Rigdon, E. E., & Straub, D. (2011). An update and extension to SEM guidelines for administrative and social science research. MIS Quarterly. https://doi.org/10.2307/23044042.
Gredler, M. E. (2004). Games and simulations and their relationships to learning. In D. H. Jonassen (Ed.), Handbook of research for educational communications and technology (2nd ed., pp. 571–582). Mahwah: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Greene, B. A. (2015). Measuring cognitive engagement with self-report scales: Reflections from over 20 years of research. Educational Psychologist, 50(1), 14–30. https://doi.org/10.1080/00461520.2014.989230.
Greene, B. A., & Miller, R. B. (1996). Influences on achievement: Goals, perceived ability, and cognitive engagement. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 21(2), 181.
Hamari, J., Shernoff, D. J., Rowe, E. B. C., & Edwards, T. (2016). Challenging games help students learn: An empirical study on engagement, flow and immersion in game-based learning. Computers in Human Behavior, 54, 170–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2015.07.045.
Hong, J. C., Hwang, M. Y., Lu, C. H., Cheng, C. L., Lee, Y. C., & Lin, C. L. (2009). Playfulness-based design in educational games: A perspective on an evolutionary contest game. Interactive Learning Environments, 17(1), 15e35.
Hou, H.-T., & Li, M.-C. (2014). Evaluating multiple aspects of a digital educational problem-solving-based adventure game. Computers in Human Behavior, 30, 29–38.
Hu, L.-T., & Bentler, P. M. (1999). Cutoff criteria for fit indexes in covariance structure analysis: Conventional criteria versus. Structural Equation Modeling, 6(1), 1–55.
Huang, W.-H. (2011). Evaluating learners’ motivational and cognitive processing in an online game-based learning environment. Computers in Human Behavior, 27(2), 694–704. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2010.07.021.
Huizenga, J., Admiraal, W., Akkerman, S., & Dam, G. (2009). Mobile game-based learning in secondary education: Engagement, motivation and learning in a mobile city game. Journal of Computer Assisted Learning, 25(4), 332–344. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2729.2009.00316.x.
Hwang, G. J., Wu, P.-H., & Chen, C.-C. (2012). An online game approach for improving students’ learning performance in web-based problem-solving activities. Computers & Education, 59, 1246–1256.
Inal, Y., & Cagiltay, K. (2007). Flow experiences of children in an interactive social game environment. British Journal of Educational Technology, 38(3), 455–464. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-8535.2007.00709.x.
Jayakanthan, R. (2002). Application of computer games in the field of education. The Electronic Library, 20(2), 98–102. https://doi.org/10.1108/02640470210697471.
Johnson, D. W., & Johnson, R. T. (1989). Cooperation and competition: A meta-analysis of the research. Hillsdale: Lawrence Erlbaum.
Johnson, D. W., & Johnson, R. T. (2009). An educational psychology success story: Social interdependence theory and cooperative learning. Educational Researcher, 38(5), 365–379. https://doi.org/10.3102/0013189x09339057.
Jonassen, D. H. (1999). Designing constructivist learning environments. In C. M. Reigeluth (Ed.), Instructional-design theories and models: A new paradigm of instructional theory (Vol. II). Mahwah: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Ke, F. (2009). A qualitative meta-analysis of computer games as learning tools. In E. F. Richard (Ed.), Handbook of research on effective electronic gaming in education (pp. 1–32). Hershey: IGI Global.
Ke, F. (2016). Designing and integrating purposeful learning in game play: A systematic review. Educational Technology Research and Development, 64(2), 219–244. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11423-015-9418-1.
Ke, F., & Grabowski, B. (2007). Gameplaying for math learning: Cooperative or not? British Journal of Educational Technology, 38(2), 249–259. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-8535.2006.00593.x.
Keller, J. M. (1993). Instructional material motivational survey. Unpublished documents: Florida State University.
