Abstract
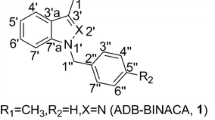
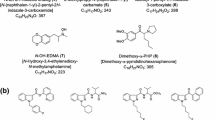
We identified two new-type cannabimimetic quinolinyl carboxylates, quinolin-8-yl 1-pentyl-(1H-indole)-3-carboxylate (QUPIC, 1) and quinolin-8-yl 1-(cyclohexylmethyl)-1H-indole-3-carboxylate (QUCHIC, 2); and two new cannabimimetic carboxamide derivatives, N-(1-amino-3,3-dimethyl-1-oxobutan-2-yl)-1-(4-fluorobenzyl)-1H-indazole-3-carboxamide (ADB-FUBINACA, 3) and N-(1-amino-3,3-dimethyl-1-oxobutan-2-yl)-1-pentyl-1H-indole-3-carboxamide (ADBICA, 4), as designer drugs in illegal products. Compound 3 was reported to have a potent affinity for cannabinoid CB1 receptor by Pfizer in 2009, but this is the first report of its detection in illegal products. No chemical or pharmacological data for compounds 1, 2, and 4 have appeared until now, making this the first report on these compounds. We also detected synthetic cannabinoids, APICA N-(5-fluoropentyl) analog (5), APINACA N-(5-fluoropentyl) analog (6), UR-144 N-(5-chloropentyl) analog (7), JWH-122 N-(5-chloropentyl) analog (8), and AM-2201 4-methoxynaphthyl analog (4-MeO-AM-2201, 9) herein as newly distributed designer drugs in Japan. It is of interest that compounds 1 and 2 were detected with their synthetic component, 8-quinolinol (10). A stimulant thiophene analog, α-pyrrolidinovalerothiophenone (α-PVT, 11), and an opioid receptor agonist, 3,4-dichloro-N-([1-(dimethylamino)cyclohexyl]methyl)benzamide (AH-7921, 12), were also detected as new types of designer drugs coexisting with several synthetic cannabinoids and cathinone derivatives in illegal products.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Uchiyama N, Kawamura M, Kikura-Hanajiri R, Goda Y (2011) Identification and quantitation of two cannabimimetic phenylacetylindoles JWH-251 and JWH-250, and four cannabimimetic naphthoylindoles JWH-081, JWH-015, JWH-200, and JWH-073 as designer drugs in illegal products. Forensic Toxicol 29:25–37
Namera A, Nakamoto A, Saito T, Nagao M (2011) Colorimetric detection and chromatographic analyses of designer drugs in biological materials: a comprehensive review. Forensic Toxicol 29:1–24
Zaitsu K, Katagi M, Tatsuno M, Sato T, Tsuchihashi H, Suzuki K (2011) Recently abused β-keto derivatives of 3,4-methylenedioxyphenylalkylamines: a review of their metabolisms and toxicological analysis. Forensic Toxicol 29:73–84
Nakajima J, Takahashi M, Seto T, Yoshida M, Kanai C, Suzuki J, Hamano T (2012) Identification and quantitation of two new naphthoylindole drugs-of-abuse, (1-(5-hydroxypentyl)-1H-indol-3-yl)(naphthalen-1-yl)methanone (AM-2202) and (1-(4-pentenyl)-1H-indol-3-yl)(naphthalen-1-yl)methanone, with other synthetic cannabinoids in unregulated “herbal” products circulated in the Tokyo area. Forensic Toxicol 30:33–44
Uchiyama N, Kawamura M, Kikura-Hanajiri R, Goda Y (2012) Identification of two new-type synthetic cannabinoids, N-(1-adamantyl)-1-pentyl-1H-indole-3-carboxamide (APICA) and N-(1-adamantyl)-1-pentyl-1H-indazole-3-carboxamide (APINACA), and detection of five synthetic cannabinoids, AM-1220, AM-2233, AM-1241, CB-13 (CRA-13), and AM-1248, as designer drugs in illegal products. Forensic Toxicol 30:114–125
Kneisel S, Bisel P, Brecht V, Broecker S, Müller M, Auwärter V (2012) Identification of the cannabimimetic AM-1220 and its azepane isomer (N-methylazepan-3-yl)-3-(1-naphthoyl)indole in a research chemical and several herbal mixtures. Forensic Toxicol 30:126–134
Kikura-Hanajiri R, Uchiyama N, Kawamura M, Goda Y (2013) Changes in the prevalence of synthetic cannabinoids and cathinone derivatives in Japan. Forensic Toxicol 31:44–53
Kikura-Hanajiri R, Uchiyama N, Kawamura M, Ogata J, Goda Y (2013) Prevalence of new designer drugs and their legal status in Japan (in Japanese with English abstract). Yakugaku Zasshi 133:31–40
EMCDDA (2012) EMCDDA–Europol 2011 annual report on the implementation of council decision 2005/387/JHA. EMCDDA/Europol, Lisbon. http://www.emcdda.europa.eu/attachements.cfm/att_155113_EN_EMCDDA-Europol%20Annual%20Report%202011_2012_final.pdf. Accessed April 2012
EMCDDA (2012) 2012 Annual report on the state of the drugs problem in Europe. EMCDDA, Lisbon. http://www.emcdda.europa.eu/attachements.cfm/att_190854_EN_TDAC12001ENC_.pdf. Accessed November 2012
Uchiyama N, Kawamura M, Kikura-Hanajiri R, Goda Y (2012) URB-754: a new class of designer drug and 12 synthetic cannabinoids detected in illegal products. Forensic Sci Int. doi:10.1016/j.forsciint.2012.08.047
Manera C, Cascio MG, Benetti V, Allarà M, Tuccinardi T, Martinelli A, Saccomanni G, Vivoli E, Ghelardini C, Di Marzo V, Ferrarini PL (2007) New 1,8-naphthyridine and quinoline derivatives as CB2 selective agonists. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 17:6505–6510
Westphal F, Junge T, Girreser U, Greibl W, Doering C (2012) Mass, NMR and IR spectroscopic characterization of pentedrone and pentylone and identification of their isocathinone by-products. Forensic Sci Int 217:157–167
Lancelot JC, Robba M, Bonnet JJ, Vaugeois JM, Costentin J (1992) Synthesis and preliminary study of the activity of thiophene analogs of pyrovalerone on the neuronal uptake of the monoamines. Eur J Med Chem 27:297–300
Uchiyama N, Matsuda S, Wakana D, Kikura-Hanajiri R, Goda Y (2013) New cannabimimetic indazole derivatives, N-(1-amino-3-methyl-1-oxobutan-2-yl)-1-pentyl-1H-indazole-3-carboxamide (AB-PINACA) and N-(1-amino-3-methyl-1-oxobutan-2-yl)-1-(4-fluorobenzyl)-1H-indazole-3-carboxamide (AB-FUBINACA), identified as designer drugs. Forensic Toxicol 31:93–100
Buchler IP, Hayes MJ, Hegde SG, Hockerman SL, Jones DE, Kortum SW, Rico JG, Tenbrink RE, Wu KK (2009) Indazole derivatives as CB1 receptor modulators and their preparation and use in the treatment of CB1-mediated diseases. Patent: WO/2009/106982 September, 2009
Aung MM, Griffin G, Huffman JW, Wu M, Keel C, Yang B, Showalter VM, Abood ME, Martin BR (2000) Influence of the N-1 alkyl chain length of cannabimimetic indoles upon CB1 and CB2 receptor binding. Drug Alcohol Depend 60:133–140
Uchiyama N, Kikura-Hanajiri R, Kawahara N, Goda Y (2009) Identification of a cannabimimetic indole as a designer drug in a herbal product. Forensic Toxicol 27:61–66
Ernst L, Schiebel HM, Theuring C, Lindigkeit R, Beuerle T (2011) Identification and characterization of JWH-122 used as new ingredient in “Spice-like” herbal incenses. Forensic Sci Int 208:e31–e35
Frost JM, Dart MJ, Tietje KR, Garrison TR, Grayson GK, Daza AV, El-Kouhen OF, Yao BB, Hsieh GC, Pai M, Zhu CZ, Chandran P, Meyer MD (2010) Indol-3-ylcycloalkyl ketones: effects of N1 substituted indole side chain variations on CB2 cannabinoid receptor activity. J Med Chem 53:295–315
Brittain RT, Kellett DN, Neat ML, Stables R (1973) Proceedings: anti-nociceptive effects in N-substituted cyclohexylmethylbenzamides. Br J Pharmacol 49:158P–159P
Hayes AG, Tyers MB (1983) Determination of receptors that mediate opiate side effects in the mouse. Br J Pharmacol 79:731–736
Uchiyama N, Kikura-Hanajiri R, Goda Y (2011) Identification of a novel cannabimimetic phenylacetylindole, cannabipiperidiethanone, as a designer drug in a herbal product and its affinity for cannabinoid CB1 and CB2 receptors. Chem Pharm Bull 59:1203–1205
EMCDDA (2011) EMCDDA—Europol 2010 annual report on the implementation of council decision 2005/387/JHA. EMCDDA-Europol, Lisbon. http://www.emcdda.europa.eu/attachements.cfm/att_132857_EN_EMCDDA-Europol%20Annual%20Report%202010A.pdf. Accessed April 2012
Zuba D, Sekuła K, Buczek A (2012) 25C-NBOMe—new potent hallucinogenic substance identified on the drug market. Forensic Sci Int. doi:10.1016/j.forsciint.2012.08.027
Zuba D, Sekuła K (2012) Analytical characterization of three hallucinogenic N-(2-methoxy)benzyl derivatives of the 2C-series of phenethylamine drugs. Drug Test Anal. doi:10.1002/dta.1397
Acknowledgments
Part of this work was supported by a Health and Labour Sciences Research Grant from the Ministry of Health, Labour, and Welfare, Japan.
Conflict of interest
There are no financial or other relations that could lead to a conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Uchiyama, N., Matsuda, S., Kawamura, M. et al. Two new-type cannabimimetic quinolinyl carboxylates, QUPIC and QUCHIC, two new cannabimimetic carboxamide derivatives, ADB-FUBINACA and ADBICA, and five synthetic cannabinoids detected with a thiophene derivative α-PVT and an opioid receptor agonist AH-7921 identified in illegal products. Forensic Toxicol 31, 223–240 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11419-013-0182-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11419-013-0182-9
Keywords
- Quinolin-8-yl 1-pentyl-(1H-indole)-3-carboxylate (QUPIC)
- Quinolin-8-yl 1-(cyclohexylmethyl)-1H-indole-3-carboxylate (QUCHIC)
- N-(1-Amino-3,3-dimethyl-1-oxobutan-2-yl)-1-(4-fluorobenzyl)-1H-indazole-3-carboxamide (ADB-FUBINACA)
- N-(1-Amino-3,3-dimethyl-1-oxobutan-2-yl)-1-pentyl-1H-indole-3-carboxamide (ADBICA)
- Synthetic cannabinoids
- α-Pyrrolidinovalerothiophenone (α-PVT)