Ketelhut, D. J., Dede, C., Clarke, J., Nelson, B., & Bowman, C. (2007). Studying situated learning in a multi-user virtual environment. In E. Baker, J. Dickieson, W. Wulfeck, & H. O’Neil (Eds.), Assessment of problem solving using simulations. Mahwah: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Kiili, K. (2006). Evaluations of an experimential gaming model. Human Technology, 2(2), 187–201.
Kline, R. (2011). Principles and practice of structural equation modeling. New York: The Guilford Press.
Lam, S., Yim, P., Law, J. S. F., & Cheung, R. W. Y. (2004). The effects of competition on achievement motivation in Chinese classrooms. British Journal of Educational Psychology, 74, 281–296.
Lee, J., & Spector, J. M. (2012). Effects of model-centered instruction on effectiveness, efficiency, and engagement with ill-structured problem solving. Instructional Science, 40, 537–557.
Li, S. C., Law, N., & Lui, K. F. A. (2006). Cognitive perturbation through dynamic modelling: a pedagogical approach to conceptual change in science. Journal of Computer Assisted Learning, 22(6), 405–422. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2729.2006.00187.x.
Malone, T. W. (1981). Toward a theory of intrinsically motivating instruction. Cognitive Science, 5(4), 333–369. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15516709cog0504_2.
Malone, T. W., & Lepper, M. R. (1987). Making learning fun: A taxonomy of intrinsic motivations for learning. In R. Snow & M. J. Farr (Eds.), Aptitude, learning, and instruction. Hillsdale: Erlbaum.
Mayer, R. E. (Ed.). (2011). Multimedia learning and games. Charlotte: Information Age.
Miller, R. B., Greene, B. A., Montalvo, G. P., Ravindran, B., & Nichols, J. D. (1996). Engagement in academic work: The role of learning goals, future consequences, pleasing others, and perceived ability. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 21(4), 388–422. https://doi.org/10.1006/ceps.1996.0028.
Nietfeld, J. L., Shores, L. R., & Hoffmann, K. F. (2014). Self-regulation and gender within a game-based learning environment. Journal of Educational Psychology, 106(4), 961–973. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0037116.
Pajares, F. (1996). Self-efficacy beliefs in academic settings. Review of Educational Research, 66(4), 543–578.
Papastergiou, M. (2009). Digital game-based learning in high school computer science education: Impact on educational effectiveness and student motivation. Computers & Education, 52(1), 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2008.06.004.
Pearce, J. M., Ainley, M., & Howard, S. (2005). The Ebb and flow of online learning. Computers in Human Behavior, 21(5), 745–771. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2004.02.019.
Pintrich, P. R. (2000). The role of goal orientation in self-regulated learning. In M. Boekaerts, P. R. Pintrich, & M. Zeidner (Eds.), Handbook of self-regulation (pp. 451–502). San Diego: Academic Press.
Rieber, L. P. (1996). Seriously considering play: Designing interactive learning environments based on the blending of microworlds, simulations, and games. Educational Technology Research and Development, 44(2), 43–48.
Sánchez, J., & Olivares, R. (2011). Problem solving and collaboration using mobile serious games. Computers & Education, 57(3), 1943–1952. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2011.04.012.
Sandoval, W. A., & Reiser, B. J. (2004). Explanation-driven inquiry: Integrating conceptual and epistemic scaffolds for scientific inquiry. Science Education, 88(3), 345–372.
Seligman, M. E. P., & Csikszentmihalyi, M. (2000). Positive psychology: An introduction. American Psychologist, 55(1), 5–14. https://doi.org/10.1037/0003-066X.55.1.5.
Sitzmann, T. (2011). A meta-analytic examination of the instructional effectiveness of computer-based simulation games. Personnel Psychology, 64, 489–528. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-6570.2011.01190.x.
Sun, C.-Y., Kuo, C.-Y., Hou, H.-T., & Lin, Y.-Y. (2017). Exploring learners’ sequential behavioral patterns, flow experience, and learning performance in an anti-phishing educational game. Educational Technology & Society, 20(1), 45–60.
Sweetser, P., & Wyeth, P. (2005). Gameflow: A model for evaluating player enjoyment in games. ACM Computers in Entertainment, 3(3), 1–24.
Tabachnick, B. G., & Fidell, L. S. (2007). Using multivariate statistics (5th ed.). Needham Heights: Allyn & Bacon.
Tennyson, R. D., & Jorczak, R. L. (2008). A conceptual framework for the empirical study of games. In H. O’Neil & R. Perez (Eds.), Computer games and team and individual learning (pp. 3–20). Mahwah: Erlbaum.
ter Vrugte, J., de Jong, T., Vandercruysse, S., Wouters, P., van Oostendorp, H., & Elen, J. (2015). How competition and heterogeneous collaboration interact in prevocational game-based mathematics education. Computers & Education, 89, 42–52.
Tüzün, H., Yilmaz-Soylu, M., Karakus, T., Inal, Y., & Kızılkaya, G. (2009). The effects of computer games on primary school students’ achievement and motivation in geography learning. Computers & Education, 52(1), 68–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2008.06.008.
Van Eck, R., & Dempsey, J. V. (2002). The effect of competition and contextualized advisement on the transfer of mathematics skills in a computer-based instructional simulation game. Educational Technology Research and Development, 50(3), 23–41. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02505023.
Vandercruysse, S., Vandewaetere, M., Cornillie, F., & Clarebout, G. (2013). Competition and students’ perceptions in a game-based language learning environment. Educational Technology Research and Development, 61(6), 927–950. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11423-013-9314-5.
Vansteenkiste, M., Simons, J., Lens, W., Sheldon, K. M., & Deci, E. L. (2004). Motivating learning, performance, and persistence: The synergistic effects of intrinsic goal contents and autonomy supportive contexts. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 87, 246–260.
Vogel, J. F., Vogel, D. S., Cannon-Bowers, J., Bowers, C. A., Muse, K., & Wright, M. (2006). Computer gaming and interactive simulations for learning: A meta-analysis. Journal of Educational Computing Research, 34(3), 229–243.
Wan, C.-S., & Choiu, W.-B. (2006). Why are adolescents addicted to online gaming? An interview study in Taiwan. Cyberpsychology & Behavior, 9(6), 762–766.
Wang, M. T., Fredricks, J. A., Ye, F., Hofkens, T. L., & Linn, J. S. (2016). The Math and Science Engagement Scales: Scale development, validation, and psychometric properties. Learning and Instruction, 43, 16–26.
White, B., & Frederiksen, J. R. (1998). Inquiry, modeling, and metacognition: Making science accessible to all students. Cognition and Instruction, 16(1), 3–118.
Williams, R. B., & Clippinger, C. A. (2002). Aggression, competition and computer games: Computer and human opponents. Computers in Human Behavior, 18(5), 495–506.
Wouters, P., van Nimwegen, C., van Oostendorp, H., & van der Spek, E. D. (2013). A meta-analysis of the cognitive and motivational effects of serious games. Journal of Educational Psychology. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0031311.
Young, M. F., Slota, S., Cutter, A. B., Jalette, G., Mullin, G., Lai, B., et al. (2012). Our princess is in another castle: A review of trends in serious gaming for education. Review of Educational Research, 82(1), 61–89.
Yu, F. Y. (2003). The mediating effects of anonymity and proximity in an online synchronized competitive learning environment. Journal of Educational Computing Research, 29(2), 153–167.
Zimmerman, B. J., & Schunk, D. H. (2001). Self-regulated learning and academic achievement: Theoretical perspectives. Mahwah: Lawrence Erlbaum.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix A. Samples of content knowledge test
Appendix A. Samples of content knowledge test

Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, CH., Law, V. & Huang, K. The roles of engagement and competition on learner’s performance and motivation in game-based science learning. Education Tech Research Dev 67, 1003–1024 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11423-019-09670-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11423-019-09670-7